When an exception is triggered, the program will not run again
Functions of exception handling:
Try to keep the program running normally
Find and solve problems as soon as possible
Exception type
-IndexError
# 1.IndexError mlist = [5,6,7] print(mlist[100])
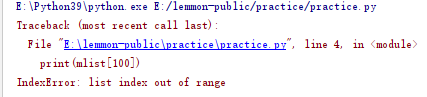
When an exception is triggered, the following code will not run again
- NameError
#2.NameError #Variable exception print(a) #No variable defined, variable not found
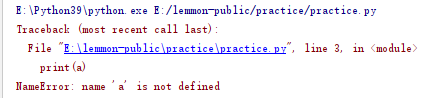
Use a variable that has not been assigned to the object
When using a variable, make sure it is defined
- SyntaxError
#3.SyntaxError
#syntax error
print("hello"))
#Unfamiliar with python syntax
Code logic syntax error, unable to execute, unable to capture
-ImportError
#8.ImportError from homework.list_change_dict import abc key = [1,2,3] a = get_dict(key,value) print(a) #Unable to import variables for module
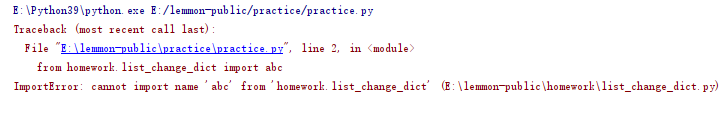
Unable to import variables for module
-TypeError
#7.TypeError from homework.list_change_dict import get_dict key = [1,2,3] a = get_dict(key) print(a) #The object type passed in does not meet the requirements
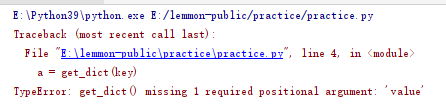
The object type passed in does not meet the requirements
-ModuleNotFoundError
#9.ModuleNotFoundError from list_change_dict import get_dict key = [1,2,3] a = get_dict(key,value) print(a) #The module was not found
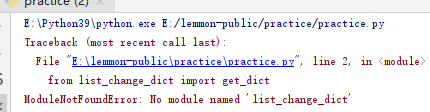
The module was not found
- KeyError
#4.KeyError
#Key exception
dict_1 = {"name":"conlin"}
print(dict_1["age"])
#This key is not in the dictionary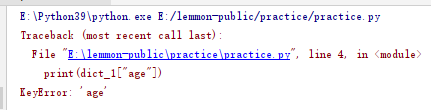
Trying to access a nonexistent key in your dictionary
-ValueError
#5.ValueError
#Data exception
print(int("abc"))
#The input value is abnormal, such as entering a number. But a string is entered. It usually occurs when the input number is calculated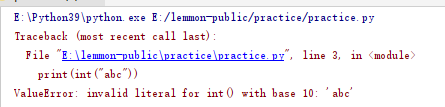
Pass in an unexpected value, even if the type is correct
-IOError
File operation input / output exception
Handling exceptions
-Analyze problems
- Exceptions are usually prompted in python
- Analysis exception prompt
- It will prompt which file and which line of code has an exception
- Then copy the exception type and information and search
-Exception capture
- Exception type found
- Anomaly analysis
- Find the code that triggers the exception
Syntax:
Write the code that may cause exceptions into try
try:
Possible exception codes
If executed normally, it will not be captured and except ion will not be executed
If an exception is triggered, go to except
except Name of exception type as variable name:
Operation after exception
Whether an exception is caught or not, it will not affect the operation of the following programs
Put the specific exception content into a variable and print it out
Exception is followed by the name of the exception type, which means that only the specified exception type is caught
Do not write the exception type name or use exception to capture all exceptions. Do not use it easily. Different exception types should be handled with different schemes
#Capture the specified type
a = [1,2,3]
index = 100
try:
value = a[index]
1/0
print("Did you trigger an exception")
except IndexError as err:
#Capture IndexError only
#Put the specific exception information into a variable
print(f"""index There is a problem with the index,Relatively serious,Trouble repair:{err}""")
except ZeroDivisionError as e:
print(f"""Calculation error,Primary error,Notify the Engineer{e}""")
#Two exceptions cannot be triggered at the same time. Only one exception can be caught
print("Continue running")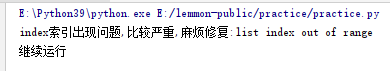
The code runs from top to bottom. When value=a[index] is executed, it is immediately caught by exception because of an exception,
Therefore, the subsequent 1 / 0 will not be executed and will not be captured by the second except ion
-Specific usage of exception types
#Specific usage
#Don't write try at the beginning. Write again when the program has reported an error
#Enter abc
age = input("Enter age")
try:
age = float(age)
if age > 18: #The operation can only be continued after normal execution. It cannot be placed outside the exception handling because the exception has not been solved
print("adult")
else:
print("under age")
except ValueError as e:
print("You entered letters,Please enter an error")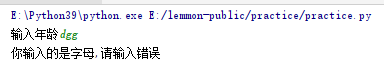
The exception code is age = float(age)
If the if is written outside the try, an error will still be reported because the age has not yet performed the conversion
The judgment can be continued only when the operation can be performed normally
-Actively throw exception
Exception types and information can be customized
raise actively throws exception information, which is usually followed by the judgment statement
#Actively throw exception
def add(a,b):
#a. B with requirements
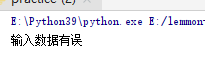
if a >10 or b < 3:
raise ValueError("Error in input data")
c = a + b
return c
print(add(6,1)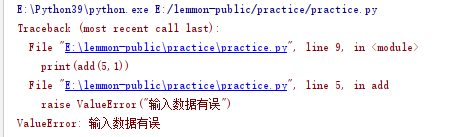
Using exception capture
#Actively throw exception
def add(a,b):
#a. B with requirements
if a >10 or b < 3:
raise ValueError("Error in input data")
c = a + b
return c
try:
a = add(6,1)
print(a)
except ValueError as err:
print(err)