subject
Assume that the file system is as shown in the figure below:
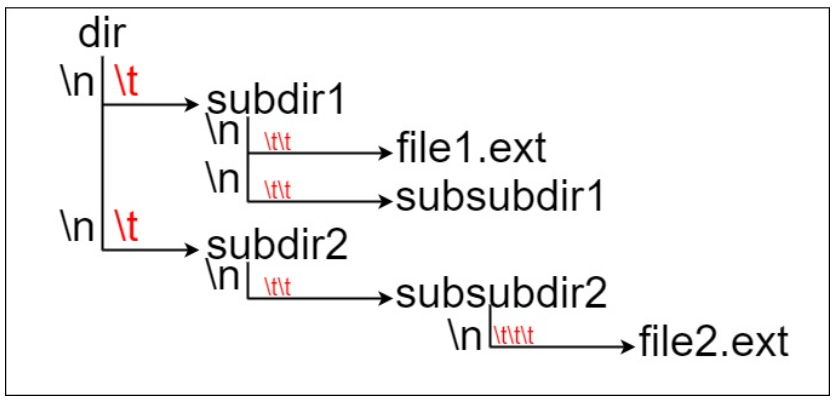
Here, dir is the only directory in the root directory. Dir contains two subdirectories, subdir1 and subdir2. Subdir1 contains the file file1.ext and subdirectory subdir1; Subdir2 contains the subdirectory subdir2, which contains the file file2.ext.
In the text format, as follows (⟶ indicates tab):
dir ⟶ subdir1 ⟶ ⟶ file1.ext ⟶ ⟶ subsubdir1 ⟶ subdir2 ⟶ ⟶ subsubdir2 ⟶ ⟶ ⟶ file2.ext
If it is a code representation, the above file system can be written as "dir\n\tsubdir1\n\t\tfile1.ext\n\t\tsubsubdir1\n\tsubdir2\n\t\tsubsubdir2\n\t\t\tfile2.ext."\ N 'and' \ t 'are line breaks and tabs, respectively.
Each file and folder in the file system has a unique absolute path, that is, it must be opened to reach the directory order where the file / directory is located. All paths are connected with '/'. In the above example, the absolute path to file2.ext is "dir / subdir2 / subdir2 / File2. Ext". Each directory name is composed of letters, numbers and / or spaces, and each file name follows the format of name.extension, where the name and extension are composed of letters, numbers and / or spaces.
Given a string input representing the file system in the above format, returns the length of the longest absolute path to the file in the file system. If there are no files in the system, return 0.
Example 1:
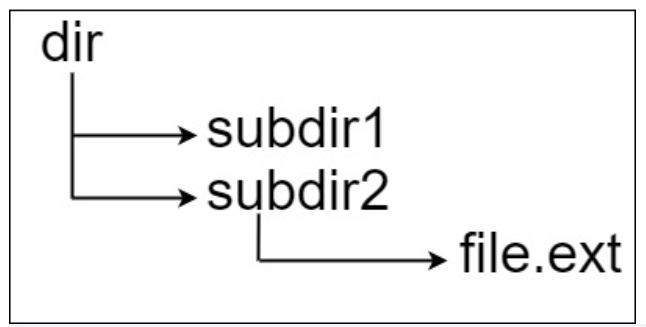
Input: input = "dir\n\tsubdir1\n\tsubdir2\n\t\tfile.ext" Output: 20 Explanation: there is only one file, and the absolute path is "dir/subdir2/file.ext" ,Path length 20 route "dir/subdir1" No files included
Example 2:
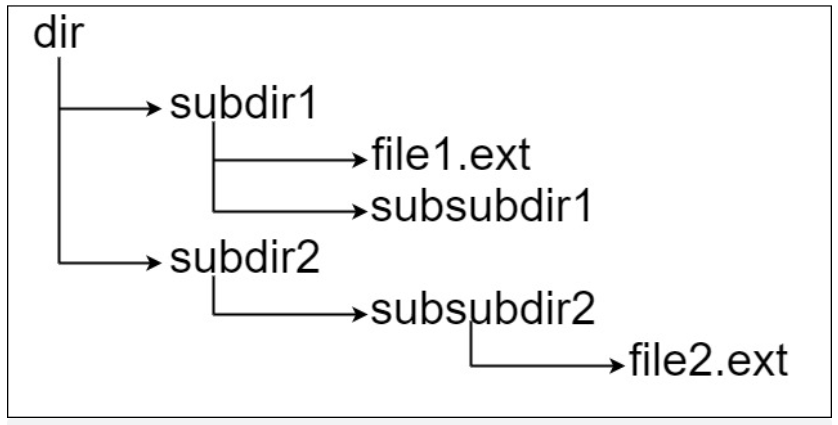
Input: input = "dir\n\tsubdir1\n\t\tfile1.ext\n\t\tsubsubdir1\n\tsubdir2\n\t\tsubsubdir2\n\t\t\tfile2.ext" Output: 32 Explanation: there are two files: "dir/subdir1/file1.ext" ,Path length 21 "dir/subdir2/subsubdir2/file2.ext" ,Path length 32 Returns 32 because this is the longest path
Example 3:
Input: input = "a" Output: 0 Explanation: no files exist
Example 4:
Input: input = "file1.txt\nfile2.txt\nlongfile.txt" Output: 12 Explanation: there are 3 files in the root directory. Because the absolute path to anything in the root directory is only the name itself, the answer is "longfile.txt" ,The path length is 12
Tips:
- 1 <= input.length <= 104
- input may contain lowercase or uppercase letters, a newline '\ n', a pointer '\ t', a dot '.', a space ', and numbers.
thinking
1. First split the string, split the string through \ n, and save it in the array for later judgment
2. Judge the current level (that is, the depth of the file). One \ t represents level 1
3. If the current level is larger than that seen before, take out the length of the content of the level and put it on the stack
4. If you encounter '.', it means that you have encountered a file. There will be no folder behind the file. You can directly judge whether the current length is the longest
5. If subdir1, as seen in the example, is already the deepest level encountered at present, and subdir2 will be encountered next time. There is only level 1, all of the current stack will be cleaned up to level 0 and recalculated.
6. At the end of the cycle, the output of the judgment length in step 4 can be
code
import java.util.Stack;
public class The longest absolute path to the file {
public static int lengthLongestPath(String input) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
int result = 0;
stack.push(0);
// 1. Split string with \ n
String[] newString = input.split("\n");
for(int i = 0 ;i < newString.length ;i++ ){
// 2. Calculate the level of the current string
int level = newString[i].lastIndexOf("\t") + 1;
// 2.1 if the level of the current string is larger than the level already calculated, clean up the data in the stack before calculation
while(stack.size() > level + 1) {
stack.pop();
}
// 2.2 get the length of all current strings
int length = stack.size()+ (newString[i].length() - level + 1);
// 3. Save the current latest length to the stack
stack.push(length);
// 5. If it is a file, it indicates that the level has reached the bottom, and the final length of the cycle of this level can be output
if(newString[i].contains(".")){
result = Math.max(result,length - 1);
}
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(lengthLongestPath("dir\\n\\tsubdir1\\n\\tsubdir2\\n\\t\\tfile.ext"));
}
}
Reference address
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/longest-absolute-file-path/