About ForkJoin:
- The forkjoin framework is a framework provided by Java 7 for parallel execution of tasks. It is a framework that divides large tasks into several small tasks, and finally collects the results of each small task to get the results of large tasks.
Core idea: divide and rule
- fork: break down tasks
- join: collect data
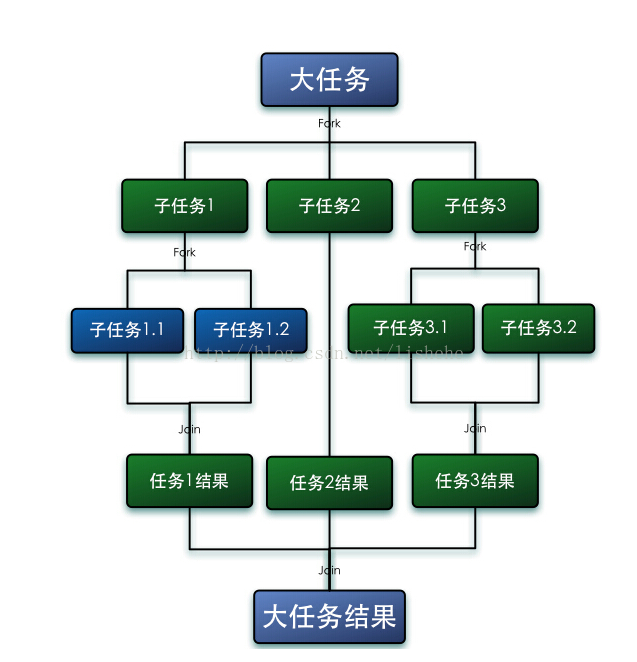
Code example
package com.fixData.util.use;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool;
import java.util.concurrent.RecursiveTask;
//forkJoin framework
public class ForkJoinTest {
// Need to process when data
private List<String> dataList;
// Thread count
private int threadNum;
public static void main(String[] args) {
new ForkJoinTest().dowork();
}
private void dowork() {
while (true) {
// Get the data to be processed through query
dataList = new ArrayList<String>();
if (dataList == null || dataList.size() < 0) {
System.out.println("dataList Length is 0!!!");
break;
}
// Processing through the forkjoin framework
ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool(100);
Task task = new Task(dataList);// Incoming data to be processed
pool.submit(task);// Submit processing
task.join();// Data collection
}
}
// Processing data
private void deal(List<String> list) {
for (String str : list) {
}
}
// Use it directly. You don't need to change anything except the class name
class Task extends RecursiveTask<String> {
// Divide data by thread
private int size = dataList.size() / threadNum == 0 ? 1 : dataList.size() / threadNum;
private List<String> data;
public Task(List<String> data) {
this.data = data;
}
@Override
protected String compute() {
if (this.data.size() <= this.size) {
System.out.println("******************************** size:" + data.size());
deal(data);
} else {
// Break down into small tasks
List<Task> tasks = new ArrayList<ForkJoinTest.Task>();
for (int index = 0; index * size < data.size(); index++) {
Task task;
if ((index + 1) * size > data.size()) {
task = new Task(data.subList(index * size, data.size()));
} else {
task = new Task(data.subList(index * size, (index + 1) * size));
}
task.fork();
tasks.add(task);
}
for (Task task : tasks) {
task.join();
}
}
return null;
}
}
}
Purpose of my work: data processing:
- I usually use it to read the data in mysql/mongo and insert it into es through multiple threads
- Or read es data, insert mysql through multithreading, or export to csv, etc