1, this point
1. Definitions
this is a keyword used within the scope
Global is rarely used, and most of it is used inside functions
2. Direction
2-1. Global usage
When used globally, this points to window
2-2. Function usage
Note: no matter how the function is defined, no matter where the function is, it only depends on the call of the function (except the arrow function)
- Normal call (direct call / global call)
Function name ()
this -> window
function fn() { console.log(this) }
fn() Normal call this -> window
- Object call
xxx. Function name ()
This - > who is in front of the point is who
var obj = {
f: fn,
name: 'I am obj object'
}
obj.f() Object call this -> obj
- Timer processing function
setTimeout(function () {}, 0)
this -> window
setTimeout(fn, 0) Timer processing function call this -> window setTimeout(obj.f(), 0) Timer processing function call this -> window
- Event handler
xxx.onclick = function () {}
This - > event source (event bound to whom)
xxx.addEventListener('event type ', function() {})
This - > event source
var div = document.querySelector('div')
//When you click div, execute obj.f
div.onclick = obj.f Event handler this -> Event source (div)
div.addElentListener('click', obj.f) Event handler this -> Event source (div)
- Self executing function
(function () {})
this -> window
Comprehensive small test:
function fn() {
console.log(this)
}
fn() this -> window
setTimeout(function () { fn() }, 0) this -> window
var div = document.querySelector('div')
div.onclick = function () {
function f() {
console.log(this)
}
fn() this -> window
}
var obj = {
name: 'I am obj object',
fn: function () {
console.log(this)
function () {
console.log(this)
}
fun() this -> window
}
}
obj.fn() this -> obj
// The function address stored by fn member in obj is assigned to the global variable f
// The global variables f and obj.fn point to the same function space
var f = obj.fn
f() this -> window
2, Change this point
this has its own directivity
There are three ways to change the direction of this:
1. call()
Usage: connect directly after the function name
Syntax:
fn.call()
obj.fn.call()
Parameters:
The first parameter is this point inside the function
Starting with the second parameter, pass the parameters to the function in turn
Features: it will execute the function immediately (not suitable for timer processing function or event processing function)
Function: pseudo array borrowing array method
function f() {
console.log(arguments)
}
Pseudo arrays don't use common array methods
But arrays can be used
every() Method call, You need to receive a function as an argument
arguments.every() because arguments No, every method, So report an error
var res = arguments.every(function (t) { return t >= 20 })
Array recall every method
every Inside this Point to the previous array
var res = [].every()
utilize call Method to execute the array every() function
var res = [].every.call()
The first parameter is every Inside this point
original every of this When pointing to an array, Traversal view array
Now? every of this point arguments, Traversal view arguments
var res = [].every.call(arguments)
call The second argument to is to pass arguments to the function
function a Is passed on to every Method
var res = [].every.call(arguments, function a(item) { return item >= 8 })
console.log(res)
}
f(10, 20, 30, 40, 50)
2. apply()
Usage: connect directly after the function name
Syntax:
fn.apply()
obj.fn.apply()
Parameters:
The first parameter is this point inside the function
The second parameter: it is an array or pseudo array, and each item in it passes parameters to the function in turn
Features: it will execute the function immediately (not suitable for timer processing function or event processing function)
Function: you can pass parameters to some function functions in the form of array
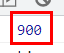
Math.max()
var arr = [100, 5, 30, 80, 900, 60] var res = Math.max.apply(null, arr) console.log(res)
3. bind()
Usage: connect directly after the function name
Syntax:
fn.bind()
obj.fn.bind()
Parameters:
The first parameter is this point inside the function
Starting with the second parameter, pass the parameters to the function in turn
characteristic:
The function is not called immediately
It will return a new function, a function that has changed the point of this
Function: change the this point of the event handler or timer handler
demonstration:
function fn(a, b) {
console.group('fn function')
console.log(this)
console.log(a)
console.log(b)
console.groupEnd()
}
var obj = {
name: 'I am obj object'
}
fn(100, 200) this -> winodw
1.use call Method to call fn Function, put the inside of the function this Change direction to obj
fn.call(obj, 100, 200)
2.use apply Method call fn Function, put the inside of the function this Change direction to obj
fn.apply(obj, [100, 'hello', 'world'])
3.use bind Method change fn Functional this point
res It's a fn A clone of the function, just inside thsi Point is locked, point obj
var res = fn.bind(obj, 'hello', 'world')
res()