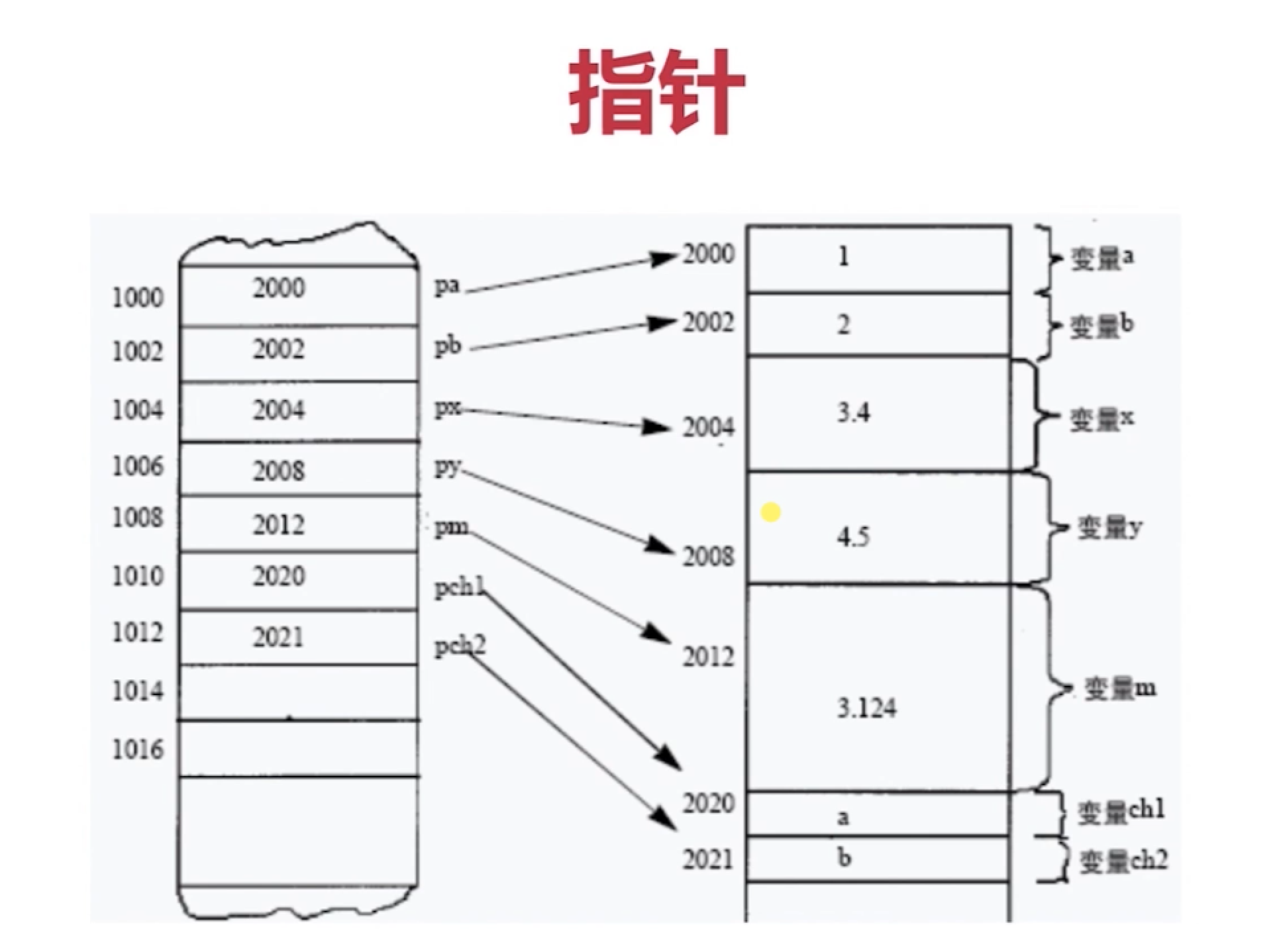
Characteristics of pointer
- He's an address in memory
- Operation of pointer itself
- What the pointer points to is actionable
How the operating system manages memory
Stack space
- 4M~8m
- When entering the function, stack data will be pressed
Heap space
- 4g size 1g is the operating system
- global variable
Memory mapping
- You can modify the contents of the hard disk by modifying the contents of the memory
- Commonly used in database
Allocation and release of memory
-
The method of allocating memory in c language
// Malloc (the size to be allocated); the allocated size here needs the exponent of 2 to be aligned void *mem = malloc(size);
-
Free memory
// Generally, the allocated content is in the heap space // If it is not released after use, memory leak and wild pointer will appear free(men);
- What is a memory leak:
- Constantly apply memory to the system
- The applied memory is not used or released
- Never allow memory leaks
- What is the wild pointer
- This pointer has been released
- Someone else created this pointer again
- In the past, I used this pointer again
Function pointer
Return value type (* pointer variable name) (parameter list);
int func(int x); // Declare a function int (*f)(int x); // Declare a function pointer f = func; // Assign the first address of func function to pointer f
#include <stdio.h>
int sum (int a, int b)
{
return (a+b);
}
int main(int argc, int *argv[])
{
// Define a function pointer
int (*f) (int, int);
// f points to sum function
f = sum;
// Executing the f function is equivalent to executing the sum function
int f_sum = f(2,3);
printf("f_sum: %d\n", f_sum);
return 0;
}Pointer is memory address: void *, char*
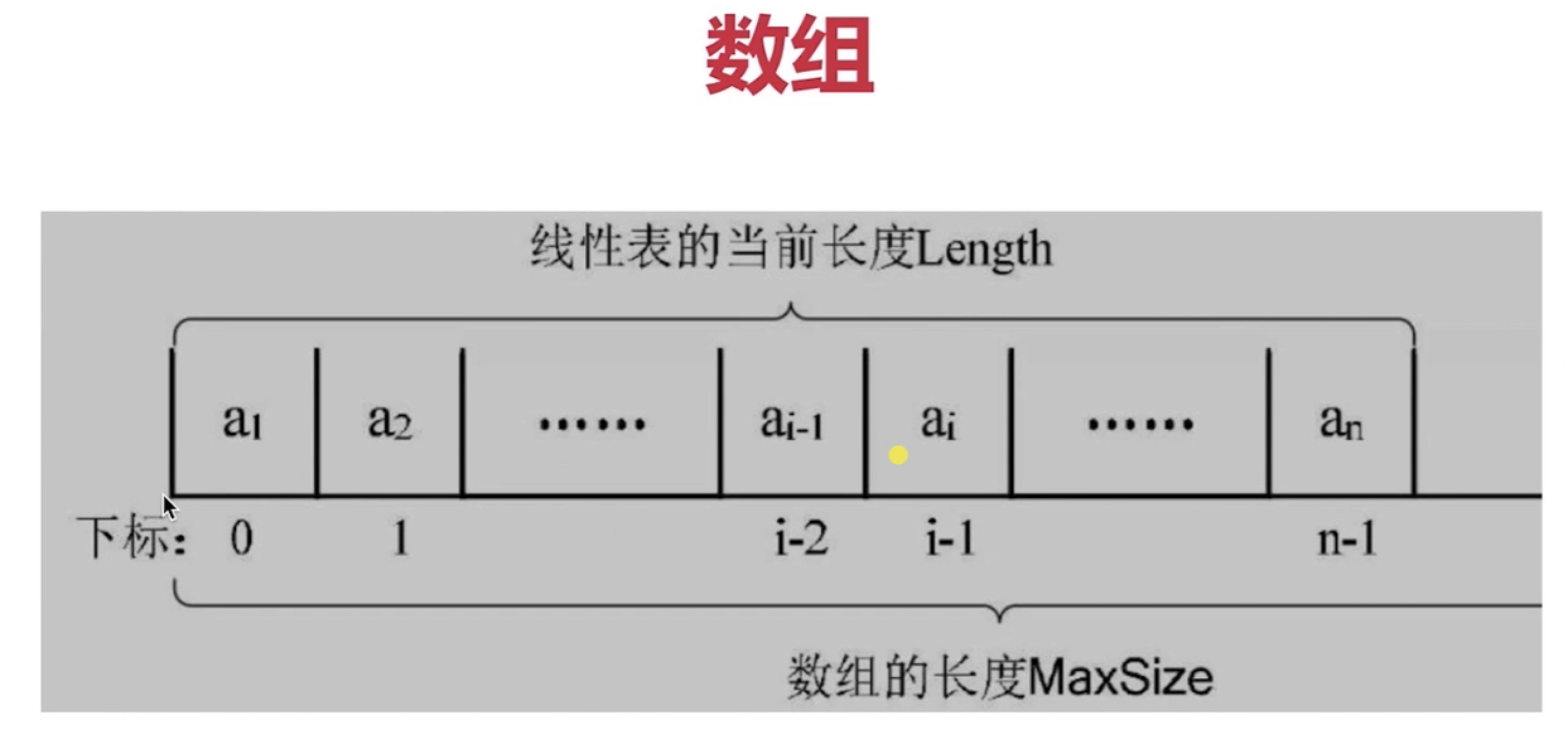
Array is: char c[2], int arr[10], referring to spaces of the same type in succession
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
// Define two pointers of type int
int *a, *b;
// Making room in the heap through malloc
a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int));
b = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int));
*a = 1;
*b = 2;
// The address of pointer A is & A, a is the address pointing to space, * a is the value pointing to space
printf("addr of a:%p, %p, %d\n", &a, a, *a);
printf("addr of b:%p, %p, %d\n", &b, b, *b);
return 0;
}
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
// Create an array c with 3 data, an array of int type takes up 4 bytes, and the address related space difference is 1 byte
int c[3] = {1,2,3};
printf("c Address:%p\t%p\tc[0]:%p\tc[1]:%p\tc[2]:%p\t\n",c, &c, &c[0], &c[1], &c[2]);
printf("%d, %d, %d\n", c[0], c[1], c[2]);
}