1, ID3 algorithm
1. Ladle
import numpy as np import pandas as pd import sklearn.tree as st import math import matplotlib import os import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
2. Read data
data = pd.read_csv('C:/Watermelon dataset.csv',header=None)
data
3. Coding
entropy
def calcEntropy(dataSet):
mD = len(dataSet)
dataLabelList = [x[-1] for x in dataSet]
dataLabelSet = set(dataLabelList)
ent = 0
for label in dataLabelSet:
mDv = dataLabelList.count(label)
prop = float(mDv) / mD
ent = ent - prop * np.math.log(prop, 2)
return ent
Split dataset
def splitDataSet(dataSet, index, feature):
splitedDataSet = []
mD = len(dataSet)
for data in dataSet:
if(data[index] == feature):
sliceTmp = data[:index]
sliceTmp.extend(data[index + 1:])
splitedDataSet.append(sliceTmp)
return splitedDataSet
Optimal feature
def chooseBestFeature(dataSet):
entD = calcEntropy(dataSet)
mD = len(dataSet)
featureNumber = len(dataSet[0]) - 1
maxGain = -100
maxIndex = -1
for i in range(featureNumber):
entDCopy = entD
featureI = [x[i] for x in dataSet]
featureSet = set(featureI)
for feature in featureSet:
splitedDataSet = splitDataSet(dataSet, i, feature) # Split dataset
mDv = len(splitedDataSet)
entDCopy = entDCopy - float(mDv) / mD * calcEntropy(splitedDataSet)
if(maxIndex == -1):
maxGain = entDCopy
maxIndex = i
elif(maxGain < entDCopy):
maxGain = entDCopy
maxIndex = i
return maxIndex
Find up to tags
def mainLabel(labelList):
labelRec = labelList[0]
maxLabelCount = -1
labelSet = set(labelList)
for label in labelSet:
if(labelList.count(label) > maxLabelCount):
maxLabelCount = labelList.count(label)
labelRec = label
return labelRec
tree
def createFullDecisionTree(dataSet, featureNames, featureNamesSet, labelListParent):
labelList = [x[-1] for x in dataSet]
if(len(dataSet) == 0):
return mainLabel(labelListParent)
elif(len(dataSet[0]) == 1): #There are no separable properties
return mainLabel(labelList) #Select the most label as the label of the dataset
elif(labelList.count(labelList[0]) == len(labelList)): # All belong to the same Label
return labelList[0]
bestFeatureIndex = chooseBestFeature(dataSet)
bestFeatureName = featureNames.pop(bestFeatureIndex)
myTree = {bestFeatureName: {}}
featureList = featureNamesSet.pop(bestFeatureIndex)
featureSet = set(featureList)
for feature in featureSet:
featureNamesNext = featureNames[:]
featureNamesSetNext = featureNamesSet[:][:]
splitedDataSet = splitDataSet(dataSet, bestFeatureIndex, feature)
myTree[bestFeatureName][feature] = createFullDecisionTree(splitedDataSet, featureNamesNext, featureNamesSetNext, labelList)
return myTree
Drawing
def readWatermelonDataSet():
dataSet = data.values.tolist()
featureNames =['color and lustre', 'Root', 'Knock', 'texture', 'Umbilicus', 'Tactile sensation']
#Get featureNamesSet
featureNamesSet = []
for i in range(len(dataSet[0]) - 1):
col = [x[i] for x in dataSet]
colSet = set(col)
featureNamesSet.append(list(colSet))
return dataSet, featureNames, featureNamesSet
matplotlib.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
matplotlib.rcParams['font.serif'] = ['SimHei']
decisionNode = dict(boxstyle="sawtooth", fc="0.8")
leafNode = dict(boxstyle="round4", fc="0.8")
arrow_args = dict(arrowstyle="<-")
def plotNode(nodeTxt, centerPt, parentPt, nodeType):
createPlot.ax1.annotate(nodeTxt, xy=parentPt, xycoords='axes fraction',
xytext=centerPt, textcoords='axes fraction',
va="center", ha="center", bbox=nodeType, arrowprops=arrow_args)
def getNumLeafs(myTree):
numLeafs = 0
firstStr = list(myTree.keys())[0]
secondDict = myTree[firstStr]
for key in secondDict.keys():
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__ == 'dict':
numLeafs += getNumLeafs(secondDict[key])
else:
numLeafs += 1
return numLeafs
def getTreeDepth(myTree):
maxDepth = 0
firstStr = list(myTree.keys())[0]
secondDic = myTree[firstStr]
for key in secondDic.keys():
if type(secondDic[key]).__name__ == 'dict':
thisDepth = 1 + getTreeDepth(secondDic[key])
else:
thisDepth = 1
if thisDepth > maxDepth:
maxDepth = thisDepth
return maxDepth
def plotMidText(cntrPt, parentPt, txtString):
xMid = (parentPt[0]-cntrPt[0])/2.0 + cntrPt[0]
yMid = (parentPt[1]-cntrPt[1])/2.0 + cntrPt[1]
createPlot.ax1.text(xMid, yMid, txtString)
def plotTree(myTree, parentPt, nodeTxt):
numLeafs = getNumLeafs(myTree=myTree)
depth = getTreeDepth(myTree=myTree)
firstStr = list(myTree.keys())[0]
cntrPt = (plotTree.xOff + (1.0 + float(numLeafs))/2.0/plotTree.totalW, plotTree.yOff)
plotMidText(cntrPt, parentPt, nodeTxt)
plotNode(firstStr, cntrPt, parentPt, decisionNode)
secondDict = myTree[firstStr]
plotTree.yOff = plotTree.yOff - 1.0/plotTree.totalD
for key in secondDict.keys():
if isinstance(secondDict[key], dict):
plotTree(secondDict[key], cntrPt, str(key))
else:
plotTree.xOff = plotTree.xOff + 1.0/plotTree.totalW
plotNode(secondDict[key], (plotTree.xOff, plotTree.yOff), cntrPt, leafNode)
plotMidText((plotTree.xOff, plotTree.yOff), cntrPt, str(key))
plotTree.yOff = plotTree.yOff + 1.0/plotTree.totalD
def createPlot(inTree):
fig = plt.figure(1, facecolor='white')
fig.clf()
axprops = dict(xticks=[], yticks=[])
createPlot.ax1 = plt.subplot(111, frameon=False, **axprops)
plotTree.totalW = float(getNumLeafs(inTree))
plotTree.totalD = float(getTreeDepth(inTree))
plotTree.xOff = -0.5/plotTree.totalW
plotTree.yOff = 1.0
plotTree(inTree, (0.5, 1.0), '')
plt.show()
dataSet, featureNames, featureNamesSet=readWatermelonDataSet()
testTree= createFullDecisionTree(dataSet, featureNames, featureNamesSet,featureNames)
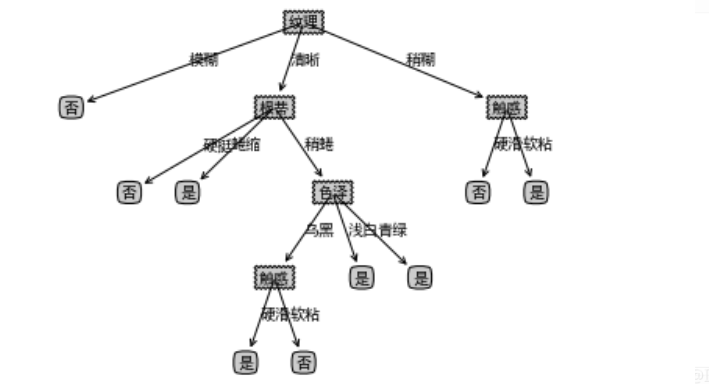
createPlot(testTree)
result
2, Implementation of sklearn ID3 and CART algorithm
1.ID3
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
data = pd.read_csv('C:/Watermelon dataset.csv',header=None)
data
label = LabelEncoder()
for col in data[data.columns[:-1]]:
data[col] = label.fit_transform(data[col])
data
# Fit with ID3
dtc = DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion='entropy')
# Fit
dtc.fit(data.iloc[:,:-1].values.tolist(),data.iloc[:,-1].values)
# Tag corresponding code
result = dtc.predict([[0,0,0,0,0,0]])
#Fitting results
result
2.CART
# Fit with CART dtc = DecisionTreeClassifier() # Fit dtc.fit(data.iloc[:,:-1].values.tolist(),data.iloc[:,-1].values) # Tag corresponding code result = dtc.predict([[0,0,0,1,0,0]]) #Fitting results result
3, Summary
1.ID3 algorithm
By calculating the information gain of each attribute, ID3 algorithm considers that the attribute with high information gain is a good attribute. Each division selects the attribute with the highest information gain as the division standard, and repeats this process until a decision tree that can perfectly classify training samples is generated.
Decision tree is used to classify data to achieve the purpose of prediction. The decision tree method first forms a decision tree according to the training set data. If the tree can not give correct classification to all objects, select some exceptions to the training set data and repeat the process until a correct decision set is formed. Decision tree represents the tree structure of decision set.
The decision tree consists of decision nodes, branches and leaves. The top node in the decision tree is the root node, and each branch is a new decision node or a leaf of the tree. Each decision node represents a problem or decision, which usually corresponds to the attributes of the object to be classified. Each leaf node represents a possible classification result. In the process of traversing from top to bottom along the decision tree, a test will be encountered at each node. Different test outputs of problems on each node will lead to different branches, and finally reach a leaf node. This process is the process of classification using the decision tree and using several variables to judge the category.
2.CART algorithm
(1) Select an independent variable, and then select a value to divide the dimensional space into two parts. All points of one part are satisfied, and all points of the other part are satisfied. For discontinuous variables, there are only two values of attribute value, that is, equal to or not equal to the value.
(2) Recursive processing, re select an attribute from the above two parts according to step (1) and continue to divide until the whole dimensional space is divided.