The compilation of 50 Matplotlib diagrams is the most useful in data analysis and visualization. This list allows you to select the visualization objects to display using Python's Matplotlib and Seaborn libraries.
1. Association
Scatter diagram Bubble chart with boundary Scatter diagram with linear regression best fit line Dithering diagram Counting diagram edge histogram Edge box diagram Correlation diagram Matrix diagram
2. Deviation
Divergent bar chart Divergent text Divergent envelope diagram Divergent lollipop chart with markers Area map
3. Sorting
Ordered bar graph Lollipop chart Package point diagram Slope map Dumbbell diagram
4. Distribution
Histogram of continuous variables Histogram of type variables Density map Square density line Joy Plot Distributed packet graph Package point + box diagram Dot + Box Plot Violin picture Population pyramid Classification diagram
5. Composition
Waffle chart Pie chart Tree diagram Bar chart
6. Changes
Time series diagram Timing chart with peak and trough marks Autocorrelation and partial autocorrelation diagram Cross correlation diagram Time series decomposition Multiple time series Use the auxiliary Y axis to draw different ranges of graphics Time series with error band Stacking area map Non stacked area map Calendar heat map Seasonal map
7. Grouping
Tree view Cluster diagram Andrews curve Parallel coordinates
# !pip install brewer2mpl
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib as mpl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
import warnings; warnings.filterwarnings(action='once')
large = 22; med = 16; small = 12
params = {'axes.titlesize': large,
'legend.fontsize': med,
'figure.figsize': (16, 10),
'axes.labelsize': med,
'axes.titlesize': med,
'xtick.labelsize': med,
'ytick.labelsize': med,
'figure.titlesize': large}
plt.rcParams.update(params)
plt.style.use('seaborn-whitegrid')
sns.set_style("white")
%matplotlib inline
# Version
print(mpl.__version__) #> 3.0.0
print(sns.__version__) #> 0.9.01. Scatter diagram
Scatteplot is a classical and basic graph used to study the relationship between two variables. If there are multiple groups in the data, you may need to visualize each group in different colors. In Matplotlib, you can use it easily.
# Import dataset
midwest = pd.read_csv("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selva86/datasets/master/midwest_filter.csv")
# Prepare Data
# Create as many colors as there are unique midwest['category']
categories = np.unique(midwest['category'])
colors = [plt.cm.tab10(i/float(len(categories)-1)) for i in range(len(categories))]
# Draw Plot for Each Category
plt.figure(figsize=(16, 10), dpi= 80, facecolor='w', edgecolor='k')
for i, category in enumerate(categories):
plt.scatter('area', 'poptotal',
data=midwest.loc[midwest.category==category, :],
s=20, c=colors[i], label=str(category))
# Decorations
plt.gca().set(xlim=(0.0, 0.1), ylim=(0, 90000),
xlabel='Area', ylabel='Population')
plt.xticks(fontsize=12); plt.yticks(fontsize=12)
plt.title("Scatterplot of Midwest Area vs Population", fontsize=22)
plt.legend(fontsize=12)
plt.show() 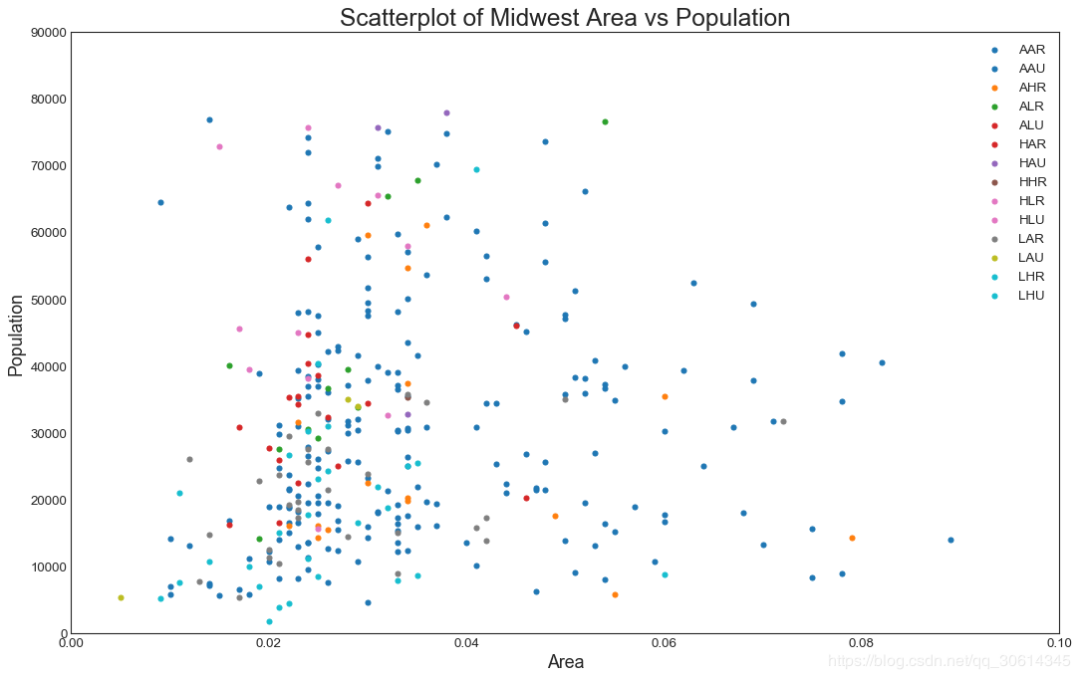
2. Bubble chart with boundary
Sometimes you want to display a set of points within the boundary to emphasize its importance. In this example, you will take the record from the data frame that should be surrounded and pass it to the record described in the following code. encircle()
from matplotlib import patches
from scipy.spatial import ConvexHull
import warnings; warnings.simplefilter('ignore')
sns.set_style("white")
# Step 1: Prepare Data
midwest = pd.read_csv("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selva86/datasets/master/midwest_filter.csv")
# As many colors as there are unique midwest['category']
categories = np.unique(midwest['category'])
colors = [plt.cm.tab10(i/float(len(categories)-1)) for i in range(len(categories))]
# Step 2: Draw Scatterplot with unique color for each category
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(16, 10), dpi= 80, facecolor='w', edgecolor='k')
for i, category in enumerate(categories):
plt.scatter('area', 'poptotal', data=midwest.loc[midwest.category==category, :], s='dot_size', c=colors[i], label=str(category), edgecolors='black', linewidths=.5)
# Step 3: Encircling
# https://stackoverflow.com/questions/44575681/how-do-i-encircle-different-data-sets-in-scatter-plot
def encircle(x,y, ax=None, **kw):
if not ax: ax=plt.gca()
p = np.c_[x,y]
hull = ConvexHull(p)
poly = plt.Polygon(p[hull.vertices,:], **kw)
ax.add_patch(poly)
# Select data to be encircled
midwest_encircle_data = midwest.loc[midwest.state=='IN', :]
# Draw polygon surrounding vertices
encircle(midwest_encircle_data.area, midwest_encircle_data.poptotal, ec="k", fc="gold", alpha=0.1)
encircle(midwest_encircle_data.area, midwest_encircle_data.poptotal, ec="firebrick", fc="none", linewidth=1.5)
# Step 4: Decorations
plt.gca().set(xlim=(0.0, 0.1), ylim=(0, 90000),
xlabel='Area', ylabel='Population')
plt.xticks(fontsize=12); plt.yticks(fontsize=12)
plt.title("Bubble Plot with Encircling", fontsize=22)
plt.legend(fontsize=12)
plt.show() 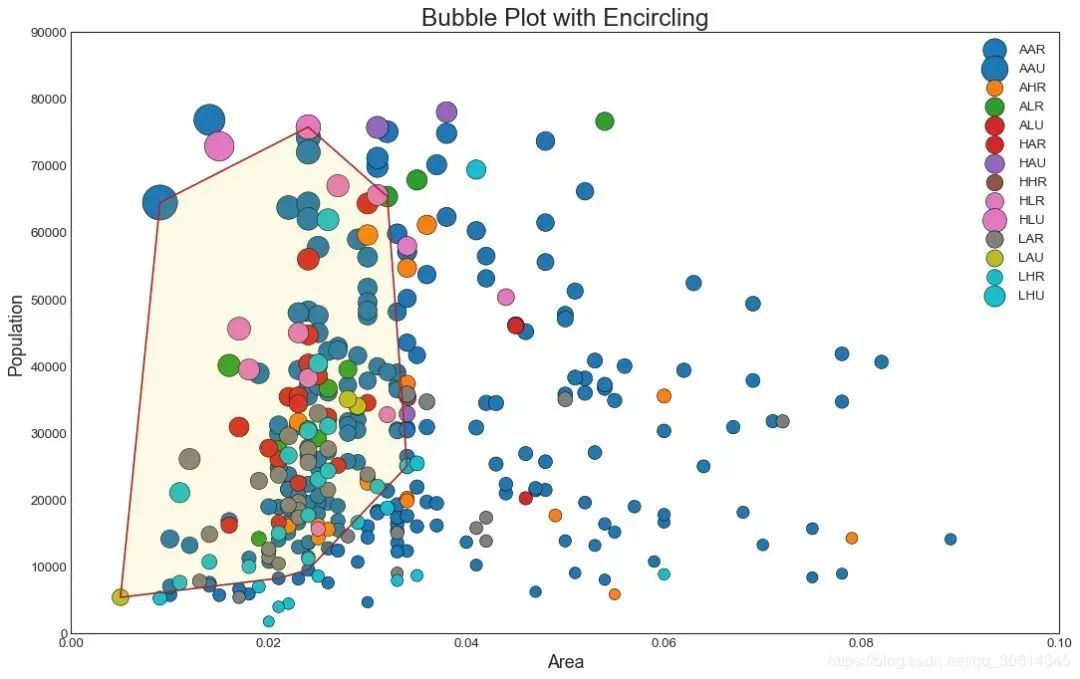
3. Scatter plot with linear regression best fit line
If you want to understand how the two variables change with each other, the most appropriate line is the way to go. The following figure shows the difference in the best fit line between groups in the data. To disable grouping and draw only one best fit line for the entire dataset, remove the parameter from the call below.
# Import Data
df = pd.read_csv("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selva86/datasets/master/mpg_ggplot2.csv")
df_select = df.loc[df.cyl.isin([4,8]), :]
# Plot
sns.set_style("white")
gridobj = sns.lmplot(x="displ", y="hwy", hue="cyl", data=df_select,
height=7, aspect=1.6, robust=True, palette='tab10',
scatter_kws=dict(s=60, linewidths=.7, edgecolors='black'))
# Decorations
gridobj.set(xlim=(0.5, 7.5), ylim=(0, 50))
plt.title("Scatterplot with line of best fit grouped by number of cylinders", fontsize=20)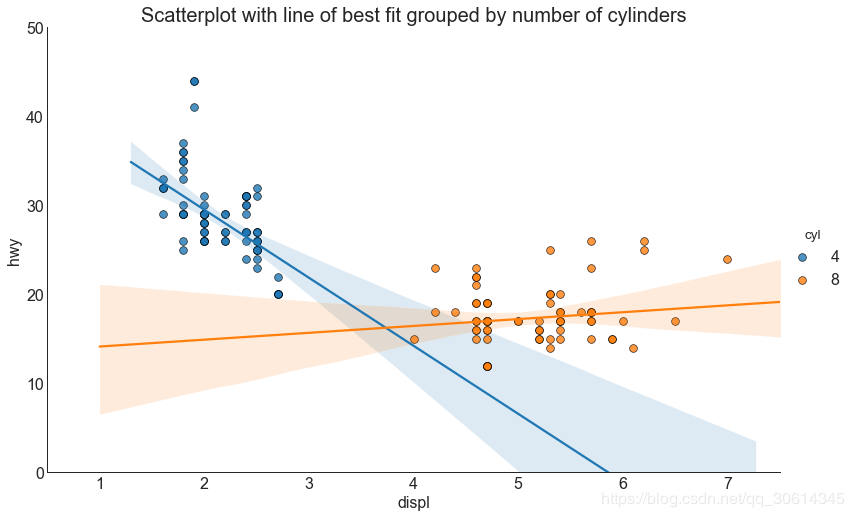
Each regression line is in its own column
Alternatively, you can display the best fit line for each group in its own column. You can do this by setting parameters in it.
# Import Data
df = pd.read_csv("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selva86/datasets/master/mpg_ggplot2.csv")
df_select = df.loc[df.cyl.isin([4,8]), :]
# Each line in its own column
sns.set_style("white")
gridobj = sns.lmplot(x="displ", y="hwy",
data=df_select,
height=7,
robust=True,
palette='Set1',
col="cyl",
scatter_kws=dict(s=60, linewidths=.7, edgecolors='black'))
# Decorations
gridobj.set(xlim=(0.5, 7.5), ylim=(0, 50))
plt.show()
4. Jitter diagram
Typically, multiple data points have exactly the same X and Y values. As a result, multiple points are drawn and hidden from each other. To avoid this, shake a little so that you can see them intuitively. It's easy to use
# Import Data
df = pd.read_csv("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selva86/datasets/master/mpg_ggplot2.csv")
# Draw Stripplot
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(16,10), dpi= 80)
sns.stripplot(df.cty, df.hwy, jitter=0.25, size=8, ax=ax, linewidth=.5)
# Decorations
plt.title('Use jittered plots to avoid overlapping of points', fontsize=22)
plt.show()
5. Counting diagram
Another option to avoid point overlap is to increase the size of the point, depending on how many points there are in the point. Therefore, the larger the size of the point, the greater the concentration of the surrounding points.
# Import Data
df = pd.read_csv("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selva86/datasets/master/mpg_ggplot2.csv")
df_counts = df.groupby(['hwy', 'cty']).size().reset_index(name='counts')
# Draw Stripplot
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(16,10), dpi= 80)
sns.stripplot(df_counts.cty, df_counts.hwy, size=df_counts.counts*2, ax=ax)
# Decorations
plt.title('Counts Plot - Size of circle is bigger as more points overlap', fontsize=22)
plt.show()
6. Edge histogram
The edge histogram has a histogram of variables along the X and Y axes. This is used to visualize the relationship between X and Y and the univariate distribution of individual X and y. This chart is often used for exploratory data analysis (EDA).
# Import Data
df = pd.read_csv("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selva86/datasets/master/mpg_ggplot2.csv")
# Create Fig and gridspec
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(16, 10), dpi= 80)
grid = plt.GridSpec(4, 4, hspace=0.5, wspace=0.2)
# Define the axes
ax_main = fig.add_subplot(grid[:-1, :-1])
ax_right = fig.add_subplot(grid[:-1, -1], xticklabels=[], yticklabels=[])
ax_bottom = fig.add_subplot(grid[-1, 0:-1], xticklabels=[], yticklabels=[])
# Scatterplot on main ax
ax_main.scatter('displ', 'hwy', s=df.cty*4, c=df.manufacturer.astype('category').cat.codes, alpha=.9, data=df, cmap="tab10", edgecolors='gray', linewidths=.5)
# histogram on the right
ax_bottom.hist(df.displ, 40, histtype='stepfilled', orientation='vertical', color='deeppink')
ax_bottom.invert_yaxis()
# histogram in the bottom
ax_right.hist(df.hwy, 40, histtype='stepfilled', orientation='horizontal', color='deeppink')
# Decorations
ax_main.set(title='Scatterplot with Histograms
displ vs hwy', xlabel='displ', ylabel='hwy')
ax_main.title.set_fontsize(20)
for item in ([ax_main.xaxis.label, ax_main.yaxis.label] + ax_main.get_xticklabels() + ax_main.get_yticklabels()):
item.set_fontsize(14)
xlabels = ax_main.get_xticks().tolist()
ax_main.set_xticklabels(xlabels)
plt.show()
7. Edge box diagram
Edge box graphs have similar uses to edge histograms. However, the box plot helps to accurately locate the median, 25th and 75th percentiles of X and Y.
# Import Data
df = pd.read_csv("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selva86/datasets/master/mpg_ggplot2.csv")
# Create Fig and gridspec
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(16, 10), dpi= 80)
grid = plt.GridSpec(4, 4, hspace=0.5, wspace=0.2)
# Define the axes
ax_main = fig.add_subplot(grid[:-1, :-1])
ax_right = fig.add_subplot(grid[:-1, -1], xticklabels=[], yticklabels=[])
ax_bottom = fig.add_subplot(grid[-1, 0:-1], xticklabels=[], yticklabels=[])
# Scatterplot on main ax
ax_main.scatter('displ', 'hwy', s=df.cty*5, c=df.manufacturer.astype('category').cat.codes, alpha=.9, data=df, cmap="Set1", edgecolors='black', linewidths=.5)
# Add a graph in each part
sns.boxplot(df.hwy, ax=ax_right, orient="v")
sns.boxplot(df.displ, ax=ax_bottom, orient="h")
# Decorations ------------------
# Remove x axis name for the boxplot
ax_bottom.set(xlabel='')
ax_right.set(ylabel='')
# Main Title, Xlabel and YLabel
ax_main.set(title='Scatterplot with Histograms
displ vs hwy', xlabel='displ', ylabel='hwy')
# Set font size of different components
ax_main.title.set_fontsize(20)
for item in ([ax_main.xaxis.label, ax_main.yaxis.label] + ax_main.get_xticklabels() + ax_main.get_yticklabels()):
item.set_fontsize(14)
plt.show()
8. Correlation diagram
Correlogram is used to visually view the correlation metrics between all possible pairs of numeric variables in a given data frame (or 2D array).
# Import Dataset
df = pd.read_csv("https://github.com/selva86/datasets/raw/master/mtcars.csv")
# Plot
plt.figure(figsize=(12,10), dpi= 80)
sns.heatmap(df.corr(), xticklabels=df.corr().columns, yticklabels=df.corr().columns, cmap='RdYlGn', center=0, annot=True)
# Decorations
plt.title('Correlogram of mtcars', fontsize=22)
plt.xticks(fontsize=12)
plt.yticks(fontsize=12)
plt.show()
9. Matrix
Pairwise graphs are a favorite in exploratory analysis to understand the relationship between all possible pairs of digital variables. It is a necessary tool for bivariate analysis.
# Load Dataset
df = sns.load_dataset('iris')
# Plot
plt.figure(figsize=(10,8), dpi= 80)
sns.pairplot(df, kind="scatter", hue="species", plot_kws=dict(s=80, edgecolor="white", linewidth=2.5))
plt.show()
# Load Dataset
df = sns.load_dataset('iris')
# Plot
plt.figure(figsize=(10,8), dpi= 80)
sns.pairplot(df, kind="reg", hue="species")
plt.show()
deviation
10. Divergent bar chart
The divergence bar is a good tool if you want to see the change of the project according to a single indicator and visualize the order and quantity of this difference. It helps to quickly distinguish the performance of groups in data, is very intuitive, and can communicate this immediately.
# Prepare Data
df = pd.read_csv("https://github.com/selva86/datasets/raw/master/mtcars.csv")
x = df.loc[:, ['mpg']]
df['mpg_z'] = (x - x.mean())/x.std()
df['colors'] = ['red' if x < 0 else 'green' for x in df['mpg_z']]
df.sort_values('mpg_z', inplace=True)
df.reset_index(inplace=True)
# Draw plot
plt.figure(figsize=(14,10), dpi= 80)
plt.hlines(y=df.index, xmin=0, xmax=df.mpg_z, color=df.colors, alpha=0.4, linewidth=5)
# Decorations
plt.gca().set(ylabel='$Model$', xlabel='$Mileage$')
plt.yticks(df.index, df.cars, fontsize=12)
plt.title('Diverging Bars of Car Mileage', fontdict={'size':20})
plt.grid(linestyle='--', alpha=0.5)
plt.show()
11. Divergent text
Scattered text is similar to divergent bars. If you want to show the value of each item in the chart in a beautiful and presentable way, it is preferred.
# Prepare Data
df = pd.read_csv("https://github.com/selva86/datasets/raw/master/mtcars.csv")
x = df.loc[:, ['mpg']]
df['mpg_z'] = (x - x.mean())/x.std()
df['colors'] = ['red' if x < 0 else 'green' for x in df['mpg_z']]
df.sort_values('mpg_z', inplace=True)
df.reset_index(inplace=True)
# Draw plot
plt.figure(figsize=(14,14), dpi= 80)
plt.hlines(y=df.index, xmin=0, xmax=df.mpg_z)
for x, y, tex in zip(df.mpg_z, df.index, df.mpg_z):
t = plt.text(x, y, round(tex, 2), horizontalalignment='right' if x < 0 else 'left',
verticalalignment='center', fontdict={'color':'red' if x < 0 else 'green', 'size':14})
# Decorations
plt.yticks(df.index, df.cars, fontsize=12)
plt.title('Diverging Text Bars of Car Mileage', fontdict={'size':20})
plt.grid(linestyle='--', alpha=0.5)
plt.xlim(-2.5, 2.5)
plt.show()
12. Divergent envelope diagram
The divergence plot is also similar to the divergence bar. However, compared with divergent bars, the absence of bars reduces the contrast and difference between groups.
# Prepare Data
df = pd.read_csv("https://github.com/selva86/datasets/raw/master/mtcars.csv")
x = df.loc[:, ['mpg']]
df['mpg_z'] = (x - x.mean())/x.std()
df['colors'] = ['red' if x < 0 else 'darkgreen' for x in df['mpg_z']]
df.sort_values('mpg_z', inplace=True)
df.reset_index(inplace=True)
# Draw plot
plt.figure(figsize=(14,16), dpi= 80)
plt.scatter(df.mpg_z, df.index, s=450, alpha=.6, color=df.colors)
for x, y, tex in zip(df.mpg_z, df.index, df.mpg_z):
t = plt.text(x, y, round(tex, 1), horizontalalignment='center',
verticalalignment='center', fontdict={'color':'white'})
# Decorations
# Lighten borders
plt.gca().spines["top"].set_alpha(.3)
plt.gca().spines["bottom"].set_alpha(.3)
plt.gca().spines["right"].set_alpha(.3)
plt.gca().spines["left"].set_alpha(.3)
plt.yticks(df.index, df.cars)
plt.title('Diverging Dotplot of Car Mileage', fontdict={'size':20})
plt.xlabel('$Mileage$')
plt.grid(linestyle='--', alpha=0.5)
plt.xlim(-2.5, 2.5)
plt.show()
13. Divergent lollipop chart with mark
Labeled lollipops provide a flexible way to visualize differences by highlighting any important data points you want to attract attention and giving appropriate reasoning in the chart.
# Prepare Data
df = pd.read_csv("https://github.com/selva86/datasets/raw/master/mtcars.csv")
x = df.loc[:, ['mpg']]
df['mpg_z'] = (x - x.mean())/x.std()
df['colors'] = 'black'
# color fiat differently
df.loc[df.cars == 'Fiat X1-9', 'colors'] = 'darkorange'
df.sort_values('mpg_z', inplace=True)
df.reset_index(inplace=True)
# Draw plot
import matplotlib.patches as patches
plt.figure(figsize=(14,16), dpi= 80)
plt.hlines(y=df.index, xmin=0, xmax=df.mpg_z, color=df.colors, alpha=0.4, linewidth=1)
plt.scatter(df.mpg_z, df.index, color=df.colors, s=[600 if x == 'Fiat X1-9' else 300 for x in df.cars], alpha=0.6)
plt.yticks(df.index, df.cars)
plt.xticks(fontsize=12)
# Annotate
plt.annotate('Mercedes Models', xy=(0.0, 11.0), xytext=(1.0, 11), xycoords='data',
fontsize=15, ha='center', va='center',
bbox=dict(boxstyle='square', fc='firebrick'),
arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle='-[, widthB=2.0, lengthB=1.5', lw=2.0, color='steelblue'), color='white')
# Add Patches
p1 = patches.Rectangle((-2.0, -1), width=.3, height=3, alpha=.2, facecolor='red')
p2 = patches.Rectangle((1.5, 27), width=.8, height=5, alpha=.2, facecolor='green')
plt.gca().add_patch(p1)
plt.gca().add_patch(p2)
# Decorate
plt.title('Diverging Bars of Car Mileage', fontdict={'size':20})
plt.grid(linestyle='--', alpha=0.5)
plt.show()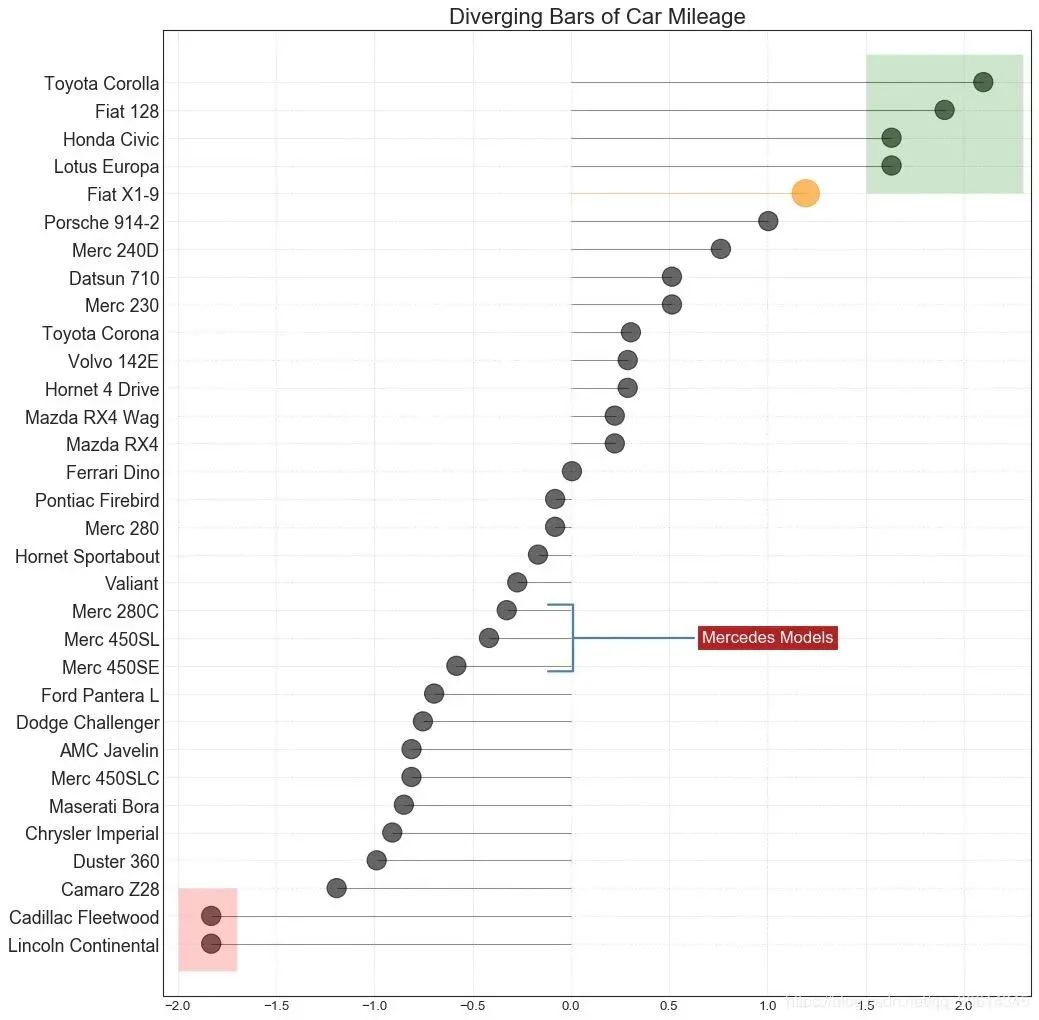
14. Area map
By coloring the area between the axis and the line, the area map emphasizes not only the peak and trough, but also the duration of the high and low points. The longer the duration of the high point, the larger the offline area.
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
# Prepare Data
df = pd.read_csv("https://github.com/selva86/datasets/raw/master/economics.csv", parse_dates=['date']).head(100)
x = np.arange(df.shape[0])
y_returns = (df.psavert.diff().fillna(0)/df.psavert.shift(1)).fillna(0) * 100
# Plot
plt.figure(figsize=(16,10), dpi= 80)
plt.fill_between(x[1:], y_returns[1:], 0, where=y_returns[1:] >= 0, facecolor='green', interpolate=True, alpha=0.7)
plt.fill_between(x[1:], y_returns[1:], 0, where=y_returns[1:] <= 0, facecolor='red', interpolate=True, alpha=0.7)
# Annotate
plt.annotate('Peak
1975', xy=(94.0, 21.0), xytext=(88.0, 28),
bbox=dict(boxstyle='square', fc='firebrick'),
arrowprops=dict(facecolor='steelblue', shrink=0.05), fontsize=15, color='white')
# Decorations
xtickvals = [str(m)[:3].upper()+"-"+str(y) for y,m in zip(df.date.dt.year, df.date.dt.month_name())]
plt.gca().set_xticks(x[::6])
plt.gca().set_xticklabels(xtickvals[::6], rotation=90, fontdict={'horizontalalignment': 'center', 'verticalalignment': 'center_baseline'})
plt.ylim(-35,35)
plt.xlim(1,100)
plt.title("Month Economics Return %", fontsize=22)
plt.ylabel('Monthly returns %')
plt.grid(alpha=0.5)
plt.show()
sort
15. Ordered bar chart
The ordered bar chart effectively conveys the ranking order of the project. However, by adding the values of the metrics above the chart, users can get accurate information from the chart itself.
# Prepare Data
df_raw = pd.read_csv("https://github.com/selva86/datasets/raw/master/mpg_ggplot2.csv")
df = df_raw[['cty', 'manufacturer']].groupby('manufacturer').apply(lambda x: x.mean())
df.sort_values('cty', inplace=True)
df.reset_index(inplace=True)
# Draw plot
import matplotlib.patches as patches
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(16,10), facecolor='white', dpi= 80)
ax.vlines(x=df.index, ymin=0, ymax=df.cty, color='firebrick', alpha=0.7, linewidth=20)
# Annotate Text
for i, cty in enumerate(df.cty):
ax.text(i, cty+0.5, round(cty, 1), horizontalalignment='center')
# Title, Label, Ticks and Ylim
ax.set_title('Bar Chart for Highway Mileage', fontdict={'size':22})
ax.set(ylabel='Miles Per Gallon', ylim=(0, 30))
plt.xticks(df.index, df.manufacturer.str.upper(), rotation=60, horizontalalignment='right', fontsize=12)
# Add patches to color the X axis labels
p1 = patches.Rectangle((.57, -0.005), width=.33, height=.13, alpha=.1, facecolor='green', transform=fig.transFigure)
p2 = patches.Rectangle((.124, -0.005), width=.446, height=.13, alpha=.1, facecolor='red', transform=fig.transFigure)
fig.add_artist(p1)
fig.add_artist(p2)
plt.show()
16. Lollipop chart
Lollipop charts provide similar purposes to ordered bar charts in a visually pleasing way.
# Prepare Data
df_raw = pd.read_csv("https://github.com/selva86/datasets/raw/master/mpg_ggplot2.csv")
df = df_raw[['cty', 'manufacturer']].groupby('manufacturer').apply(lambda x: x.mean())
df.sort_values('cty', inplace=True)
df.reset_index(inplace=True)
# Draw plot
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(16,10), dpi= 80)
ax.vlines(x=df.index, ymin=0, ymax=df.cty, color='firebrick', alpha=0.7, linewidth=2)
ax.scatter(x=df.index, y=df.cty, s=75, color='firebrick', alpha=0.7)
# Title, Label, Ticks and Ylim
ax.set_title('Lollipop Chart for Highway Mileage', fontdict={'size':22})
ax.set_ylabel('Miles Per Gallon')
ax.set_xticks(df.index)
ax.set_xticklabels(df.manufacturer.str.upper(), rotation=60, fontdict={'horizontalalignment': 'right', 'size':12})
ax.set_ylim(0, 30)
# Annotate
for row in df.itertuples():
ax.text(row.Index, row.cty+.5, s=round(row.cty, 2), horizontalalignment= 'center', verticalalignment='bottom', fontsize=14)
plt.show()
17. Package point diagram
The point chart conveys the ranking order of the items. Because it is aligned along the horizontal axis, you can more easily see the distance between the points.
# Prepare Data
df_raw = pd.read_csv("https://github.com/selva86/datasets/raw/master/mpg_ggplot2.csv")
df = df_raw[['cty', 'manufacturer']].groupby('manufacturer').apply(lambda x: x.mean())
df.sort_values('cty', inplace=True)
df.reset_index(inplace=True)
# Draw plot
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(16,10), dpi= 80)
ax.hlines(y=df.index, xmin=11, xmax=26, color='gray', alpha=0.7, linewidth=1, linestyles='dashdot')
ax.scatter(y=df.index, x=df.cty, s=75, color='firebrick', alpha=0.7)
# Title, Label, Ticks and Ylim
ax.set_title('Dot Plot for Highway Mileage', fontdict={'size':22})
ax.set_xlabel('Miles Per Gallon')
ax.set_yticks(df.index)
ax.set_yticklabels(df.manufacturer.str.title(), fontdict={'horizontalalignment': 'right'})
ax.set_xlim(10, 27)
plt.show()
18. Slope diagram
Slope plots are best suited for comparing "before" and "after" positions for a given person / project.
import matplotlib.lines as mlines
# Import Data
df = pd.read_csv("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selva86/datasets/master/gdppercap.csv")
left_label = [str(c) + ', '+ str(round(y)) for c, y in zip(df.continent, df['1952'])]
right_label = [str(c) + ', '+ str(round(y)) for c, y in zip(df.continent, df['1957'])]
klass = ['red' if (y1-y2) < 0 else 'green' for y1, y2 in zip(df['1952'], df['1957'])]
# draw line
# https://stackoverflow.com/questions/36470343/how-to-draw-a-line-with-matplotlib/36479941
def newline(p1, p2, color='black'):
ax = plt.gca()
l = mlines.Line2D([p1[0],p2[0]], [p1[1],p2[1]], color='red' if p1[1]-p2[1] > 0 else 'green', marker='o', markersize=6)
ax.add_line(l)
return l
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1,1,figsize=(14,14), dpi= 80)
# Vertical Lines
ax.vlines(x=1, ymin=500, ymax=13000, color='black', alpha=0.7, linewidth=1, linestyles='dotted')
ax.vlines(x=3, ymin=500, ymax=13000, color='black', alpha=0.7, linewidth=1, linestyles='dotted')
# Points
ax.scatter(y=df['1952'], x=np.repeat(1, df.shape[0]), s=10, color='black', alpha=0.7)
ax.scatter(y=df['1957'], x=np.repeat(3, df.shape[0]), s=10, color='black', alpha=0.7)
# Line Segmentsand Annotation
for p1, p2, c in zip(df['1952'], df['1957'], df['continent']):
newline([1,p1], [3,p2])
ax.text(1-0.05, p1, c + ', ' + str(round(p1)), horizontalalignment='right', verticalalignment='center', fontdict={'size':14})
ax.text(3+0.05, p2, c + ', ' + str(round(p2)), horizontalalignment='left', verticalalignment='center', fontdict={'size':14})
# 'Before' and 'After' Annotations
ax.text(1-0.05, 13000, 'BEFORE', horizontalalignment='right', verticalalignment='center', fontdict={'size':18, 'weight':700})
ax.text(3+0.05, 13000, 'AFTER', horizontalalignment='left', verticalalignment='center', fontdict={'size':18, 'weight':700})
# Decoration
ax.set_title("Slopechart: Comparing GDP Per Capita between 1952 vs 1957", fontdict={'size':22})
ax.set(xlim=(0,4), ylim=(0,14000), ylabel='Mean GDP Per Capita')
ax.set_xticks([1,3])
ax.set_xticklabels(["1952", "1957"])
plt.yticks(np.arange(500, 13000, 2000), fontsize=12)
# Lighten borders
plt.gca().spines["top"].set_alpha(.0)
plt.gca().spines["bottom"].set_alpha(.0)
plt.gca().spines["right"].set_alpha(.0)
plt.gca().spines["left"].set_alpha(.0)
plt.show()
19. Dumbbell diagram
Dumbbell charts convey the "front" and "back" positions of various items and the order of items. It is useful if you want to visualize the impact of a particular project / plan on different objects.
import matplotlib.lines as mlines
# Import Data
df = pd.read_csv("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selva86/datasets/master/health.csv")
df.sort_values('pct_2014', inplace=True)
df.reset_index(inplace=True)
# Func to draw line segment
def newline(p1, p2, color='black'):
ax = plt.gca()
l = mlines.Line2D([p1[0],p2[0]], [p1[1],p2[1]], color='skyblue')
ax.add_line(l)
return l
# Figure and Axes
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1,1,figsize=(14,14), facecolor='#f7f7f7', dpi= 80)
# Vertical Lines
ax.vlines(x=.05, ymin=0, ymax=26, color='black', alpha=1, linewidth=1, linestyles='dotted')
ax.vlines(x=.10, ymin=0, ymax=26, color='black', alpha=1, linewidth=1, linestyles='dotted')
ax.vlines(x=.15, ymin=0, ymax=26, color='black', alpha=1, linewidth=1, linestyles='dotted')
ax.vlines(x=.20, ymin=0, ymax=26, color='black', alpha=1, linewidth=1, linestyles='dotted')
# Points
ax.scatter(y=df['index'], x=df['pct_2013'], s=50, color='#0e668b', alpha=0.7)
ax.scatter(y=df['index'], x=df['pct_2014'], s=50, color='#a3c4dc', alpha=0.7)
# Line Segments
for i, p1, p2 in zip(df['index'], df['pct_2013'], df['pct_2014']):
newline([p1, i], [p2, i])
# Decoration
ax.set_facecolor('#f7f7f7')
ax.set_title("Dumbell Chart: Pct Change - 2013 vs 2014", fontdict={'size':22})
ax.set(xlim=(0,.25), ylim=(-1, 27), ylabel='Mean GDP Per Capita')
ax.set_xticks([.05, .1, .15, .20])
ax.set_xticklabels(['5%', '15%', '20%', '25%'])
ax.set_xticklabels(['5%', '15%', '20%', '25%'])
plt.show()
distribution
20. Histogram of continuous variables
The histogram shows the frequency distribution of a given variable. The following representation groups frequency bars based on classification variables to better understand continuous and series variables.
# Import Data
df = pd.read_csv("https://github.com/selva86/datasets/raw/master/mpg_ggplot2.csv")
# Prepare data
x_var = 'displ'
groupby_var = 'class'
df_agg = df.loc[:, [x_var, groupby_var]].groupby(groupby_var)
vals = [df[x_var].values.tolist() for i, df in df_agg]
# Draw
plt.figure(figsize=(16,9), dpi= 80)
colors = [plt.cm.Spectral(i/float(len(vals)-1)) for i in range(len(vals))]
n, bins, patches = plt.hist(vals, 30, stacked=True, density=False, color=colors[:len(vals)])
# Decoration
plt.legend({group:col for group, col in zip(np.unique(df[groupby_var]).tolist(), colors[:len(vals)])})
plt.title(f"Stacked Histogram of ${x_var}$ colored by ${groupby_var}$", fontsize=22)
plt.xlabel(x_var)
plt.ylabel("Frequency")
plt.ylim(0, 25)
plt.xticks(ticks=bins[::3], labels=[round(b,1) for b in bins[::3]])
plt.show()
21. Histogram of type variables
The histogram of a classified variable shows the frequency distribution of the variable. By coloring the bar graph, you can associate the distribution with another classification variable that represents color.
# Import Data
df = pd.read_csv("https://github.com/selva86/datasets/raw/master/mpg_ggplot2.csv")
# Prepare data
x_var = 'manufacturer'
groupby_var = 'class'
df_agg = df.loc[:, [x_var, groupby_var]].groupby(groupby_var)
vals = [df[x_var].values.tolist() for i, df in df_agg]
# Draw
plt.figure(figsize=(16,9), dpi= 80)
colors = [plt.cm.Spectral(i/float(len(vals)-1)) for i in range(len(vals))]
n, bins, patches = plt.hist(vals, df[x_var].unique().__len__(), stacked=True, density=False, color=colors[:len(vals)])
# Decoration
plt.legend({group:col for group, col in zip(np.unique(df[groupby_var]).tolist(), colors[:len(vals)])})
plt.title(f"Stacked Histogram of ${x_var}$ colored by ${groupby_var}$", fontsize=22)
plt.xlabel(x_var)
plt.ylabel("Frequency")
plt.ylim(0, 40)
plt.xticks(ticks=bins, labels=np.unique(df[x_var]).tolist(), rotation=90, horizontalalignment='left')
plt.show()
22. Density map
Density map is a common tool to visualize the distribution of continuous variables. By grouping them with the response variable, you can examine the relationship between X and Y. In the following case, how the distribution of urban mileage changes with the number of cylinders is described for representative purposes.
# Import Data
df = pd.read_csv("https://github.com/selva86/datasets/raw/master/mpg_ggplot2.csv")
# Draw Plot
plt.figure(figsize=(16,10), dpi= 80)
sns.kdeplot(df.loc[df['cyl'] == 4, "cty"], shade=True, color="g", label="Cyl=4", alpha=.7)
sns.kdeplot(df.loc[df['cyl'] == 5, "cty"], shade=True, color="deeppink", label="Cyl=5", alpha=.7)
sns.kdeplot(df.loc[df['cyl'] == 6, "cty"], shade=True, color="dodgerblue", label="Cyl=6", alpha=.7)
sns.kdeplot(df.loc[df['cyl'] == 8, "cty"], shade=True, color="orange", label="Cyl=8", alpha=.7)
# Decoration
plt.title('Density Plot of City Mileage by n_Cylinders', fontsize=22)
plt.legend()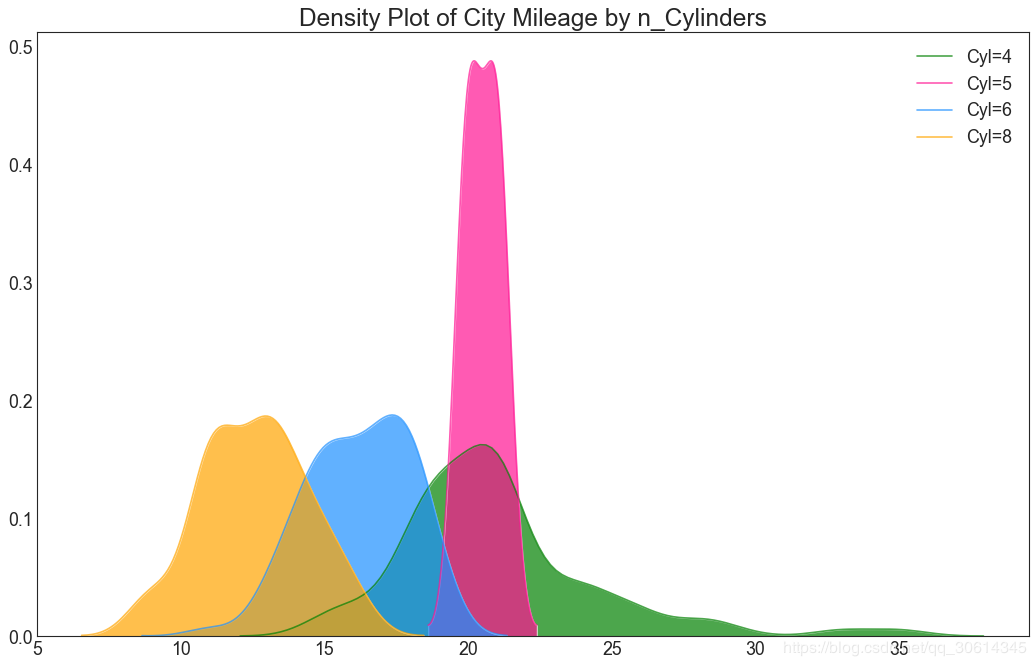
23. Straight density line diagram
The density curve with histogram brings together the collective information conveyed by the two charts so that you can put them in one graph instead of two graphs.
# Import Data
df = pd.read_csv("https://github.com/selva86/datasets/raw/master/mpg_ggplot2.csv")
# Draw Plot
plt.figure(figsize=(13,10), dpi= 80)
sns.distplot(df.loc[df['class'] == 'compact', "cty"], color="dodgerblue", label="Compact", hist_kws={'alpha':.7}, kde_kws={'linewidth':3})
sns.distplot(df.loc[df['class'] == 'suv', "cty"], color="orange", label="SUV", hist_kws={'alpha':.7}, kde_kws={'linewidth':3})
sns.distplot(df.loc[df['class'] == 'minivan', "cty"], color="g", label="minivan", hist_kws={'alpha':.7}, kde_kws={'linewidth':3})
plt.ylim(0, 0.35)
# Decoration
plt.title('Density Plot of City Mileage by Vehicle Type', fontsize=22)
plt.legend()
plt.show()
24. Joy Plot
Joy Plot allows the density curves of different groups to overlap, which is a good way to visualize the distribution of a large number of groups relative to each other. It looks pleasing to the eye and clearly conveys the right message. It can easily build matplotlib using joypy based packages.
# !pip install joypy
# Import Data
mpg = pd.read_csv("https://github.com/selva86/datasets/raw/master/mpg_ggplot2.csv")
# Draw Plot
plt.figure(figsize=(16,10), dpi= 80)
fig, axes = joypy.joyplot(mpg, column=['hwy', 'cty'], by="class", ylim='own', figsize=(14,10))
# Decoration
plt.title('Joy Plot of City and Highway Mileage by Class', fontsize=22)
plt.show()
25. Distributed point diagram
The distribution point map shows the univariate distribution of points divided by groups. The darker the number of points, the higher the concentration of data points in this area. By coloring the median differently, the true positioning of the group becomes obvious immediately.
import matplotlib.patches as mpatches
# Prepare Data
df_raw = pd.read_csv("https://github.com/selva86/datasets/raw/master/mpg_ggplot2.csv")
cyl_colors = {4:'tab:red', 5:'tab:green', 6:'tab:blue', 8:'tab:orange'}
df_raw['cyl_color'] = df_raw.cyl.map(cyl_colors)
# Mean and Median city mileage by make
df = df_raw[['cty', 'manufacturer']].groupby('manufacturer').apply(lambda x: x.mean())
df.sort_values('cty', ascending=False, inplace=True)
df.reset_index(inplace=True)
df_median = df_raw[['cty', 'manufacturer']].groupby('manufacturer').apply(lambda x: x.median())
# Draw horizontal lines
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(16,10), dpi= 80)
ax.hlines(y=df.index, xmin=0, xmax=40, color='gray', alpha=0.5, linewidth=.5, linestyles='dashdot')
# Draw the Dots
for i, make in enumerate(df.manufacturer):
df_make = df_raw.loc[df_raw.manufacturer==make, :]
ax.scatter(y=np.repeat(i, df_make.shape[0]), x='cty', data=df_make, s=75, edgecolors='gray', c='w', alpha=0.5)
ax.scatter(y=i, x='cty', data=df_median.loc[df_median.index==make, :], s=75, c='firebrick')
# Annotate
ax.text(33, 13, "$red ; dots ; are ; the : median$", fontdict={'size':12}, color='firebrick')
# Decorations
red_patch = plt.plot([],[], marker="o", ms=10, ls="", mec=None, color='firebrick', label="Median")
plt.legend(handles=red_patch)
ax.set_title('Distribution of City Mileage by Make', fontdict={'size':22})
ax.set_xlabel('Miles Per Gallon (City)', alpha=0.7)
ax.set_yticks(df.index)
ax.set_yticklabels(df.manufacturer.str.title(), fontdict={'horizontalalignment': 'right'}, alpha=0.7)
ax.set_xlim(1, 40)
plt.xticks(alpha=0.7)
plt.gca().spines["top"].set_visible(False)
plt.gca().spines["bottom"].set_visible(False)
plt.gca().spines["right"].set_visible(False)
plt.gca().spines["left"].set_visible(False)
plt.grid(axis='both', alpha=.4, linewidth=.1)
plt.show()
This article is referenced from:
https://www.machinelearningplus.com/plots/top-50-matplotlib-visualizations-the-master-plots-python/