MyBatis
Advanced mapping/association queries:
- One-to-one/many-to-one
- One to many
- Many to many
The main usage is the collection attribute and association attribute of resultMap.
association
Association: Used for mapping the information of association query to a single object, mapping the information of association query to a pojo object, mostly for one-to-one/many-to-one scenarios.
collection
collection: Mapping multiple records of an associated query to a set, usually mapping the associated query information to a list set for one-to-many/many-to-many scenarios.
Relational query
A simple example, the mapping of departments and employees
Dept.java
public class Dept {
private Integer id ; // Department number
private String name ; // Department name
private String address ; // Department address
// Employees in Departments
private List<Employee> employees ;Database:
create table DEMO_MAWEI_DEPT
(
D_ID NUMBER not null,
D_NAME VARCHAR2(50) not null,
D_ADDRESS VARCHAR2(100)
)Data: 
Employee: Employee.java
public class Employee {
private int id ; // Employee number
private String name; // Employee name
private Dept dept ; // Department in charge
private String address ; // Home address
// Owned Computer
private List<Computer> computers ;Database:
create table DEMO_MAWEI_EMPLOYEE
(
E_ID NUMBER not null,
E_NAME VARCHAR2(50) not null,
D_ID NUMBER not null,
E_ADDRESS VARCHAR2(100)
)Data: 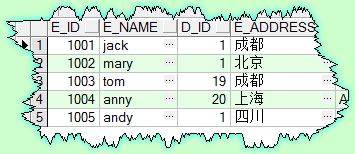
Computer: Computer.java
public class Computer {
private Integer id ; // Computer number
private String name ; // Computer name
private Double money ; // Computer value
// User
private Employee employee;
Database:
create table DEMO_MAWEI_COMPUTER
(
C_ID NUMBER not null,
C_NAME VARCHAR2(50),
C_MONEY NUMBER(10,2),
E_ID NUMBER
)Data: 
Some of these setting s and getting are not written and can be self-filled, as well as the MAVEN configuration and mybatis configuration can be seen in the previous article.
Introduction to MyBatis (I)
One-to-one/many-to-one
In terms of: mapping between employees and departments, one employee corresponds to one department (multiple employees correspond to one department)
Employee.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.wm.mybatis.dao.IEmployeeMapperDao">
<resultMap type="Employee" id="employeeMap">
<id property="id" column="e_id"/>
<result property="name" column="e_name"/>
<result property="address" column="e_address"/>
<! - One-to-one/many-to-one:
association: Information used to map association queries to individual objects
property attributes: Attribute correspondences in the Employee class
resultMap attribute: A result set mapping that corresponds to the attribute Dept class mapping file in the Employee class
Namespace + resultMap id
-->
<association property="dept" resultMap="com.wm.mybatis.dao.IDeptMapperDao.resultDept" />
</resultMap>
<! - Obtain employee information through id - >
<select id="getEmployeeById" parameterType="int" resultMap="employeeMap">
<![CDATA[
select *
from base_55demo.demo_mawei_employee t inner join
base_55demo.demo_mawei_dept d
on d.d_id = t.d_id
and t.e_id = #{id}
]]>
</select>
</mapper>Where resultMap: association: is used to map the information associated with querying a single object
<association property="dept" resultMap="com.wm.mybatis.dao.IDeptMapperDao.resultDept" />It is associated with an existing resultMap. = Namespace + resultMap ID.
There can also be another way of writing:
<!-- Another way of writing -->
<resultMap type="Employee" id="employeeMap2">
<id property="id" column="e_id"/>
<result property="name" column="e_name"/>
<result property="address" column="e_address"/>
<association property="dept" javaType="Dept" >
<id property="id" column="d_id" />
<result property="name" column="d_name" />
<result property="address" column="d_address" />
</association>
</resultMap>Test:
public class EmployeeMapperDaoImpl implements IEmployeeMapperDao{
@Override
public Employee getEmployeeById(int id) {
Employee employee = null ;
try {
SqlSession session = SessionManagerUtil.getSession();
employee = (Employee)session.selectOne(IEmployeeMapperDao.class.getName()+".getEmployeeById", id);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
SessionManagerUtil.closeSession();
}
return employee;
}
}Result:
public class TestEmployeeMapper {
@Test
public void getEmployeeById(){
EmployeeMapperDaoImpl dao = new EmployeeMapperDaoImpl();
Employee employee = dao.getEmployeeById(1001);
System.out.println(employee);
}
}
One to many
Departmental and employee mapping: There are multiple employees in a department.
Dept.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.wm.mybatis.dao.IDeptMapperDao">
<resultMap type="Dept" id="resultDeptMap">
<result property="id" column="d_id" />
<result property="name" column="d_name" />
<result property="address" column="d_address" />
<!-- One to many List list
collection:Mapping multiple records from associated queries to collections
property: employees by Dept Corresponding attributes in classes
-->
<collection property="employees" ofType="com.wm.mybatis.POJO.Employee" column="d_id" >
<id property="id" column="e_id" javaType="int" jdbcType="INTEGER"/>
<result property="name" column="e_name" javaType="string" jdbcType="VARCHAR"/>
<result property="address" column="e_address" javaType="string" jdbcType="VARCHAR"/>
<result property="d_id" column="d_id" javaType="int" jdbcType="INTEGER"/>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<!-- The most basic Dept Result Set Mapping -->
<resultMap type="Dept" id="resultDept">
<id property="id" column="d_id" />
<result property="name" column="d_name" />
<result property="address" column="d_address" />
</resultMap>
<select id="findDeptById" parameterType="int" resultMap="resultDeptMap">
<![CDATA[
select d.*,e.*
from demo_mawei_dept d,
demo_mawei_employee e
where d.d_id = e.d_id
and d.d_id = #{id}
]]>
</select>
</mapper>resultMap: collection: Maps multiple records of the associated query to the list collection.
In fact, collection can be abbreviated as an existing mapping result set.
<! - Another way of writing - >.
<resultMap type="Dept" id="resultDeptMap2">
<id property="id" column="d_id"/>
<result property="name" column="d_name"/>
<result property="address" column="d_address"/>
<!--
property: Attributes in the corresponding Dept class
ResultMap: A simplest result set mapping for Employee = namespace + ID of resultMap
-->
<collection property="employees" resultMap="com.wm.mybatis.dao.IEmployeeMapperDao.basicEmployee" />
</resultMap>In Employee.xml: the corresponding basic result set mapping:
(com.wm.mybatis.dao.IEmployeeMapperDao.basicEmployee)
<!-- The most basic Employee Result set -->
<resultMap type="Employee" id="basicEmployee">
<id property="id" column="e_id"/>
<result property="name" column="e_name"/>
<result property="address" column="e_address"/>
</resultMap>Test:
public class DeptMapperDaoImpl implements IDeptMapperDao{
@Override
public Dept findDeptById(int id) {
Dept dept = null ;
try {
SqlSession session = SessionManagerUtil.getSession();
dept = session.selectOne(IDeptMapperDao.class.getName()+".findDeptById", id) ;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally{
SessionManagerUtil.closeSession();
}
return dept;
}
}Result:
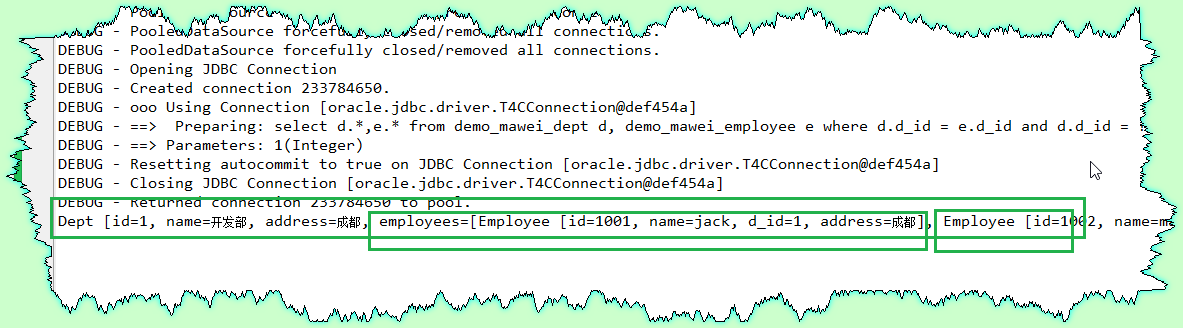
public class TestDeptMapper {
@Test
public void findDeptById(){
IDeptMapperDao dao = new DeptMapperDaoImpl();
Dept dept = dao.findDeptById(1);
System.out.println(dept);
}
}
Many to many
Just as: there are many employees in the department, and each employee has more than one computer.
Dept.xml
<select id="getDeptByIdWithComputer" parameterType="int" resultMap="deptMore2More2">
<![CDATA[
select *
from base_55demo.demo_mawei_dept d,
base_55demo.demo_mawei_employee e,
base_55demo.demo_mawei_computer c
where d.d_id = e.d_id
and e.e_id = c.e_id
and d.d_id = #{id}
]]>
</select>
<!-- Many to many -->
<resultMap type="Dept" id="deptMore2More2">
<id property="id" column="d_id"/>
<result property="name" column="d_name"/>
<result property="address" column="d_address"/>
<!-- Departments and Employees property: Dept Class properties ofType: Corresponding types (with aliases configured) -->
<collection property="employees" ofType="Employee">
<id property="id" column="e_id"/>
<result property="name" column="e_name"/>
<result property="address" column="e_address"/>
<!-- Employees and computers property: Computer Class properties ofType: Corresponding types (with aliases configured)-->
<collection property="computers" ofType="Computer">
<id property="id" column="c_id"/>
<result property="name" column="c_name"/>
<result property="money" column="c_money"/>
</collection>
</collection>
</resultMap>Among them: resultMap is implemented by nested collection.
But you can also refer to existing result sets:
resultMap simplification:
<! - Another way of writing - >.
<resultMap type="Dept" id="deptMore2More">
<id property="id" column="d_id"/>
<result property="name" column="d_name"/>
<result property="address" column="d_address"/>
<! - Existing resu lt set mapping department and employee mapping - >
<collection property="employees" resultMap="com.wm.mybatis.dao.IEmployeeMapperDao.employeeWithComputer" />
</resultMap>Departmental and employee mapping:
(com.wm.mybatis.dao.IEmployeeMapperDao.employeeWithComputer)
<! - Joint Computer Owner - > Joint Computer Owner, Joint Computer Owner, Joint Computer Owner, Joint Computer Owner, Joint Computer Owner, Joint Computer Owner, Joint Computer Owner,
<resultMap type="Employee" id="employeeWithComputer">
<id property="id" column="e_id"/>
<result property="name" column="e_name"/>
<result property="address" column="e_address"/>
<! - The existing resu lt set maps the mapping of employees and computers - >
<collection property="computers" resultMap="com.wm.mybatis.dao.IComputerMapperDao.basicComputer" />
</resultMap>Employee and computer mapping:
(com.wm.mybatis.dao.IComputerMapperDao.basicComputer)
Computer.xml:
<mapper namespace="com.wm.mybatis.dao.IComputerMapperDao">
<resultMap type="Computer" id="basicComputer">
<id property="id" column="c_id"/>
<result property="name" column="c_name"/>
<result property="money" column="c_money"/>
</resultMap>
</mapper>Test:
DeptMapperDaoImpl.java
@Override
public Dept getDeptByIdWithComputer(int id) {
Dept dept = null ;
try {
SqlSession session = SessionManagerUtil.getSession();
dept = session.selectOne(IDeptMapperDao.class.getName()+".getDeptByIdWithComputer", id) ;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally{
SessionManagerUtil.closeSession();
}
return dept;
}Result:
@Test
public void getDeptByIdWithComputer(){
IDeptMapperDao dao = new DeptMapperDaoImpl();
Dept dept = dao.getDeptByIdWithComputer(19);
System.out.println(dept);
}
Advanced mapping: Association queries are basically nested with the label of resultMap: collection and association.