After class questions 1-5
1. How many layers are the network communication protocols divided into? What are the problems solved by each layer?
>>OSI layer 7 protocol
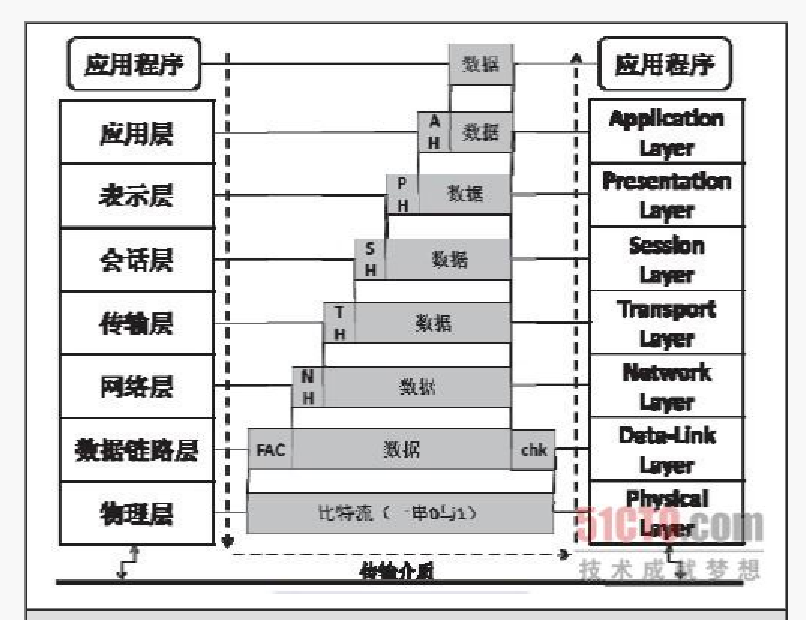
| OSI seven layer network model | function |
| application layer | Directly provide services for the user's application process |
| Presentation layer | Provides a standard format for network transmission |
| Session layer | It provides the establishment, maintenance and termination of sessions between two hosts in the network |
| Transport layer | Provide reliable service for process communication between two hosts |
| network layer | It provides communication services for different hosts in packet switching network, including routing, address resolution, etc |
| data link layer | Point to point frame transmission between two adjacent nodes |
| physical layer | Bitstream transmission |
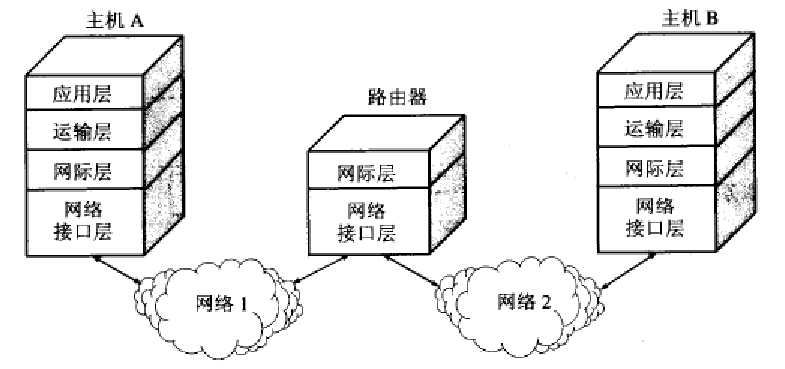
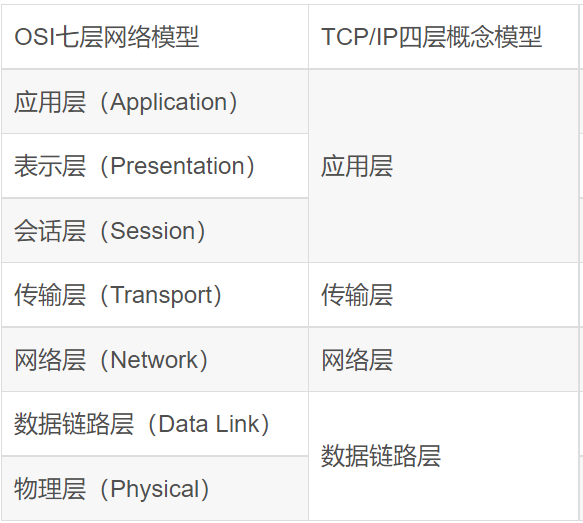
>> TCP / IP four layer protocol
2. What are the differences between TCP and UPD protocols? Why is TCP a reliable connection oriented protocol?
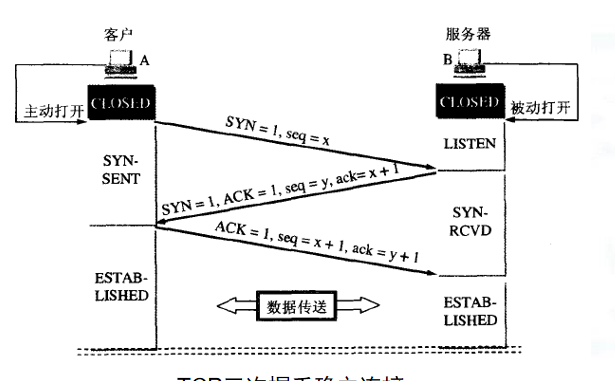
TCP is a connection oriented, reliable and byte stream based transport layer communication protocol. Features: three handshakes
UDP (User Datagram Protocol) is a transaction oriented, stream based, simple and unreliable information transmission protocol.
| TCP | UDP | |
| communication mode | A connection must be established before data transmission, so there is an additional time for connection establishment in TCP | The complete address information is given in each datagram, so there is no need to establish a connection between the sender and the receiver |
| Amount of data transmitted | Once the connection is established, the socket s of both sides can transmit a large amount of data in a unified format | There is a size limit when transmitting data. Each transmitted datagram must be within 64KB |
| Transmission data reliability | It is reliable and can ensure that the receiver can completely and correctly obtain all data sent by the sender | Unreliable. The datagrams sent do not necessarily arrive at the receiver in the same order, and there is no guarantee that the receiver will receive them |
| Respective characteristics | Large transmission capacity and strong reliability | Simple operation and high transmission efficiency |
TCP connection oriented: connection oriented. Three handshakes are required to establish a connection before the server communicates with the client, and four waves are required to disconnect after the communication. Establish a connection before transmitting data
3. In JAVA language, what level of protocol does network programming start from? When programming, under what circumstances do you choose JAVA high-level network programming and under what circumstances do you choose low-level network programming?
Transport layer.
Low level network programming is TCP and UDP, while high-level network programming is URL based
4. Where should the destination address and port number be indicated during socket programming? Where do you point out when using datagrams?
During the binding operation in the second step, the destination address and destination port number need to be specified.
(Note: the port in Socket communication needs to be customized.)
For example:
Socket socket=new Socket("127.0.0.1",4700)
When using datagrams, you should create a new datagram packet object before sending data. You should also give the complete destination address while giving the buffer for storing the sent data
5. Use URLConnection object to write a program to return to the home page of a website and store the content of the home page in the file.
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
public class html {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
URL url= new URL("https://www.qq.com/");
URLConnection con = url.openConnection();
BufferedReader in= new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(con.getInputStream(), "UTF-8"));
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:\\test.txt");
String line;
while((line = in.readLine()) != null ) {
line = line + "\n";
fos.write(line.getBytes("UTF-8"));
fos.flush();
}
is.close();
fos.close();
}
}
6. Follow example 15.4 to write a multi client / server communication program based on TCP Socket.
//client
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
public class client3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try{
Socket socket=new Socket("127.0.0.1",4700);
BufferedReader sin=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
PrintWriter os= new PrintWriter(socket.getOutputStream());
BufferedReader is=new BufferedReader((new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream())));
String readline;
readline=sin.readLine();
while(!readline.equals("bye")){
os.println(readline);
os.flush();
System.out.println("Client:"+readline);
System.out.println("server:"+is.readLine());
readline=sin.readLine();
}
os.close();
is.close();
socket.close();
}catch(Exception e){
System.out.println("Error:"+e);
}
}
}
//Server
package socket;
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
class ServerThread extends Thread {
Socket socket=null; //Save the Socket object related to this thread
int clientnum; //Save the customer count of this thread
public ServerThread(Socket socket,int num) { //Constructor
this.socket=socket; //Initialize socket variable
clientnum=num+1; //Initializing the clientnum variable
}
public void run() { //Thread body
try{
String line;
BufferedReader is=new BufferedReader(new
InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream()));
PrintWriter os=new PrintWriter(socket.getOutputStream());
BufferedReader sin=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
System.out.println("Client:"+ clientnum +is.readLine());
line=sin.readLine();
while(!line.equals("bye")){//If the string is "bye", stop the loop
os.println(line);//Output the string to the client
os.flush();//Refresh the output stream so that the Client receives the string immediately
System.out.println("Server:"+line);
System.out.println("Client:"+ clientnum +is.readLine());
line=sin.readLine();//Reads a string from the system standard input
}//Continue the cycle
os.close(); //Close Socket output stream
is.close(); //Close Socket input stream
socket.close(); //Close Socket
}catch(Exception e){
System.out.println("Error:"+e);//Error, print error message
}
}
}
public class Multitalkserver {
static int clientnum=0; //Static member variable, which records the number of current customers
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException {
ServerSocket serverSocket=null;
boolean listening=true;
try{
//Create a ServerSocket to listen to customer requests on port 4700
serverSocket=new ServerSocket(4700);
}catch(IOException e) {
System.out.println("Could not listen on port:4700.");
System.exit(-1); //sign out
}
while(listening){ //Loop listening
//Listen to the customer request, create a service thread according to the obtained Socket object and customer count, and start it
new socket.ServerThread(serverSocket.accept(),clientnum).start();
clientnum++; //Increase customer count
}
serverSocket.close(); //Close ServerSocket
}
}
7. Follow example 15.5 to write a multi client / server communication program based on UDP datagram.
//client
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
public class QuoteClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
if(args.length!=1){
//If the Server name is not given when starting, print an error message and exit
System.out.println("Usage:java QuoteClient <hostname>");
return;
}
DatagramSocket socket=new DatagramSocket();//Create datagram socket
byte[] buf=new byte[256]; //Create buffer
buf = "hello".getBytes();
InetAddress address=InetAddress.getByName(args[0]);
//Create DatagramPacket object
DatagramPacket packet=new DatagramPacket(buf, buf.length, address, 4445);
socket.send(packet); //send out
//Create a new datagram packet object to receive datagrams
packet=new DatagramPacket(buf,buf.length);
socket.receive(packet); //receive
//Generate the corresponding string according to the received byte array
String received=new String(packet.getData());
//Print the generated string
System.out.println("Quote of the Moment:"+received );
//Close socket
socket.close();
}
}
//Server
public class QuoteServer{
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException {
new QuoteServerThread().start();//Start a QuoteServerThread thread
}
}
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
public class QuoteServerThread extends Thread {
protected DatagramSocket socket=null;//DatagramSocket object associated with this thread
protected BufferedReader in=null; //A Reader used to read files
protected boolean moreQuotes=true; //Flag variable, continue
public QuoteServerThread() throws IOException { //Parameterless construction method
this("QuoteServerThread");
}
public QuoteServerThread(String name) throws IOException {
super(name); //Call the constructor of the parent class
socket=new DatagramSocket(4445);//Create a datagram socket on port 4445
in= new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));}
public void run() {//Thread body
while(moreQuotes) {
try{
byte[] buf=new byte[256]; //Create buffer
DatagramPacket packet=new DatagramPacket(buf,buf.length);
socket.receive(packet); //Receive datagram
System.out.println(new String(packet.getData()));
String dString= in.readLine(); //Terminal input string
//If it is bye, exit after sending a message to the client
if(dString.equals("bye")){ moreQuotes=false;}
buf=dString.getBytes();//Convert a String into a byte array for transfer
InetAddress address = packet.getAddress(); //Client address
int port=packet.getPort(); // Client port number
//Building and sending DatagramPacket objects
packet=new DatagramPacket(buf,buf.length,address,port);
socket.send(packet); //Send datagram
}catch(IOException e) { //exception handling
e.printStackTrace(); //Print error stack
moreQuotes=false; //Flag variable is set to false to end the loop
}
}
socket.close(); //Close datagram socket
}
}
8. What are the differences between C/S communication based on TCP Socket and C/S communication based on UDP datagram? What support does Java provide?
TCP protocol Socket
UDP protocol - datagram socket and datagram packet
Datagram socket: used to send or receive datagrams. It is a sending or receiving point of datagram delivery service.
Datagram packet: used to represent a datagram