Dom
One: Dom concept
Introduction to Dom: The Document Object model is a complete set of methods for manipulating documents - Document - html, an object in a document, a top-level object in the dom, an object in window s, and arguably the best.
Dom Node: All the steps that make up the entire html process are equivalent to all the labels, text, attributes, comments that make up the whole web page - each part of the content that makes up the web page is treated as a node, and the whole web page is made up of many nodes.Nodes are mainly: (labels, text, attributes, comments) / element nodes (labels), because in the actual operation, element nodes are more important, so when you get or create a node, you usually operate on element nodes, such as comment nodes, which are relatively less used by text nodes.
Dom tree: Simply speaking, a Dom tree is made up of many nodes. On the basis of root node HTML, the rest of the nodes are children. The data structure that makes up a tree is a Dom tree.
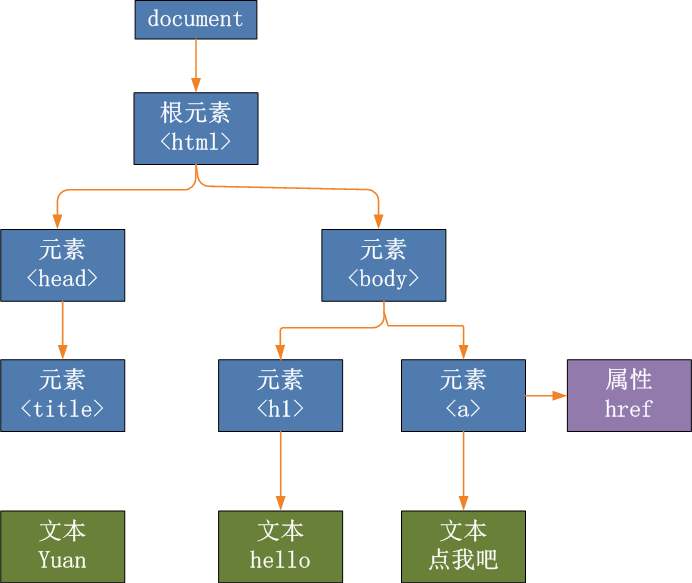
The representation of the dom tree.
1 console.log(document) // document 2 console.log(document.documentElement) // Obtain html Label 3 console.log(document.body) // Obtain body Label 4 console.log(document.head) // Obtain head Label 5 console.log(document.title) // Obtain title Label 6 7 // Obtained with id Labeled dom Method must be used document call getElementById 8 console.log(document.getElementById('id')) // adopt id 9 10 //getElementsByTagName This method can be used in addition to document In addition, element calls can be used 11 console.log(document.getElementsByTagName('div')) // By tag name 12 13 console.log(document.getElementsByClassName('.box')) // adopt class Name acquisition 14 console.log(document.getElementsByName('name')) // adopt name Name to get 15 console.log(document.querySelector('.box')) // adopt css Selector to get 16 console.log(document.querySelectorAll('div')) // adopt css Selector to get all the labels 17 18 // Summary: Passed id and name Get label can only be used document Called,By tag name,class Name, css Selectors can call methods from parent elements to get labels for child elements
1 <div id="ids"> 2 <!-- dom Is Document Object Model --> 3 <div class="box">text</div> 4 <p>text</p> 5 <div class="box" name="1"></div> 6 Text Properties 7 </div>
1 var ids = document.getElementById('ids') 2 var nodes = ids.childNodes // Obtain ids All child nodes under 3 console.log(nodes) // Nodes is a list of collections of all child nodes under ids 4 console.log(nodes[0].nodeType) // Text Node Type 3 5 console.log(nodes[0].nodeName) // Text Node Name #text 6 console.log(nodes[0].nodeValue) // Text node value is the text content and space is the text node 7 8 console.log(nodes[1].nodeType) // Comment Node Type 8 9 console.log(nodes[1].nodeName) // Comment Node Name #comment 10 console.log(nodes[1].nodeValue) // Annotation Node Value Is Annotation Content 11 12 console.log(nodes[3].nodeType) // Element Node Type 1 13 console.log(nodes[3].nodeName) // Element Node Name Uppercase Label Name 14 console.log(nodes[3].nodeValue) // Element Node Value null
3: Operation of the node
Again, the div tag I wrote with ID named ids demonstrates how a node works
1 var ids = document.querySelector('#ids') // Get parent element 2 3 console.log(ids.childNodes) // Obtain ids All child nodes under 4 console.log(ids.children) // Obtain ids All child element nodes under 5 6 console.log(ids.firstChild) // Obtain ids First child node under 7 console.log(ids.firstElementChild) // Obtain ids First child element node under 8 9 console.log(ids.lastChild) // Obtain ids Last child node under 10 console.log(ids.lastElementChild) // Obtain ids Last child element node under 11 12 console.log(ids.nextSibling) // Next sibling node 13 console.log(ids.nextElementSibling) // Next sibling element node 14 15 console.log(ids.previousSibling) // Get the last sibling node 16 console.log(ids.previousElementSibling) // Get the last sibling element node // Not only the same label, but also different labels 17 18 console.log(ids.parentNode) // Get Parent Node 19 console.log(ids.parentElement) // Get parent element node
1 var div = document.createElement('div') // Create labels 2 document.body.appendChild(div) // Place the div element at the end of the body tag 3 4 // Append: parent container.appendChild(Child Elements); Insert child elements at the end of parent container 5 var span = document.createElement('span') 6 div1.appendChild(span) // take span Labels on div In Label 7 span.textContent = 'Hello' 8 9 // Insert label in div Insert a b Label to span Before Note 10 var b = document.createElement('b') 11 // Insert Writing Form One: 12 div.insertBefore(b,span) 13 // Insert Writing Form Two: 14 div.insertBefore(b,div.lastElementChild) 15 16 // Create a text node: document.createTextNode("text") 17 // Place in div Of b In Label 18 var text = document.createTextNode('I am a created text node') 19 // Insert the created text node into the div Before the first element node in 20 div.insertBefore(text,div.firstElementChild) 21 console.log(div) 22 23 // Copy Element Elements.cloneNode(Depth Boolean) 24 var b1 = b.cloneNode(false) // Shallow copy 25 var b2 = b.cloneNode(true) // Deep copy 26 console.log(b1,b2)
Node operation-delete
var b = document.createElement('b') document.body.appendChild(b) // Copy Element var b1 = b.cloneNode(false) var b2 = b.cloneNode(false) b1.remove() // delete b1 element var dl = document.createElement('dl') document.body.appendChild(dl) dl.appendChild(b2) dl.removeChild(b2) // Delete and Repeat dl In b2 element // Note that this does not remove the clean need b2 = null document.body.appendChild(b2) // This line of code proves b2 Not deleted clean, cache is still in progress b2 = null // When b2 Assigned to null time b2 Is completely deleted clean, can no longer be called // document.body.appendChild(b2) // b2 cannot be called here and an error has occurred
1 var input = document.createElement('input') // Establish input Label 2 var div = document.createElement('div') // Establish div Label 3 document.body.appendChild(div) // take div Elements are inserted in body Tail of 4 document.body.replaceChild(input,div) // Replace Element
1 var div0 = document.createElement('div') 2 document.body.appendChild(div0) 3 div0.setAttribute('Slag glow','One Knife 999') // Add attributes to elements 4 div0.setAttribute('class','999') // Attribute 2 5 6 // 2: Attributes of the element - Delete - element.removeAttribute(Property Name) 7 div0.removeAttribute('Slag glow') // Remove Attribute Slag Glow 8 9 // 3: Attributes of the element - change - In fact, it is the operation of adding attributes. When attributes do not exist, they are added, when attributes exist, they are modified on the original basis. 10 div0.setAttribute('class','666666') 11 12 // 4:Attributes of the element - Get (view) property values - element.getAttribute(Property Name) 13 console.log(div0.getAttribute('class')) 14 15 // Expand Knowledge 1: DOM Elements are object models and object attributes are not displayed on labels(For example: a Labeled href Properties, img Of src attribute) 16 // Extend 1 case:1: img.src = 'The address of the picture you want to put in' 2: a.href = 'The address of the picture you want to put in' 3: div.a = 10 - to div Add a property named a Value is 10 17 // Extend 2: DOM All elements are object,So setting attributes is based on object attributes. When conflicting values of label attributes and object attributes are encountered, the value of object attributes is taken as the criterion. 18 // Extend 2 cases: 19 var ck=document.querySelector("input") 20 ck.setAttribute("checked","") // input Add Attributes checked ,input Set up checked When, is for true == Selected 21 ck.checked=false // When the label attribute value conflicts with the object attribute value, the object attribute value is taken as the criterion. checked Is for false == Trim White Space
1 // 1: Label Style - increase 2 // Method 1: Increase inline (note inline) style elements by adding attributes.setAttribute(Property Name,Attribute Value) 3 var div0 = document.createElement('div') 4 document.body.appendChild(div0) 5 div0.setAttribute("style","width:50px;height:50px;background-color:red") 6 // Method 2: - element.style.The style name you want to add = 'Style Value' 7 div0.style.margin = '5px' 8 9 // 2: Tag Style Acquisition 10 console.log(div0.style.width) // Only inline styles can be obtained, not internal and external styles 11 // Universal Access: getComputedStyle(element) Inside, outside and inside styles are available 12 console.log( getComputedStyle(div0).width) 13 14 // 3 :Gets the rectangular bounding range of the element ( IE8 Only later) 15 // Syntax: Element..getBoundingClientRect() 16 // IE Compatibility method: element.currentStyle.Style Properties 17 var res = div0.getBoundingClientRect() 18 console.log(res) 19 // This method is also an object model with eight attributes, one for each of the following 20 /*{ 21 width, // offsetWidth 22 height, // offsetHeight 23 left, // Distance from the leftmost window to the visible window 24 top, // Distance from the top to the visible window 25 right, // left+width Distance from the far right to the visible window 26 bottom, // top+height Distance from bottom to visible window 27 x, // left Coordinate X-axis 28 y // top Coordinate Y-axis 29 } 30 */