ssl protocol
Secure Socket Layer: Secure Socket Layer, ssl is a set of security protocols, which are called by application layer. When http calls ssl protocol, it is called https. When ftp calls ssl protocol, it is called sftp.
lls is a collection of protocols, including:
Handshake protocol: including negotiating security parameters and password suite, server authentication (optional client authentication), key exchange
ChangeCipherSpec protocol: A message indicates that the handshake protocol has been completed
Alert protocol: Some abnormal error reminders in handshake protocol are divided into two levels: fatal and warning. Fatal type error will directly interrupt the SSL link, while warning level error SSL link can continue, but will give error warning.
Record protocol: Including message segmentation, compression, message authentication and integrity protection, encryption, etc.
HTTPS protocol: It is a combination of "http protocol" and "SSL/TLS protocol". HTTP over SSL or HTTP over TLS, which encrypts the text data of the http protocol, becomes a binary form of transmission. 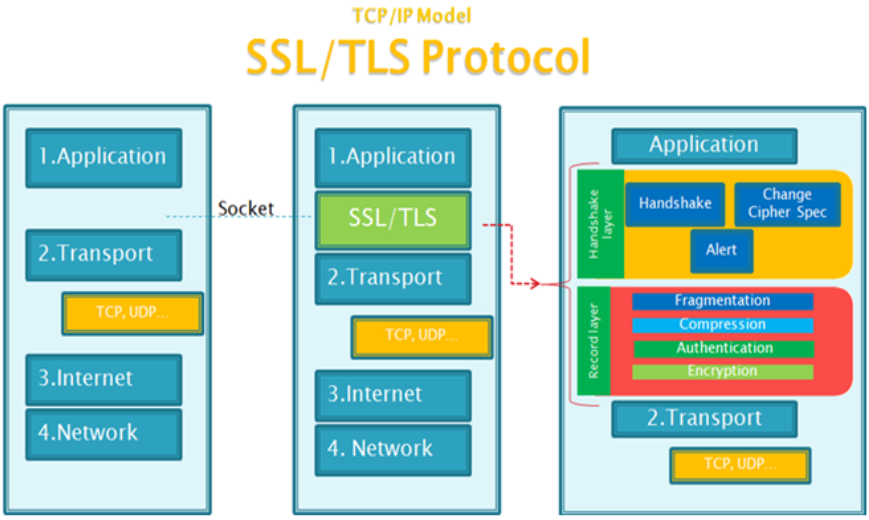
Origin of ssl
Netscape:1994
v1.0,
1995: sslv2.0
1996: v3.0
IETF:1999
tlsv1.0
2006: tls v1.1 RFC4346
2008: tls v1.2
2015: tls v1.3
Hierarchical design
- Bottom level: implementation of basic algorithm primitives, aes, rsa, md5
- Up to the upper level, the implementation of various algorithms;
- Up to the next level: semi-finished products realized by combinatorial calculation method;
- Various finished cryptographic protocol software assembled with various components;
Communication flow
Two phases of ssl communication:
The two-stage protocol is divided into handshake phase and application phase.
Handshake phase (negotiation phase): client and server authenticate each other's identity (depending on the PKI system, using digital certificates to authenticate), and negotiate security parameters, cryptographic suites and master keys used in communication. All keys used in subsequent communications are generated through MasterSecret.
Application phase: Enter after the completion of the handshake phase. In the application phase, the two sides use the key negotiated in the handshake phase to communicate securely.
https communication flow:
The client initiates a request to the server, which sends its certificate to the client.
The client decrypts using the public key of the ca embedded in the system, and the success of decryption means that the ca is legitimate.
If there is a need for the client to send its certificate to the server
The client generates its own symmetric key and encrypts it with the public key of the server. Send it to the server.
The server decrypts the received encrypted symmetric key using its own private key.
Both sides use symmetric key to communicate. (http protocol calls ssl protocol to encrypt their own data, and the encrypted HTTP data is binary)
Open source implementation of ssl protocol: OpenSSL
ssl emerges as a protocol. protocol is a concept defined specifically. the implementation of ssl in openssl is also a set of open source software.
openssl includes three components:
openssl: Multipurpose command line tool, package openssl
libcrypto: Encryption algorithm library, package openssl-libs
libssl: Encryption algorithm implementation module library, package nss
openssl tool use
openssl supports interactive mode, specifying parameters.
Interactive:
? Help
OpenSSL> ?
openssl:Error: '?' is an invalid command.
Standard commands
asn1parse ca ciphers cms
crl crl2pkcs7 dgst dh
dhparam dsa dsaparam ec
ecparam enc engine errstr
gendh gendsa genpkey genrsa
nseq ocsp passwd pkcs12
pkcs7 pkcs8 pkey pkeyparam
pkeyutl prime rand req
rsa rsautl s_client s_server
s_time sess_id smime speed
spkac ts verify version
x509
Message Digest commands (see the `dgst' command for more details)
man dgst View the help of such commands
md2 md4 md5 rmd160
sha sha1
Cipher commands (see the `enc' command for more details)
man enc View the help of such commands
aes-128-cbc aes-128-ecb aes-192-cbc aes-192-ecb
aes-256-cbc aes-256-ecb base64 bf
bf-cbc bf-cfb bf-ecb bf-ofb
camellia-128-cbc camellia-128-ecb camellia-192-cbc camellia-192-ecb
camellia-256-cbc camellia-256-ecb cast cast-cbc
cast5-cbc cast5-cfb cast5-ecb cast5-ofb
des des-cbc des-cfb des-ecb
des-ede des-ede-cbc des-ede-cfb des-ede-ofb
des-ede3 des-ede3-cbc des-ede3-cfb des-ede3-ofb
des-ofb des3 desx idea
idea-cbc idea-cfb idea-ecb idea-ofb
rc2 rc2-40-cbc rc2-64-cbc rc2-cbc
rc2-cfb rc2-ecb rc2-ofb rc4
rc4-40 seed seed-cbc seed-cfb
seed-ecb seed-ofb zlib Non-interactive:
enc: (encrypt) Encryption or decryption for symmetric encryption
- e: Encryption
- d: decryption
- des3: Specify the encryption algorithm as DES3
-a
- salt: salt
- in: Input file
- out: Output file
Example:
encryption
# openssl enc -e -des3 -a -salt -in /etc/passwd -out ./haha.ssl
enter des-ede3-cbc encryption password:
Verifying - enter des-ede3-cbc encryption password:
# ll /etc/passwd ./haha.ssl
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 3329 7month 14 18:21 /etc/passwd
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 4542 7month 16 17:02 ./haha.ssl
//Decrypt:
# openssl enc -d -des3 -a -salt -in ./haha.ssl -out ./haha.txt
enter des-ede3-cbc decryption password:dgst is used for one-way encryption, i.e. generating hash values
- md5: specifying algorithm
Example:
# openssl dgst -md5 haha.txt
MD5(haha.txt)= 7d75659008a5a2f28cac1d2582d28491
- passwd generates the hash value of the password:
- 1 (Number 1): md5 algorithm
- salt Designated salt
example
[root@localhost ~]# openssl passwd -1
Password:
Verifying - Password:
$1$2otXR/.E$e2e0kTulm8LiSAKEgjKeD/
Designate salt, but after adding salt, only one password is entered.
# openssl passwd -1 -salt asd
Password:
$1$asd$49QSDotWo6cyq5JpfBDQ4.
rand: generating random numbers
Format openssl rand encoding byte number.
- base64 uses base64 encoding format
- hex uses hex encoding format
# openssl rand -hex 2
380d
`# openssl rand -base64 2
UR8=
genrsa Generate the private key (only generate the private key, and the public key is extracted from the private key)
-out Generated key file
-des Encryption of generated asymmetric key files using symmetric keys (optional parameters)
//Format OpenSSL genrsa-out file-des asymmetric key length (how many bits)
//Generating Asymmetric Key
openssl genrsa -out /root/haha.key
Generating RSA private key, 1024 bit long modulus
..................................++++++
..................++++++
e is 65537 (0x10001)
//Specifies that the generated key file is encrypted and encrypted using a symmetric key
# openssl genrsa -out /root/haha-des.key -des 1024
Generating RSA private key, 1024 bit long modulus
......++++++
.++++++
e is 65537 (0x10001)
Enter pass phrase for /root/haha-des.key:
Verifying - Enter pass phrase for /root/haha-des.key:
//Use umash to determine file permissions
# (umask 066 ; openssl genrsa -out jinbus.key -des 2048)
Generating RSA private key, 2048 bit long modulus
.................................+++
...................+++
e is 65537 (0x10001)
Enter pass phrase for jinbus.key:
Verifying - Enter pass phrase for jinbus.key:
[root@localhost ~]# ll jinbus.key
-rw------- 1 root root 1738 7month 16 17:39 jinbus.keyrsa display key
- in Gets the Private Key File of the Public Key
- pubout Gets Public Key from Private Key
- out saves the file with the acquired public key
Example:
//View the private key in the file
# openssl rsa -in jinbus.key
Enter pass phrase for jinbus.key:
writing RSA key
-----BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY-----
MIIEowIBAAKCAQEA3WuQa0EZ91BC2M9an99TqX5FJlBCqDSXuM/DS6RDzPuY6CwQ
l7nC11sMGxqC3ilXcfIKuCiKAX6uuAXI3Kskno5o8ftjyS1caiOdboTuUpqVaWFw
iGCygbNWKKrgV01b3FN/InrX46SGB4KlJ/soCl+kNa3MF4PiVowGKaVzepJJD8X6
hElaVIumQPKjSx7ZKiI/e89HnwxAGUTxtr6Oq3EcCSuXPKhz+FaAw9GsW0wKevyw
sUkGsEAWA2DZRyw3n5+rsVJn+BbIoURIW2cPiXhSnSl2xP57ThtogPtro2iv3O3C
7+9xczsahG3GbN+NwK4FGT+JZH5AJj18rk+6ywIDAQABAoIBADhUojQ3JsT9fVQt
RJABwAYR4sPBjYO/hY32BWhcDQe8RoVimIIRN1mUhzrp/rtIZz/M5R8+6QVCVm7o
wdYqEDHqZxaQ7y0CRk2Wa/nvBbasLzDVIkz/1MocduH3vwVW3/TopSJ/gCcg9xw4
B45pXiFtfZhOc+rTmaSNERBNUFixH0ryxFBqkuPb1bUaWumnOhMSIwgpkiCzy3on
v8/BuLHP3ySFb+94QvOsqInV2uYqXfLw7Tks2ETxmapvssWHzigrnvl5JyFb/UMH
rw5y4DCT+Ha9Brp22KuzBJx04UeCfAjVAlAiLUnjJH/IupNmCQhIsxW72IM+DdnJ
GkM4K3kCgYEA/uOVvFpwegQ/LAVKpNyOs+KYz17Oj/VXcrxjiCjFm213bH/Mnb+k
jhP/HNov2AGQTvNk+FwzjGIX+fMosNcb7+VegKA/opxWSJbw4tdaJK0SZmTFWJ33
JyXdKrsW8nA7cxKKaAwrKdnHBo9RXR3VomxsgmjvVVyt04FPJp1zLy8CgYEA3mKi
Jr7cbwYkcMKuBx9JkROTO3mAnPkicYuxH71FPPMB8mnPLQDEK/gne2Wcad57Olmv
hDgAhyEYHdgIay3FU3Fy0kWozXUha+U3MIq7BhuMH43AsjxgoGHbUzM8v6OKyDOY
HBbH9UzUW6WuLaP39q+xrq/mWQxN4cDA4xqyZyUCgYBWsewVM6G8LsOZ4nbgGlDD
aJhXOEUD/Avxb5hfEJcd5Z7QHavoH+4FkVGda60ISIfgArNeMmYqIpdLIeS+OXw8
HYUGNPtQAOLsL8LhNSRpAyEWCMKDAL+25g8S4K3OalQeMLk46KKpynQCjC69gE9Q
vpYtySlWnH5XSU01sioiawKBgQCENJzzbcn8Uul9A6+T2lzQ25NO6zezmkSIviQp
m0q7JjiFFbQtq+Pzw84tBMZNBg+6K7E1aFmf++Orck/m78n8hlhdez4UDss0qor5
16/BvMS7yXjCPTSwhBxwROibgS0zQcDvCfgL84XXihKXXYA/bkmycS3+yFrQl9fT
634d5QKBgBbPFkeAaGjzmLgIAfG1l/SIwjJhvH2n+xUt2YtV0VR9A07HKR/dda/9
L8vOlfegi3bODf+gwABOecbfKayzv6P+yQX6gBLaNvCXr1eE2Ob76Iwi2wb7UplL
3AU54zZlDFvH8YRl5fUVZGeJjyvGatViwuVDLvYCEz5tGos4rTyo
-----END RSA PRIVATE KEY-----req request
- New: Generate a new certificate signing request
- x509: Special for CA to generate self-visa
- key: The private key file used to generate the request
- days n: validity period of certificate
- Out/PATH/TO/SOMECERTFILE: Certificate Preservation Path
x509 Views Information in Certificates
Format: openssl x509 -in file name - noout
-text|issuer|subject|serial|dates
OpenSSL x509-in certificate-noout-text: View Certificate
ca generates ca certificate
- days Certificate Validity Period
- Application documents for in certificate
- certificates generated by out