Simple query
- Select several tuples in the table
- Select several columns in the table
- order by clause
- group by clause
- Aggregate function
Select several columns in the table
Query the student number and name of all students
select sno,sname from student
Select several rows in the table
Eliminate rows with duplicate values
DISTINCT
Query the student number of the elective course
select distinct sno from sc
Query the student number of students with failed grades
select distinct sno from sc where grade<60
Query the name, department and age of students not between 20-23 years old
select sname,sdept,sage from student where sage not between 20 and 23
Query the names and gender of students in the departments of information science, mathematics and computer science
select sname,ssex
from student
where sdept in('is','ma','cs')
The query is not the name and gender of students in the Department of information science, mathematics and computer science
select sname,ssex
from student
where sdept not in ('is','ma','cs')
Students surnamed Zhang, Li and Liu in the query table
select * from student where sname like '[Zhang Li Liu]%'
Query the name, student number and gender of all students not surnamed Liu
select sname,sno,ssex from student where sname not like 'Liu%'
Query students whose last student number is not 2.3.5
select * from student where sno like '%[^235]'
select * from student where sno not like '%[235]'
Order by clause
ASC: Ascending Descending: DESC
Query the student number and grades of students who have taken No. 3 course, and the query results are arranged in descending order of scores
select sno,grade from sc where cno='3' order by grade desc
Query the information of all students. The query results are arranged in ascending order by the Department name of the Department, and the students in the same department are arranged in descending order by age
select * from student order by sdept,sage desc
When using select statements, sometimes you only want to list the first few rows of results in the result set. You can use the top predicate to limit the output results
Check the names, ages, and departments of the three oldest students
select top 3 sname,sage,sdept from student order by sage desc
select top 2 with ties * from student order by sage
Aggregate function
- COUNT(*): the number of tuples in the statistics table
- Count (column name): counts the number of values in this column
- SUM: calculate column value synthesis
- AVG
- MAX
- MIN
In the above functions, except COUNT(*), other functions ignore NULL value during calculation
Count the total number of students
select count(*) Total number from student
Count the number of students who have taken courses
select count(sno) Number of selected courses from sc
Calculate the total score of student 9512101
select sum(grade) Total score from sc where sno = '9512101'
Calculate the average test scores of students in course 'c01'
select avg(grade) Average score from sc where cno='c01'
Query the highest and lowest scores of students who have taken the course 'c01'
select max(grade) Highest score,min(grade) Lowest score from sc where cno='c01'
Aggregate functions cannot appear in the where clause
Query the name of the oldest student
select sname from student where sage=max(sage)
This kind of writing is wrong!!!!
GROUP BY clause
- The calculation can be controlled at the group level. The purpose of grouping is to refine the action object of the calculation function
- The grouping statement is located after the where clause
Count the number of courses selected for each course, and list the course number and number
Classify the course selection information according to each course number
Count the number of student numbers of each course
select cno Course number,count(sno) Number of selected courses from sc group by cno
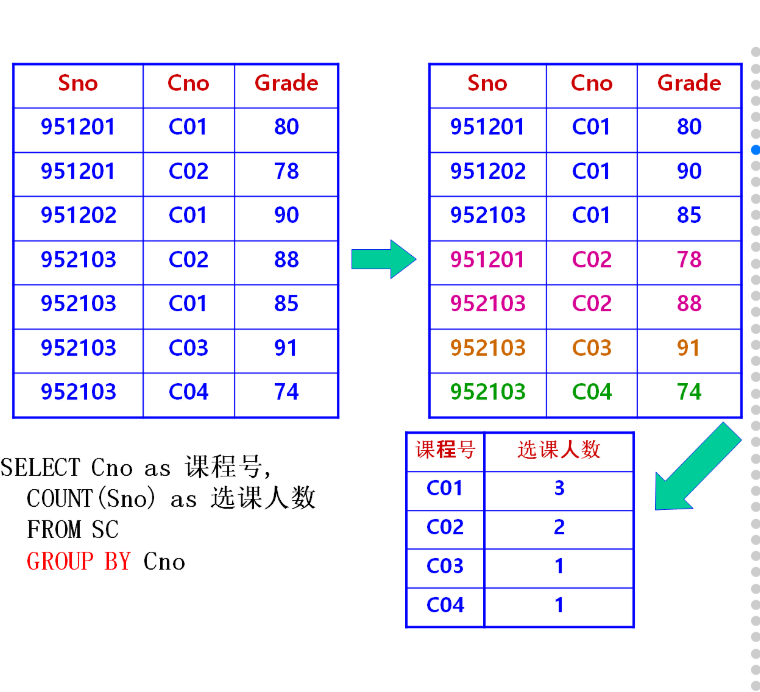
Query the number of courses and average score of each student
select sno Student number,count(cno) Number of courses selected, avg(grade) Average score from sc group by sno
Using HAVING
- HAVING is used to select groups. It is a bit like the where clause, but it is used for groups rather than individual records
- Calculation functions can be used in the HAVING clause, but not in the WHERE clause
- HAVING is usually used with the GROUP BY clause
Query the student number of students who have taken more than 3 courses
SELECT SNO FROM SC GROUP BY Sno HAVING COUNT(Cno)>=3
Query the average score and the number of courses selected of students whose number of courses is greater than or equal to 4
select sno Student number, avg(grade) Average score,count(cno) Number of courses selected from sc group by sno having count(cno)>=4

select sno Student number,sum(grade) Total score from sc group by sno having sum(grade)>200
Query the number of students in the computer department and information science department
select sdept,count(*)Number of students
from student
group by sdept
having sdept in('CS','IS')
The column name after select must be included in the aggregate function or group by clause, and the column name after having must be included in the group by clause of the aggregate function
select sdept,count(*)Number of students
from student
where sdept in('cs','is')
group by sdept
Multi table join query
- First select the first tuple in Table 1, and then scan table 2 from the beginning to find the tuple that meets the connection conditions.
- Once found, the first tuple in Table 2 is spliced with the hospital group to form a tuple in the result table
- After all table 2 queries are completed, take the second tuple in Table 1, and then scan table 2 from the beginning. Connect the tuples that meet the conditions one by one and add them to the result
- Repeat this process until all tuples in Table 1 are processed
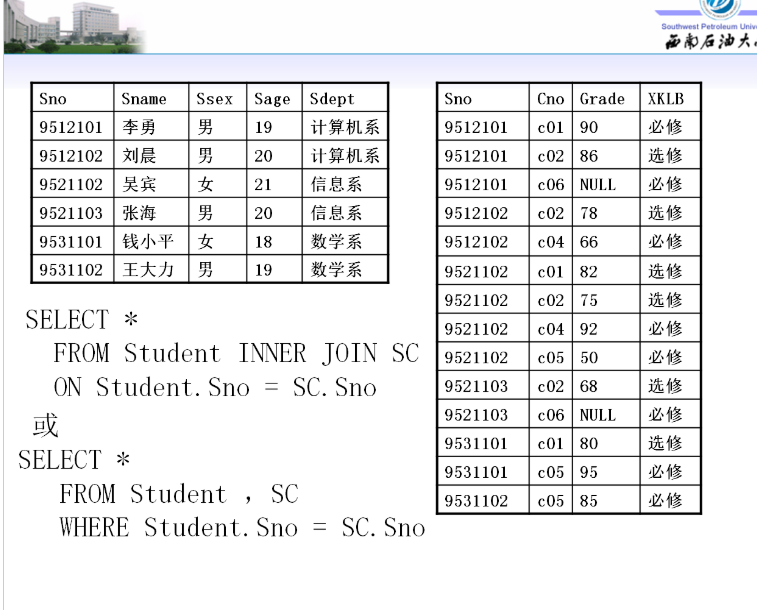
Query the basic information of each student and their courses
select * from student inner join sc on student.sno=sc.sno
select * from student,sc where student.sno=sc.sno
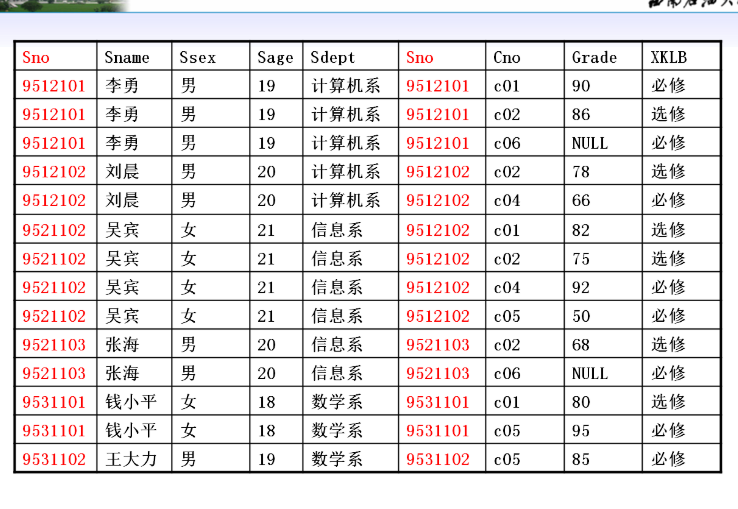
The join results in the two tables contain all the columns of the two tables. The sno column is repeated twice, which is unnecessary. Therefore, these duplicate columns should be removed in writing query statements
select student.sno,sname,ssex,sage,sdept,cno,grade,xklb from student,sc where student.sno=sc.sno
Query the course situation of students in the information department. It is required to list the students' names, course numbers and grades
select sname,cno,grade from student,sc where student.sno=sc.sno where sdept='Information system'
Query the students who have taken VB courses in the 'information department', and list the students' names, course names and grades
select sname full name,cname Course name,grade achievement from student ,sc,course where student.sno=sc.sno and course.cno=sc.cno where sdept='Information system' and cname='VB'
External connection
- Only the data in one table must meet the connection conditions, while the data in another table can not meet the conditions
- The information of tuples that do not meet the connection conditions can be output
Query students' course status, including students who have taken courses and students who have not taken courses
select student.sno,sname,cno,grade from student left outer join sc on student.sno=sc.sno
You can also use the right outer connection
select student.sno,sname,cno,grade from sc right outer join student on student.sno=sc.sno

Subquery
- A select from where statement is called a query block
- Nesting a query in another select, insert, update, delete statement is called nested query
select sname from student where sno in (select sno from sc where cno='2')
Subquery with IN predicate
If the value of the expression is equal to a value in the collection, this test is true. If the expression is not equal to all the values in the collection, it returns false
Identify students in the same department as Liu Chen
This query request can be distributed to complete
- Determine Liu Chen's department name
select sdept from student where sname='Liu Chen'
- Find all students studying in IS department
select sno,sname,sdept from student where sdept='IS'
select sno,sname,sdept from student where sdept in(select sdept from student where sname='Liu Chen') and sname!='Liu Chen'
First execute the sub query, and then find all students studying in this department on the results of the sub query
Query the student number and name of students with scores greater than 90
select sno Student number,sname full name from student where sno in( select sno from sc where grade > 90)
Join query with multiple tables
select student.sno ,sname from student,sc where student.sno=sc.sno and grade>90
Query the student number and name of students who have taken the basic course of database
select sno Student number,sname full name from student where sno in (select sno from sc,course where sc.cno=course.cno and cname='Database foundation course')
Implementation with multi table connection
select student.sno,sname from student,sc,course where student.sno=sc.sno and sc.cno=course.cno and cname='Database foundation course')
Query the number of courses and average score of students taking database and application courses
select student.sno Student number,count(*) Number of courses selected, avg(grade) from student,sc,course where student.sno=sc.sno and course.cno=sc.cno and cname='Database and Application Course' group by student.sno
select student,sno Student number,count(*) Number of courses selected,avg(grade) Average score from student,sc where student.sno=sc.sno and cno in(select cno from course where cname='Database and Application') group by student.sno
Subquery with comparison operator
Assuming that a student can only study in one department and must belong to one department, you can use = instead of in below
select sno,sname,sdept from student where sdept=(select sdept from student where sname ='Liu Chen')
Query the student number and grade of students who have taken the 'c02' course and whose grade is higher than the average score of this course
SELECT sno ,grade from sc where cno='c02' and grade>(select avg(grade) from sc where cno='c02')
Query the name and age of students younger than a student in the Department of Information Science in other departments
select sname,sage from student where sage<any(select age from student where sdept='is') and sdept <>'is'
select sname,sage from student where sage< (select max(sage) from student where sdept='is') and sdept<>'is'
All students in other departments know their names and ages better than those in the Department of information science
select sname,sage from student where sage<all(select sage from student where sdept='is' ) and sdept<> 'is'
select sname,sage from student where sage<(select min(age) from student where sdept='is') and sdept<> 'is'
Irrelevant subquery concept
When performing set based test or comparison test with sub query, the sub query is executed first, and then the outer query is executed based on the results of the sub query. The sub query is executed only once, and the conditions of the sub query do not depend on the outer query. Such sub query will become irrelevant sub query or nested sub query
Subquery with EXISTS predicate
Query the names of all students who have taken c01 course
select sname from studennt where exists (select * from sc where sno=student.sno and cno='c01')