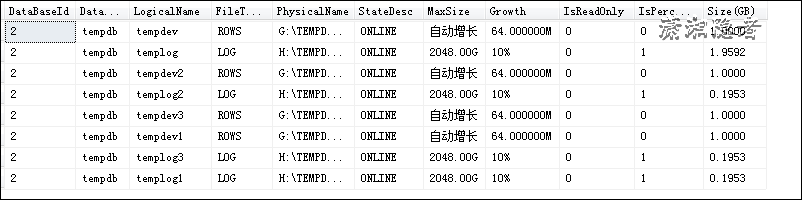
sys.master_files have been used to calculate the size and usage of tempdb databases, but it is found that sys.master_files can not accurately calculate the size of tempdb databases. As follows:
SELECT database_id AS DataBaseId,DB_NAME(database_id) AS DataBaseName,Name AS LogicalName,type_desc AS FileTypeDesc,Physical_Name AS PhysicalName,State_Desc AS StateDesc,CASE WHEN max_size = 0 THEN N'No growth allowed'WHEN max_size = -1 THEN N'Automatic growth'ELSE LTRIM(STR(max_size * 8.0 / 1024 / 1024, 14, 2))+ 'G'END AS MaxSize,CASE WHEN is_percent_growth = 1THEN RTRIM(CAST(Growth AS CHAR(10))) + '%'ELSE RTRIM(CAST(Growth*8.0/1024 AS CHAR(10))) + 'M'END AS Growth,Is_Read_Only AS IsReadOnly,Is_Percent_Growth AS IsPercentGrowth,CAST(size * 8.0 / 1024 / 1024 AS DECIMAL(8, 4)) AS [Size(GB)]FROM sys.master_filesWHERE database_id =2ORDER BY 1
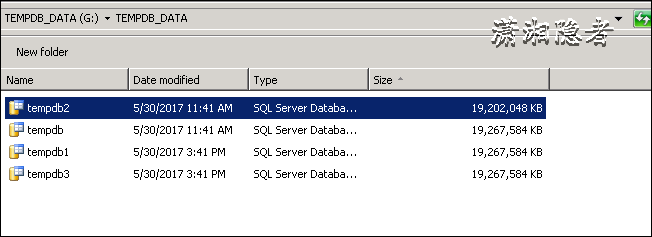
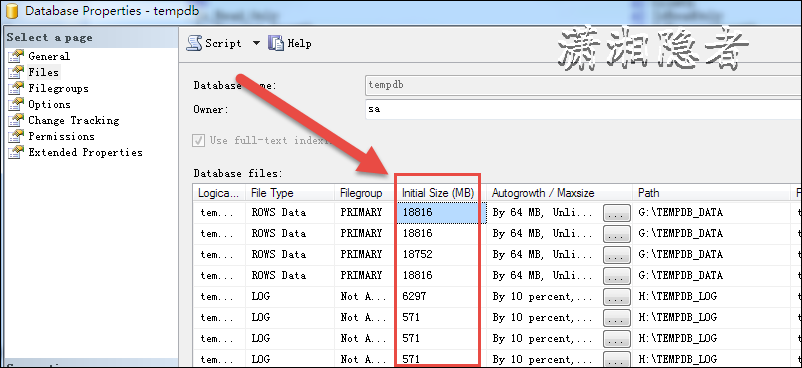
In Windows windows, you will see that the actual size of these files is more than 18G, not 1G. Size (GB) using sys.master_files statistics is only the initialization size of tempdb files. Of course, you use UI to look at tempdb properties in SSMS and find that the size value is correct.
If you use Profile tracking to look at the specific SQL as follows, you will find that its statistical data comes from the view sys.database_files.
USE tempdb;GOSELECT s.name AS [Name] ,CAST(FILEPROPERTY(s.name, 'SpaceUsed') AS FLOAT) * CONVERT(FLOAT, 8) AS [UsedSpace] ,CAST(CASE WHEN s.growth = 0 THEN ( CASE WHEN s.type = 2 THEN 0ELSE 99END )ELSE s.is_percent_growthEND AS INT) AS [GrowthType] ,s.physical_name AS [FileName] ,s.size * CONVERT(FLOAT, 8) AS [Size] ,CASE WHEN s.max_size = -1 THEN -1ELSE s.max_size * CONVERT(FLOAT, 8)END AS [MaxSize] ,s.file_id AS [ID] ,'Server[@Name='+ QUOTENAME(CAST(SERVERPROPERTY(N'Servername') AS sysname), '''')+ ']' + '/Database[@Name=' + QUOTENAME(DB_NAME(), '''') + ']'+ '/LogFile[@Name=' + QUOTENAME(s.name, '''') + ']' AS [Urn] ,CAST(CASE s.is_percent_growthWHEN 1 THEN s.growthELSE s.growth * 8END AS FLOAT) AS [Growth] ,s.is_media_read_only AS [IsReadOnlyMedia] ,s.is_read_only AS [IsReadOnly] ,CAST(CASE s.stateWHEN 6 THEN 1ELSE 0END AS BIT) AS [IsOffline] ,s.is_sparse AS [IsSparse]FROM sys.database_files AS sWHERE ( s.type = 1 )ORDER BY [Name] ASC;
The specific definition of sys.database_files is as follows
SET quoted_identifier ONSET ansi_nulls ONgoCREATE VIEW sys.database_filesASSELECT file_id = f.fileid,file_guid = f.fileguid,type = f.filetype,type_desc = ft.NAME,data_space_id = f.grpid,NAME = f.lname,physical_name = f.pname,state = CONVERT(TINYINT, CASE f.filestate-- Map enum EMDFileState to AvailablityStatesWHEN 0 THEN 0WHEN 10 THEN 0 -- ONLINEWHEN 4 THEN 7 -- DEFUNCTWHEN 5 THEN 3WHEN 9 THEN 3 -- RECOVERY_PENDINGWHEN 7 THEN 1WHEN 8 THEN 1WHEN 11 THEN 1 -- RESTORINGWHEN 12 THEN 4 -- SUSPECTELSE 6END),-- OFFLINEstate_desc = st.NAME,size = Isnull(Filepropertybyid(f.fileid, 'size'), size),max_size = f.maxsize,f.growth,is_media_read_only = Sysconv(bit, f.status & 8),-- FIL_READONLY_MEDIAis_read_only = Sysconv(bit, f.status & 16),-- FIL_READONLYis_sparse = Sysconv(bit, f.status & 256),-- FIL_SPARSE_FILEis_percent_growth = Sysconv(bit, f.status & 32),-- FIL_PERCENT_GROWTHis_name_reserved = Sysconv(bit, CASE f.filestateWHEN 3 THEN 1ELSE 0END),-- x_efs_DroppedReusePendingcreate_lsn = Getnumericlsn(f.createlsn),drop_lsn = Getnumericlsn(f.droplsn),read_only_lsn = Getnumericlsn(f.readonlylsn),read_write_lsn = Getnumericlsn(f.readwritelsn),differential_base_lsn = Getnumericlsn(f.diffbaselsn),differential_base_guid = f.diffbaseguid,differential_base_time = NULLIF(f.diffbasetime, 0),redo_start_lsn = Getnumericlsn(f.redostartlsn),redo_start_fork_guid = f.redostartforkguid,redo_target_lsn = Getnumericlsn(f.redotargetlsn),redo_target_fork_guid = f.forkguid,backup_lsn = Getnumericlsn(f.backuplsn)FROM sys.sysprufiles fLEFT JOIN sys.syspalvalues stON st.class = 'DBFS'AND st.value = f.filestateLEFT JOIN sys.syspalvalues ftON ft.class = 'DBFT'AND ft.value = f.filetypeWHERE filestate NOT IN ( 1, 2 ) -- x_efs_Dummy, x_efs_Droppedgo
sys.master_files are defined as follows:
SET quoted_identifier ONSET ansi_nulls ONgoCREATE VIEW sys.master_filesASSELECT database_id = f.dbid,file_id = f.fileid,file_guid = f.fileguid,type = f.filetype,type_desc = ft.NAME,data_space_id = f.grpid,NAME = f.lname,physical_name = f.pname,state = CONVERT(TINYINT, CASE f.filestate-- Map enum EMDFileState to AvailablityStatesWHEN 0 THEN 0WHEN 10 THEN 0 -- ONLINEWHEN 4 THEN 7 -- DEFUNCTWHEN 5 THEN 3WHEN 9 THEN 3 -- RECOVERY_PENDINGWHEN 7 THEN 1WHEN 8 THEN 1WHEN 11 THEN 1 -- RESTORINGWHEN 12 THEN 4 -- SUSPECTELSE 6END),-- OFFLINEstate_desc = st.NAME,f.size,max_size = f.maxsize,f.growth,is_media_read_only = Sysconv(bit, f.status & 8),-- FIL_READONLY_MEDIAis_read_only = Sysconv(bit, f.status & 16),-- FIL_READONLYis_sparse = Sysconv(bit, f.status & 256),-- FIL_SPARSE_FILEis_percent_growth = Sysconv(bit, f.status & 32),-- FIL_PERCENT_GROWTHis_name_reserved = Sysconv(bit, CASE f.filestateWHEN 3 THEN 1ELSE 0END),-- x_efs_DroppedReusePendingcreate_lsn = Getnumericlsn(f.createlsn),drop_lsn = Getnumericlsn(f.droplsn),read_only_lsn = Getnumericlsn(f.readonlylsn),read_write_lsn = Getnumericlsn(f.readwritelsn),differential_base_lsn = Getnumericlsn(f.diffbaselsn),differential_base_guid = f.diffbaseguid,differential_base_time = NULLIF(f.diffbasetime, 0),redo_start_lsn = Getnumericlsn(f.redostartlsn),redo_start_fork_guid = f.redostartforkguid,redo_target_lsn = Getnumericlsn(f.redotargetlsn),redo_target_fork_guid = f.forkguid,backup_lsn = Getnumericlsn(f.backuplsn)FROM master.sys.sysbrickfiles fLEFT JOIN sys.syspalvalues stON st.class = 'DBFS'AND st.value = f.filestateLEFT JOIN sys.syspalvalues ftON ft.class = 'DBFT'AND ft.value = f.filetypeWHERE f.dbid < 0x7fff -- consistent with sys.databasesAND f.pruid = 0AND f.filestate NOT IN ( 1, 2 ) -- x_efs_Dummy, x_efs_DroppedAND Has_access('MF', 1) = 1go
As you can see from the above SQL script, the size of the statistical database comes from two tables, sys.sysprufiles and master.sys.sysbrickfiles, respectively, and then it's hard to get a deeper understanding of the specific reasons. In the link https://connect.microsoft.com/SQLServer/feedback/details/377223/sys-master-files-does-not-show-accurate-size-information, there are some descriptions of tempdb-related issues:
1. The view sys.master_files is something new and is updated asynchronously. It doesn't updates immediately.
2. When you re-start your SQL Server, SQL Server will re-create tempdb based on sys.master_files.
3. The sys.master_files tell you about any tempdb data file which was there on your system (the number of tempdb files) with which your server have started.
4. While sys.database_files shows currently used tempdb files. Its quite possible that not all tempdb data files came online.
5. You can read the errorlog look for any error meesage did any of the files did not come online.
6. After you started sql server somebody might have executed SQL commands to remove or add tempdb files.
In general, the data in sys.master_files is updated asynchronously, not synchronously. It will not be updated immediately. When you restart your SQL Server, it will recreate and initialize the tempdb file size according to the sys.master_files median at startup time. sys.database_files displays the tempdb file currently in use. Probably not all tempdb data files are online. So, if you want to query the exact size of tempdb, you need to use sys.database_files to query!