Gateway is to do filtering or blocking operations to make our services more secure. When users access our services, they must first pass through the gateway and then forward it to our micro-services by the gateway.
1. New Gateway Service Module
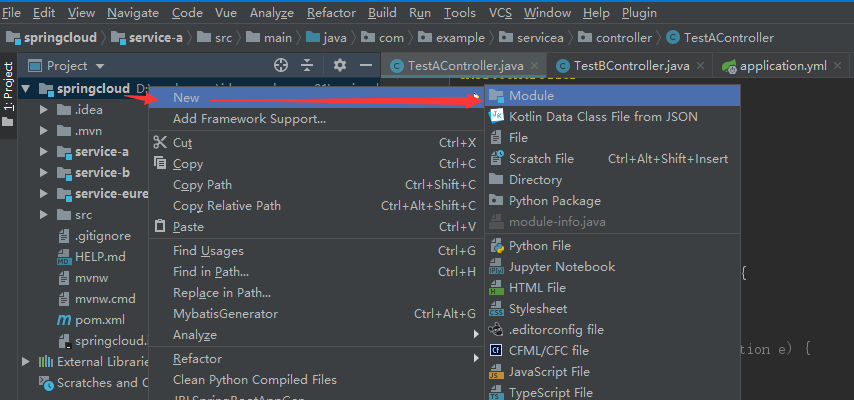
2. Still choose springboot Project
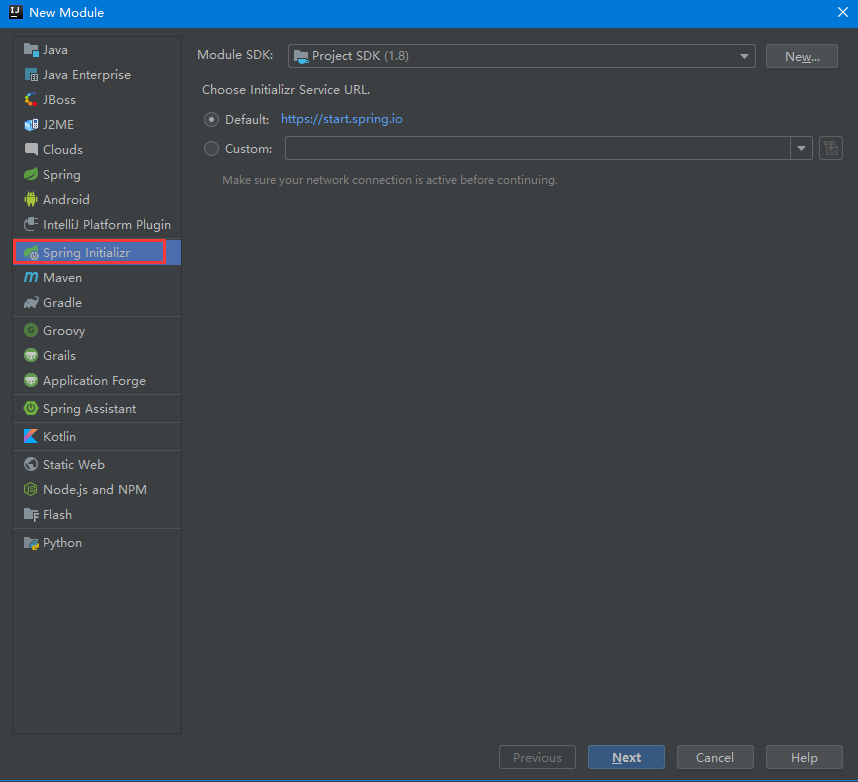
3. Name the old rule
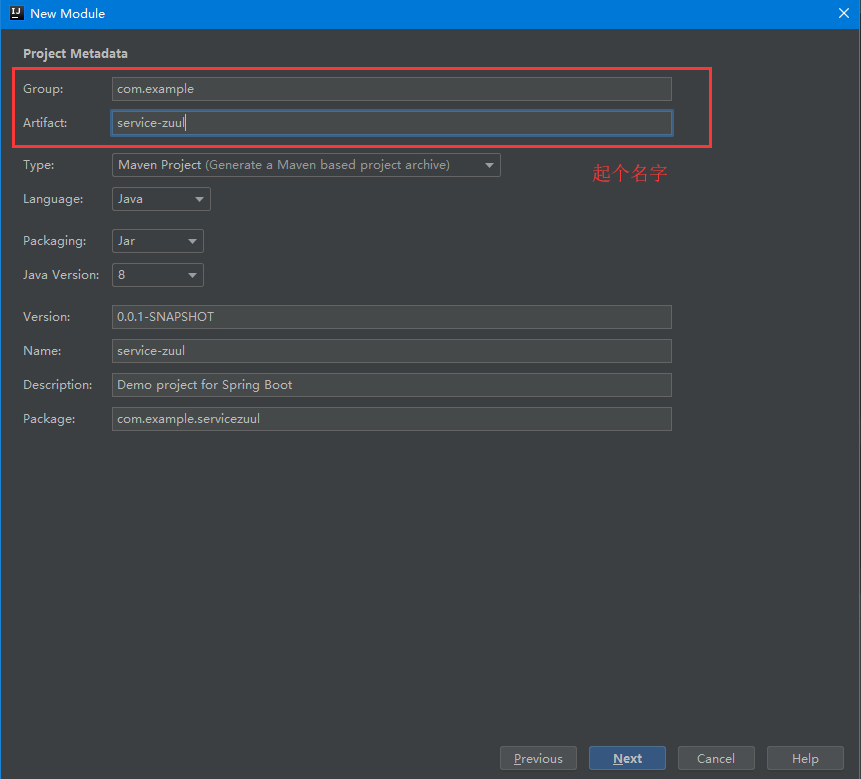
4. Check Registry Client
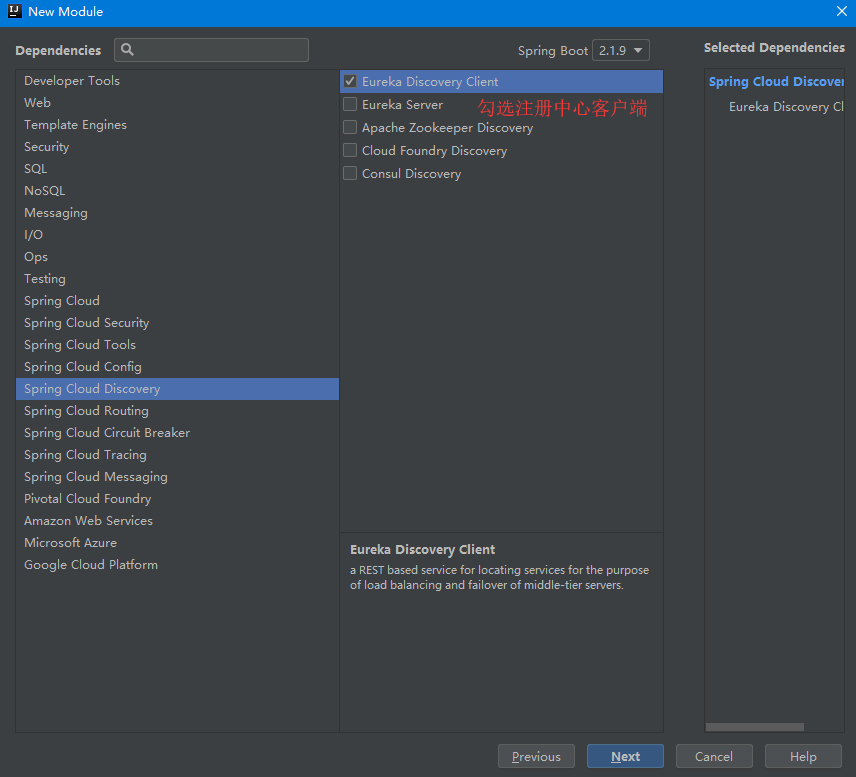
5. Check zuul Gateway Module
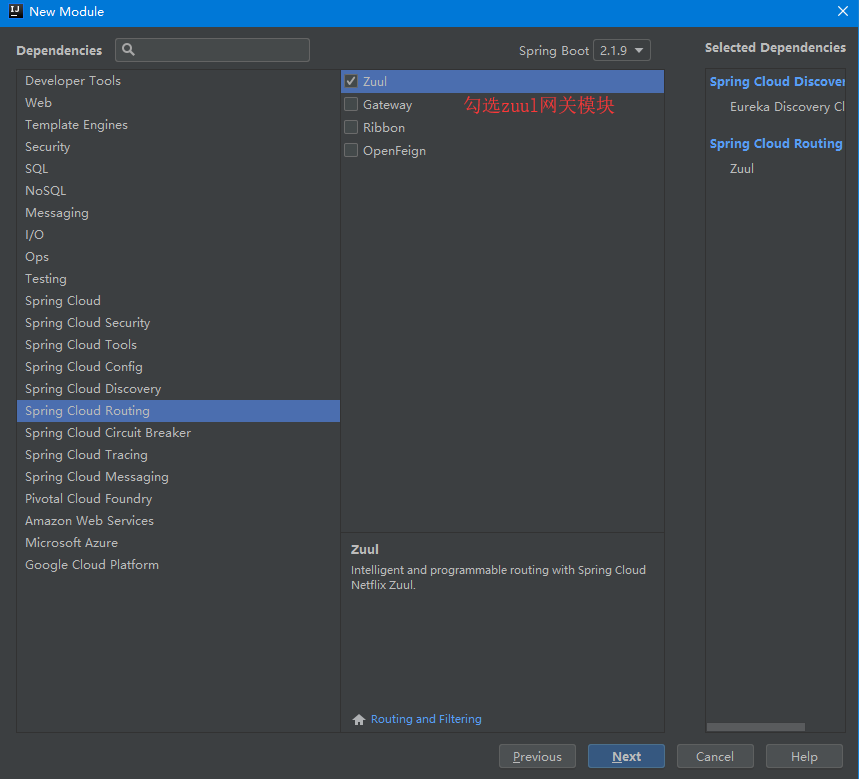
6. Write configuration files
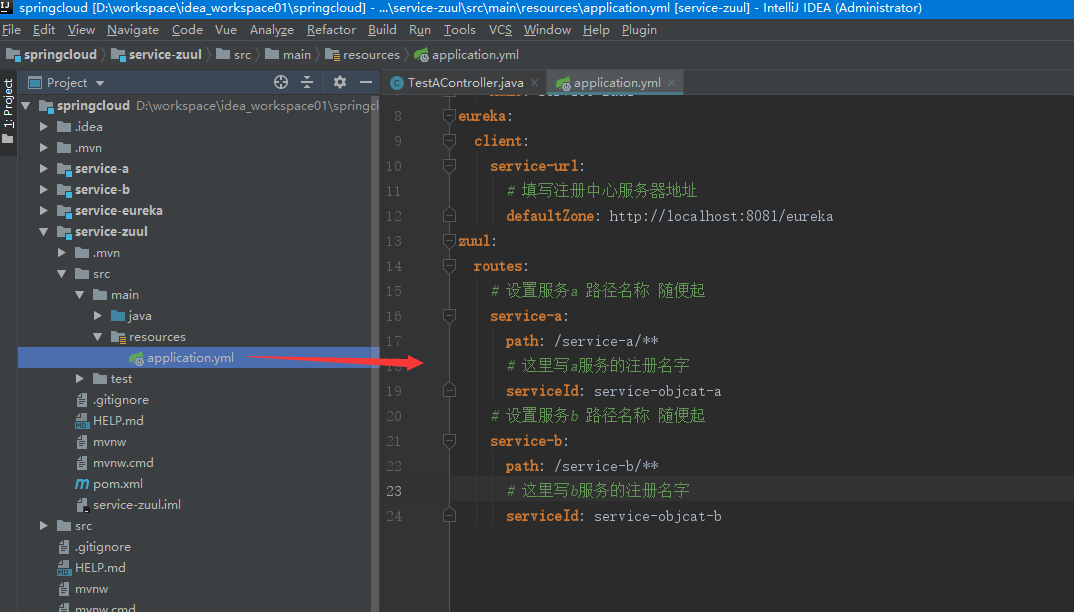
server: # Service port number port: 8085 spring: application: # Service Name - Use names to communicate between services name: service-zuul eureka: client: service-url: # Fill in the Registry Server Address defaultZone: http://localhost:8081/eureka zuul: routes: # Setting the name of service a path is optional service-a: path: /service-a/** # Here is the registration name of a service. serviceId: service-objcat-a # Set the name of service b path as you like service-b: path: /service-b/** # Here is the registration name of service b. serviceId: service-objcat-b
7. Create a package name of com.objcat.filter, and create a TokenFilter-like inheritance of ZuulFilter to implement filtering rules
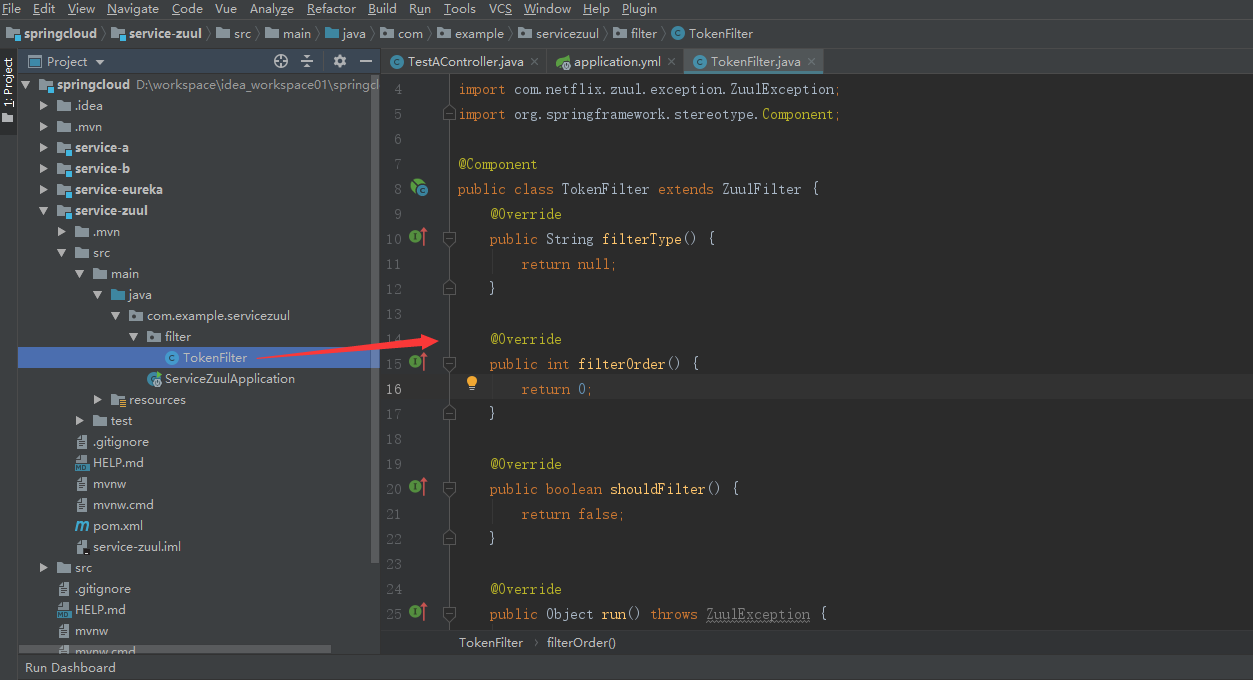
8. Rewrite the method in ZuulFilter and write the filtering logic in run() method
import com.netflix.zuul.ZuulFilter; import com.netflix.zuul.context.RequestContext; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; public class TokenFilter extends ZuulFilter { /** * The filter type pre represents the logical operation before the request */ @Override public String filterType() { return "pre"; } /** * Filter execution sequence * The order of filter execution when a request has multiple filters at the same stage */ @Override public int filterOrder() { return 0; } /** * Whether to turn on filtering or not */ @Override public boolean shouldFilter() { return true; } /** * Writing Business Logic Code for Filter Interception */ @Override public Object run() { RequestContext currentContext = RequestContext.getCurrentContext(); HttpServletRequest request = currentContext.getRequest(); String token = request.getParameter("token"); if (token == null) { currentContext.setSendZuulResponse(false); currentContext.setResponseBody("token is null"); currentContext.setResponseStatusCode(401); } return null; } }
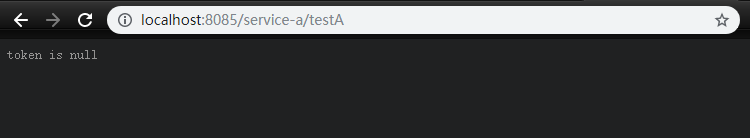
The logic is simple to verify whether the request token sent by the client is empty or not. If it is empty, it cannot be returned by token is null.
9. Configure the gateway entry file. Don't forget to instantiate the filter in this place or it won't work.
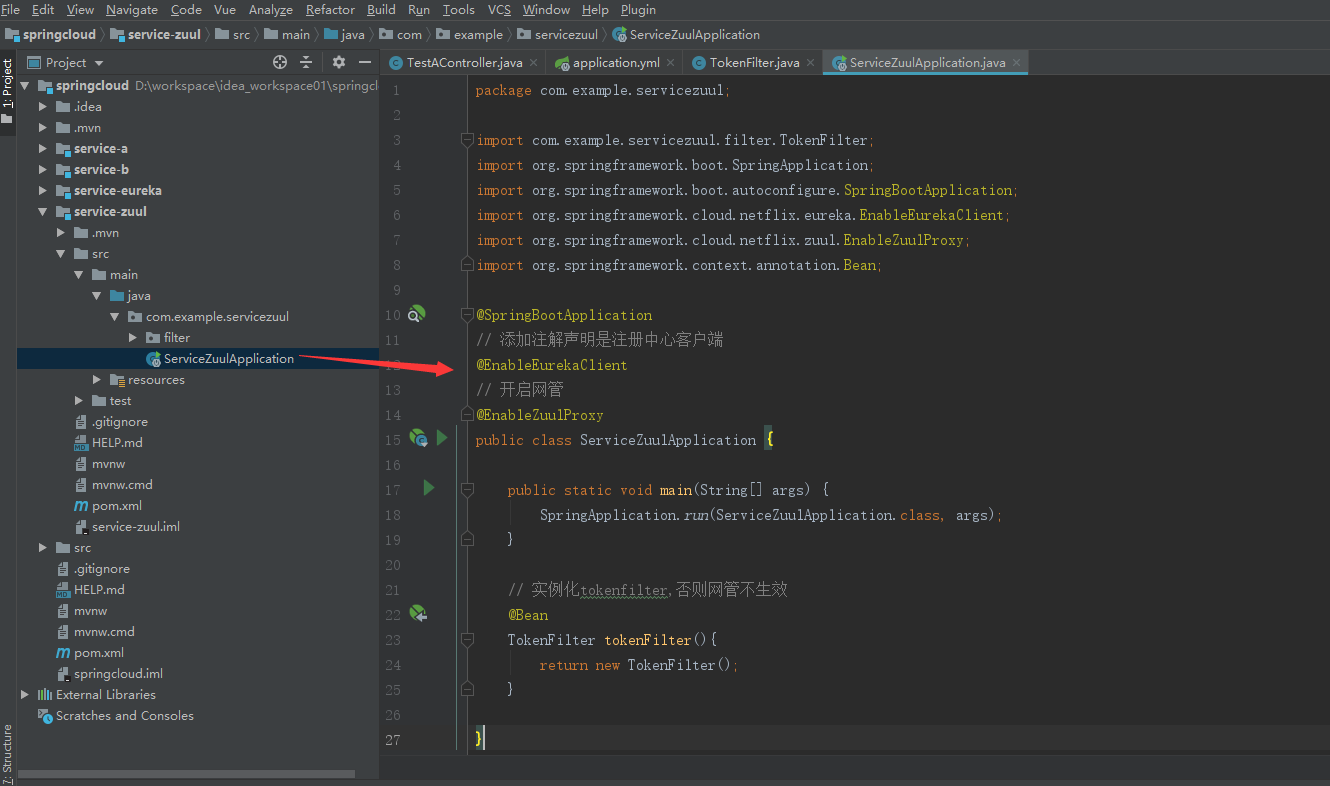
import com.example.servicezuul.filter.TokenFilter; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EnableEurekaClient; import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.zuul.EnableZuulProxy; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; @SpringBootApplication // Adding annotation declaration is registry client @EnableEurekaClient // Open Network Management @EnableZuulProxy public class ServiceZuulApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(ServiceZuulApplication.class, args); } // instantiation tokenfilter,Otherwise, the network management will not take effect. @Bean TokenFilter tokenFilter(){ return new TokenFilter(); } }
10. Accessing a Service through Gateway
You only need to use the address of the gateway + the port number of the gateway + the alias path of the service (configuration file) + the api name to access it.
http://localhost:8085/service-a/testA
http://localhost:8085/service-a/testA?token=123
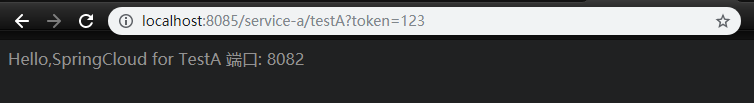
When there is no token, the return is token is null, and when token has value, it can be accessed normally.
The request forwarded by this gateway is called a reverse proxy. You can hide the real address of your local server.
Higher security is achieved by exposing only the address of the external gateway and forwarding it to the server by the gateway.