Server SpringBoot 2.x: localhost:8082
Front-end Vue2.x: localhost:81
The port numbers of the front and back end are different, which is cross-domain, resulting in a new session ID generated for each visit when the front end accesses the back end. The solutions are as follows:
Backend:
1. Add filters:
package com.nsoft.gkzp.syscore.config.filter; import org.apache.logging.log4j.LogManager; import org.apache.logging.log4j.Logger; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod; import javax.servlet.*; import javax.servlet.annotation.WebFilter; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import java.io.IOException; @WebFilter(urlPatterns = "/*", filterName = "corsFilter") public class CorsFilter implements Filter { final private static Logger logger = LogManager.getLogger(CorsFilter.class); @Override public void destroy() { } /** * This filter only deals with cross-domain issues * @param servletRequest * @param servletResponse * @param chain * @throws ServletException * @throws IOException */ @Override public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain chain) throws ServletException, IOException { HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) servletRequest; HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) servletResponse; String origin = request.getHeader("Origin"); if(origin == null) { origin = request.getHeader("Referer"); } response.setHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Origin", origin);// Allow access to cross-domain resources for specified domains(It can't be written here.*,*Representatives receive access to all domain names, such as Write*The next line of code is invalid. Keep in mind) response.setHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Credentials", "true");//true Representatives allow clients to carry cookie(here origin Value cannot be“*",Can only specify a single domain name) response.setHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Methods", "GET, HEAD, POST, PUT, DELETE, TRACE, OPTIONS, PATCH"); /// Actual request method name that allows browsers to send after a successful check request response.setHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Headers", "Authorization,Origin, X-Requested-With, Content-Type, Accept,Access-Token");// Request headers that allow browsers to send //response.setHeader("Access-Control-Max-Age", "86400"); // Browser Cache Preview Request Result Time,Company:second chain.doFilter(request,response); } @Override public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException { } }
2. springboot2. When configuring filters, the startup class must add @ServletComponentScan to load the filters
package com.nsoft.gkzp; import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.boot.web.server.ConfigurableWebServerFactory; import org.springframework.boot.web.server.ErrorPage; import org.springframework.boot.web.server.WebServerFactoryCustomizer; import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletComponentScan; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus; import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.CorsRegistry; import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer; import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurerAdapter; /** * springboot Entrance * MapperScan("com.nsoft.gkzp.**.dao")To scan mapper, the class under dao does not need to add the @mapper annotation * ServletComponentScan A filter has been added, so the @Servlet ComponentScan annotation is added here to scan spring to the filter (eg:com.nsoft.gkzp.syscore.config.filter.CorsFilter) */ @SpringBootApplication @ServletComponentScan @MapperScan("com.nsoft.gkzp.**.dao") public class GzyGkzpApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(GzyGkzpApplication.class, args); } /** * When springboot integrates the front end of vue, Vue uses url jump time 404 error. This code solves this problem. * Refer to https://blog.csdn.net/Mr_EvanChen/article/details/83625082. */ @Bean public WebServerFactoryCustomizer<ConfigurableWebServerFactory> webServerFactoryCustomizer(){ return factory -> { ErrorPage error404Page = new ErrorPage(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND, "/index.html"); factory.addErrorPages(error404Page); }; } }
3. In spring-session 2.x, Cookie contains SameSite, whose default value is Lax.
SameSite Cookie is used to prevent CSRF attacks. It has two values: Strict, Lax
SameSite = Strict: Means a strict pattern, indicating that this cookie cannot be a third-party cookie under any circumstances;
SameSite = Lax: This means relaxed mode. A get request can be used as a third-party cookie, but can't carry cookies for cross-domain post access (it's a pain, our checking interface is a POST request).
package com.nsoft.gkzp.syscore.config; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.session.web.http.CookieSerializer; import org.springframework.session.web.http.DefaultCookieSerializer;/**
* https://www.cnblogs.com/hujinshui/p/11025848.html
* spring-session 2.x In Cookie, SameSite is introduced. Its default value is Lax.
* SameSite Cookie It is used to prevent CSRF attacks. It has two values: Strict and Lax.
* SameSite = Strict: It means strict mode, which means that this cookie can not be used as a third-party cookie under any circumstances.
* SameSite = Lax: In a relaxed mode, a get request can be used as a third-party cookie, but cannot carry cookies for cross-domain post access.
* Summary: Front-end requests to the background, each session is different, each session is a new session, resulting in no access to user information
*/@Configuration public class SpringSessionConfig { public SpringSessionConfig() { } @Bean public CookieSerializer httpSessionIdResolver() { DefaultCookieSerializer cookieSerializer = new DefaultCookieSerializer(); // Cancel the same site settings only cookieSerializer.setSameSite(null); return cookieSerializer; } }
Front end:
1. In main.js (front-end axios)
import axios from 'axios'; axios.defaults.withCredentials=true;//Let ajax carry cookie s
After a day and a half, I changed many times, but I still can't. Later, I found that proxy agent was used in the front end. It has also dealt with cross-domain problems. When I searched online, I found that some articles also used this. But I just can't do it here.
My original code:
1) Write the registration page:
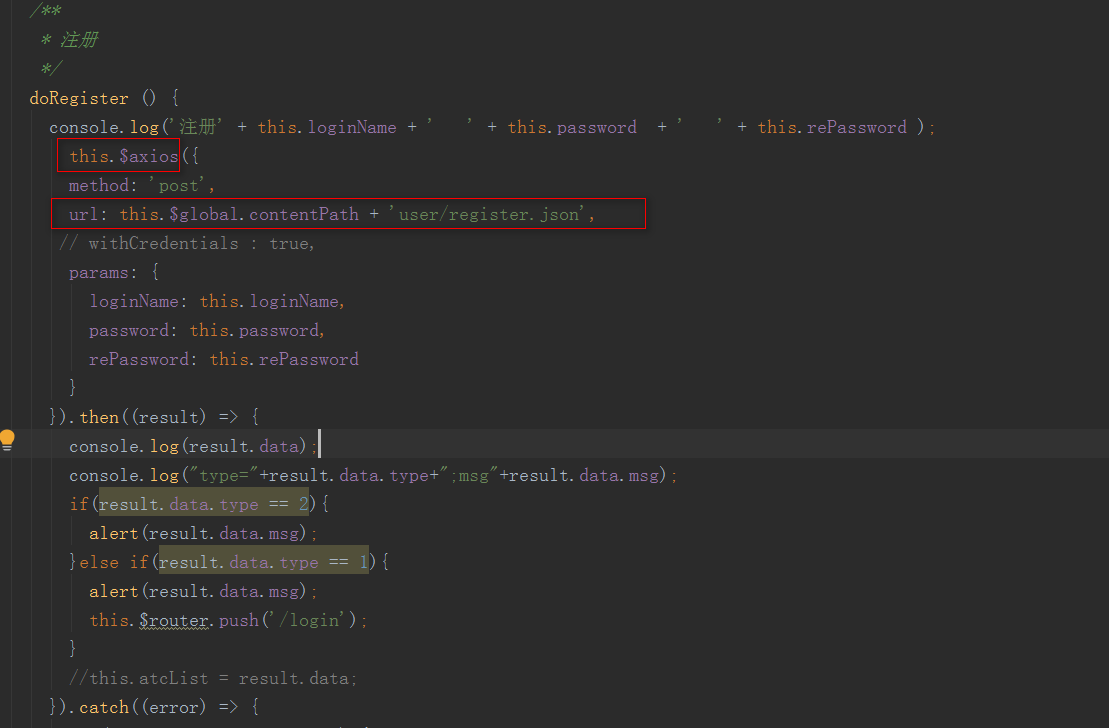
2) The global configuration is as follows:
main.js
// xenv tags current environment true: development environment false:production environment const xenv = true; // Register global variables Vue.prototype.$global = { //contentPath tags the root path, mainly for URLs that axios request back-end data contentPath: xenv ? '/api/' : router.options.base };
(xenv is set to true; so the value of the root path contentPath must be'/ api /', and'/ api /'is configured as a proxy in vue.config.js, as follows. )
vue.config.js
devServer: { open: true, host: '0.0.0.0', port: 80, https: false, hotOnly: false, before: app => { }, proxy: { // Configuration across domains '/api': { target: 'http://127.0.0.1:8082/', ws: true, changOrigin: true, pathRewrite: { '^/api': '/' } } } },
2. Without using proxy proxy proxy proxy proxy proxy proxy proxy proxy proxy, the root directory is written to'http://127.0.0.1:8082/'.
main.js:
// xenv tags current environment true: development environment false:production environment const xenv = true; // Register global variables Vue.prototype.$global = { // contentPath tags the root path, mainly for URLs that axios request back-end data // contentPath: xenv ? '/api/' : router.options.base contentPath: 'http://127.0.0.1:8082/' };
Reference: