Integrate Mybatis
<dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>2.1.2</version> </dependency>
Steps:
1) . configure data source related properties (see Druid in the previous section)
2) . creating tables for databases
3) , create a JavaBean
4) , annotated version
//Specify that this is a mapper that operates the database //@Mapper public interface DepartmentMapper { @Select("select * from department where id=#{id}") public Department getDeptById(Integer id); @Delete("delete from department where id=#{id}") public int deleteDeptById(Integer id); @Options(useGeneratedKeys = true,keyProperty = "id") @Insert("insert into department(department_name) values(#{departmentName})") public int insertDept(Department department); @Update("update department set department_name=#{departmentName} where id=#{id}") public int updateDept(Department department); }
Question:
Define the configuration rules of Mybatis; add a ConfigurationCustomizer to the container;
@org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration public class MyBatisConfig { @Bean public ConfigurationCustomizer configurationCustomizer(){ return new ConfigurationCustomizer(){ @Override public void customize(Configuration configuration) { configuration.setMapUnderscoreToCamelCase(true); } }; } }
//Use MapperScan to scan all Mapper interfaces in batches @MapperScan(value = "com.eppear.springboot.mapper") @SpringBootApplication public class SpringBoot06DataMybatisApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(SpringBoot06DataMybatisApplication.class, args); } }
5) , profile version
mybatis: # Specify global profile location config-location: classpath:mybatis/mybatis-config.xml # Specify sql mapping file location mapper-locations: classpath:mybatis/mapper/*.xml
More references
http://mybatis.org/spring-boot-starter/mybatis-spring-boot-autoconfigure/index.html
6.4. Integrating SpringData JPA
6.4.1 introduction to SpringData
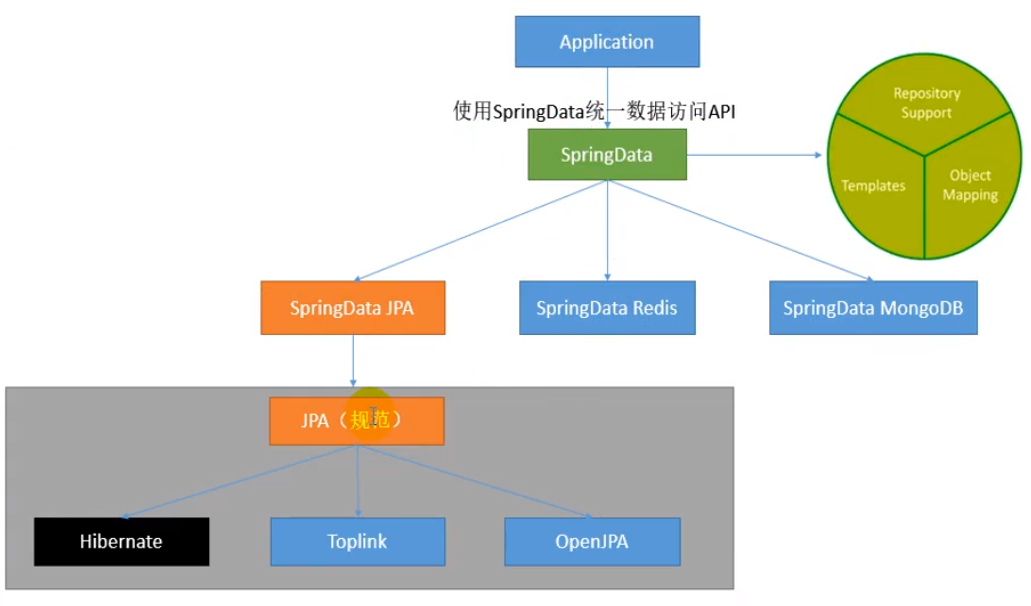
6.4.2 integrate SpringData JPA
JPA: ORM ( Object Relational Mapping) ; 1) Write an entity class (bean) and data table for mapping, and configure the mapping relationship;
//Using JPA annotations to configure mapping relationships @Entity //Tell JPA that this is an entity class (a class mapped to a data table) @Table(name = "tbl_user") //@Table to specify which data table to correspond to; if the default table name is omitted, it is user; public class User { @Id //This is a primary key @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)//Self increasing primary key private Integer id; @Column(name = "last_name",length = 50) //This is a column corresponding to the data table private String lastName; @Column //Omitting the default column name is the property name private String email;
2) Write a Dao interface to operate the data table (Repository) corresponding to the entity class
//Inherit JpaRepository to complete the operation of database public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User,Integer> { }
3) . basic configuration
spring: datasource: url: jdbc:mysql://192.168.15.22/jpa username: root password: 123456 driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver jpa: hibernate: # Update or create data table structure ddl-auto: update # Console display SQL show-sql: true