4.7 error handling mechanism
4.7.1. Default error handling mechanism of SpringBoot
1. Default effect:
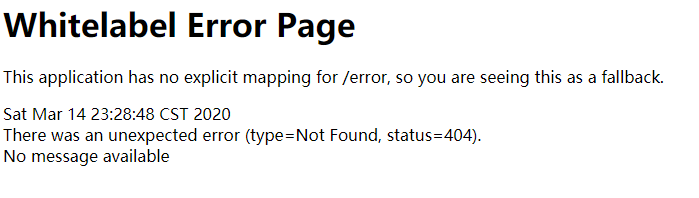
1) Return to an error page
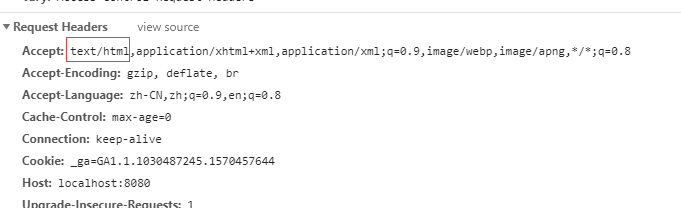
Request headers sent by browser:
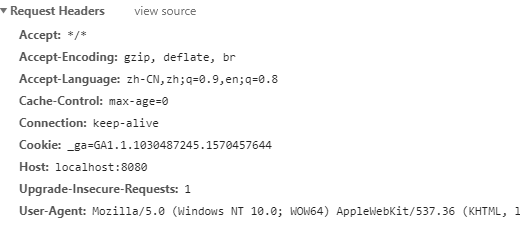
2) If it is another client, it will respond to a json data by default.
{ "timestamp":"2020-03-14T15:56:48.897+0000", "status":404, "error":"Not Found", "message":"No message available", "path":"/kldf" }
2. Principle:
Refer to ErrorMvCAutoConfiguration; automatic configuration of error handling;
The following components were added to the container
1),DefaultErrorAttributes:
//Help us share information on the page @Override public Map<String, Object> getErrorAttributes(WebRequest webRequest, boolean includeStackTrace) { Map<String, Object> errorAttributes = new LinkedHashMap<>(); errorAttributes.put("timestamp", new Date()); addStatus(errorAttributes, webRequest); addErrorDetails(errorAttributes, webRequest, includeStackTrace); addPath(errorAttributes, webRequest); return errorAttributes; }
2) . BasicErrorController: process default / error request
@Controller @RequestMapping("${server.error.path:${error.path:/error}}") public class BasicErrorController extends AbstractErrorController { @RequestMapping(produces = MediaType.TEXT_HTML_VALUE) //Generate html type data; requests sent by browsers come to this processing method public ModelAndView errorHtml(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) { HttpStatus status = getStatus(request); Map<String, Object> model = Collections .unmodifiableMap(getErrorAttributes(request, isIncludeStackTrace(request, MediaType.TEXT_HTML))); response.setStatus(status.value()); //Error page view name found ModelAndView modelAndView = resolveErrorView(request, response, status, model); return (modelAndView != null) ? modelAndView : new ModelAndView("error", model); } @RequestMapping //Generate json data, and other clients come to this method for processing; public ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>> error(HttpServletRequest request) { HttpStatus status = getStatus(request); if (status == HttpStatus.NO_CONTENT) { return new ResponseEntity<>(status); } Map<String, Object> body = getErrorAttributes(request, isIncludeStackTrace(request, MediaType.ALL)); return new ResponseEntity<>(body, status); }
3),ErrorProperties
public class ErrorProperties { /** * Path of the error controller. */ @Value("${error.path:/error}") private String path = "/error"; //After an error occurs in the system, it comes to the error request for processing;
4),DefaultErrorViewResolver
@Override public ModelAndView resolveErrorView(HttpServletRequest request, HttpStatus status, Map<String, Object> model) { ModelAndView modelAndView = resolve(String.valueOf(status.value()), model); if (modelAndView == null && SERIES_VIEWS.containsKey(status.series())) { modelAndView = resolve(SERIES_VIEWS.get(status.series()), model); } return modelAndView; } private ModelAndView resolve(String viewName, Map<String, Object> model) { //By default, SpringBoot can find a page; error/404 String errorViewName = "error/" + viewName; //The template engine can resolve this page address, and then it can use the template engine to resolve it TemplateAvailabilityProvider provider = this.templateAvailabilityProviders.getProvider(errorViewName, this.applicationContext); if (provider != null) { //Return to the view address specified by errorViewName when the template engine is available return new ModelAndView(errorViewName, model); } // If the template engine is not available, find the page corresponding to errorViewName under the static resource folder error/404.html return resolveResource(errorViewName, model); }
3, steps
Once an error such as 4xx or 5xx occurs in the system, the ErrorPageCustomizer will take effect (customizing the error response rules); the / error request will come and be processed by the BasicErrorController;
Response page; which page to go to is parsed by defaultrorviewresolver;
protected ModelAndView resolveErrorView(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, HttpStatus status, Map<String, Object> model) { //All errorviewresolvers wait until ModelAndView for (ErrorViewResolver resolver : this.errorViewResolvers) { ModelAndView modelAndView = resolver.resolveErrorView(request, status, model); if (modelAndView != null) { return modelAndView; } } return null; }
4.7.2. If customized error response
1. How to customize error page
1) If there is a template engine; error / status code; [name the error page as error status code. html and put it in the error folder in the template engine folder], the error of this status code will come to the corresponding page;
We can use 4xx and 5xx as the file names of error pages to match all errors of this type, precision first (precise status code. html is preferred);
Information available on the page:
Timestamp: timestamp
Status: status code
Error: error prompt
Exception: exception object
Errors: JSR303 data validation errors are all here
2) . there is no template engine (the template engine cannot find the error page), which can be found under the static resource folder;
3) , none of the above error pages, i.e. the default error prompt page of SpringBoot;
2. How to customize wrong json data
1) . custom exception handling & return custom json data;
@ControllerAdvice public class MyExceptionHandler { //1. The browser client returns json @ResponseBody @ExceptionHandler(UserNotExistException.class) public Map<String,Object> handleException(Exception e){ Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("code","user.notexist"); map.put("message",e.getMessage()); return map; } } //No adaptive effect
2) , forward to / error for adaptive response effect processing
@ExceptionHandler(UserNotExistException.class) public String handleException(Exception e, HttpServletRequest request){ Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>(); //Pass in our own error status code 4xx 5xx /** * Integer statusCode = (Integer) request .getAttribute("javax.servlet.error.status_code"); */ request.setAttribute("javax.servlet.error.status_code",500); map.put("code","user.notexist"); map.put("message","User error"); request.setAttribute("ext",map); //Forward to / error return "forward:/error"; }
3. Take our customized data out
After an error is detected, the / error request will come and be processed by the BasicErrorController. The data that can be obtained after the response is obtained by getErrorAttributes (the method specified by AbstractErrorController);
1) , write an implementation class of ErrorController (or a subclass of AbstractErrorController) completely and put it in the container;
2) , the data that can be used on the page, or the data that can be used returned by json, are obtained through errorAttributes.getErrorAttributes;
In the container, DefaultErrorAttributes.getErrorAttributes() is used for data processing by default;
Custom ErrorAttributes
//Add our own defined ErrorAttributes to the container @Component public class MyErrorAttributes extends DefaultErrorAttributes { //The map of the return value is all the fields that the page and json can get @Override public Map<String, Object> getErrorAttributes(WebRequest webRequest, boolean includeStackTrace) { Map<String, Object> map = super.getErrorAttributes(webRequest, includeStackTrace); map.put("company","atguigu"); //Data carried by our exception handler Map<String,Object> ext = (Map<String, Object>) webRequest.getAttribute("ext", 0); map.put("ext",ext); return map; } }
The final effect: the response is adaptive, and you can change what you need to return by customizing getErrorAttributes
{ "timestamp": "2020-03-15T12:05:06.783+0000", "status": 404, "error": "Not Found", "message": "No message available", "path": "/aad", "company": "atguigu", "ext": null }