This article describes how SpringBoot integrates MyBatis
I'm sure you've learned something about Spring Boot and MyBatis by reading this article, so I'll go straight to dry.
First import dependencies into POM
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.3.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.21</version>
</dependency>Then there is the configuration of the application.properties file (only a partial configuration of mybatis is provided)
server.port=80 spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springboot spring.datasource.username=Your own account spring.datasource.password=Your own password spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
First, prepare a table for the user table I defined. If you are too lazy to write by yourself, you can copy the following code.
--Create a database create database springboot; --Create table CREATE TABLE `user` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `username` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL, `sex` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
Create entity classes and associate them with constructed tables
package com.rambler.domain;
public class User {
private int id;
private String username;
private String sex;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public User(String username, String sex) {
this.username = username;
this.sex = sex;
}
public User(){
}
}
Define relevant Mapper
package com.rambler.mapper;
import com.rambler.domain.User;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Insert;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select;
@Mapper
public interface UserMapper {
@Select("select * from user where id = #{id}")
User getUserById(@Param("id") int id);
@Insert("insert into user(username,sex) values(#{username},#{sex})")
void InsertUser(@Param("username")String username,@Param("sex")String sex);
}
This is just a demonstration, so the logical structure is relatively simple, so the service layer is omitted and the User Mapper is injected directly into Controller.
package com.rambler.controller;
import com.rambler.mapper.UserMapper;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/Article")
public class ArticleController {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ArticleController.class,args);
}
@RequestMapping("/getUser")
public Object getUserById(Integer id){
return userMapper.getUserById(id);
}
@RequestMapping("/insertUser")
public void insertUser(String username,String sex){
userMapper.InsertUser(username,sex);
}
}
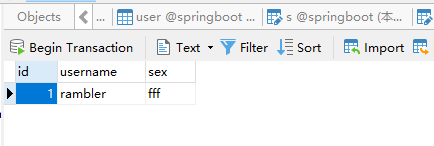
Test results, no specific page, directly return to json, or in the database to see the effect, access the following url
http://localhost/Article/insertUser?username=rambler&sex=fff
View results