I. overview
The design idea of Spring web MVC is to distribute requests to handlers around Dispatcher Servlet.
Dispatcher Servlet's workflow for processing a request is as follows:
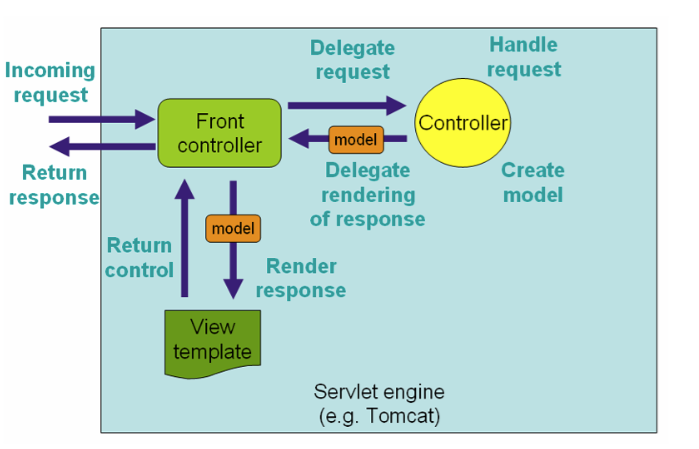
Dispatcher Servlet is a real Servlet (inherited from HttpServlet), so when building a Spring MVC program, you need to configure the requests Dispatcher Servlet needs to handle, such as in web.xml:
<servlet> <servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping>
In the Web MVC framework, each Dispatcher Servlet has its own Web Application Context, which inherits all bean s defined under the root Web Application Context. A typical hierarchical structure is as follows:
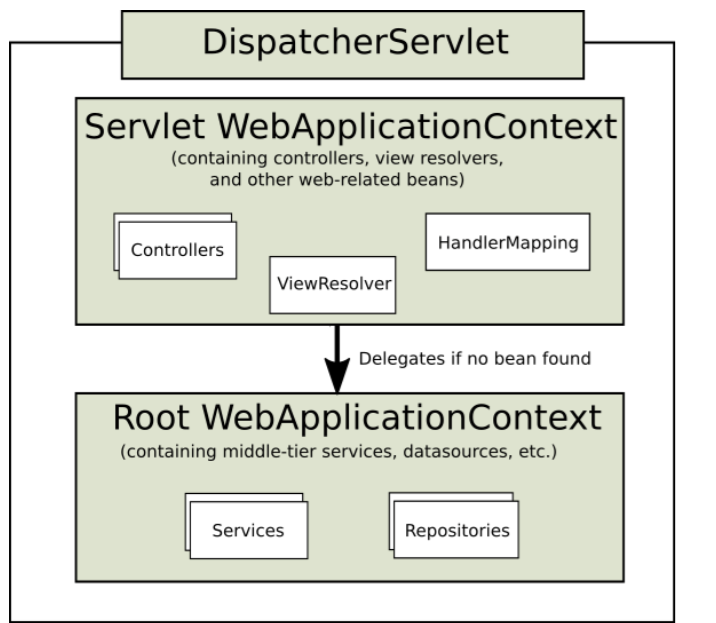
When Dispatcher Servlet is initialized, Spring MVC will look for a configuration file named [servlet-name]-servlet.xml in the WEB-INF folder. This Spring configuration creates new beans or rewrites beans under Root Context, so we create the configuration file dispatcher-servlet.xml as follows:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context = "http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.2.xsd"> <!--Scanning and injection only@Controller and@ControllerAdvice--> <context:component-scan base-package="com.alex.learning" use-default-filters="false"> <context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller" /> <context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice" /> </context:component-scan> <mvc:annotation-driven /> </beans>
II. Dispacher Servlet initialization
The class diagram structure of Dispacher Servlet is as follows:
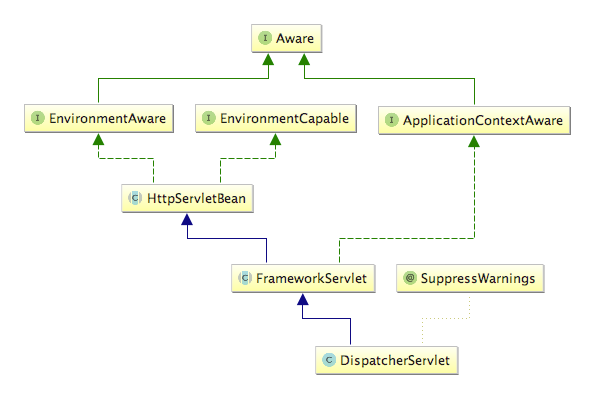
Framework Servlet: The base class of Spring web framework, which provides functions integrated with Spring Application Context.
HttpServletBean: Inherited from HttpServlet, it's a simple extension, and initialization begins with this kind of overridden init method.
The initialization process is as follows:
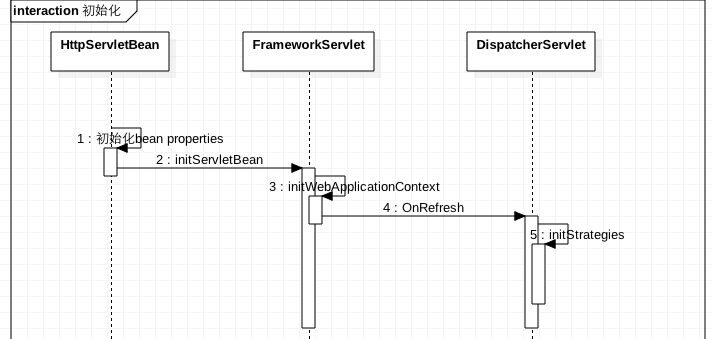
The init method of HttpServletBean is the entry method of Dispatcher Servlet initialization:
// Write the parameters in the configuration file into the bean property of the servlet and call the initialization method of the subclass @Override public final void init() throws ServletException { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Initializing servlet '" + getServletName() + "'"); } // Initialize the necessary parameters into the Bean try { PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties); BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this); ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext()); bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment())); initBeanWrapper(bw); bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true); } catch (BeansException ex) { logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + getServletName() + "'", ex); throw ex; } // Framework Servlet initialization initServletBean(); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Servlet '" + getServletName() + "' configured successfully"); } }
The initServletBean method of Framework Servlet:
// The Properties of the bean have been set up to create the Web Application Context for the Servlet @Override protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException { getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "'"); if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) { this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "': initialization started"); } long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); try { // Initialize Web Application Context this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext(); // Default empty implementation, rewriting subclasses initFrameworkServlet(); } catch (ServletException ex) { this.logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex); throw ex; } catch (RuntimeException ex) { this.logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex); throw ex; } if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) { long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime; this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "': initialization completed in " + elapsedTime + " ms"); } }
As you can see, initialize initWeb Application Context () that calls the Framework Servlet primarily
// Initialize Web Application Context protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() { // Get the root Web Application Context for this web app WebApplicationContext rootContext = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext()); WebApplicationContext wac = null; if (this.webApplicationContext != null) { // There is a Web Application Context injected when Servlet is created wac = this.webApplicationContext; if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) { ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac; if (!cwac.isActive()) { // Currently, context has not refreshed - > set parent context and application_context_id if (cwac.getParent() == null) { // No parent context, set to rootContext cwac.setParent(rootContext); } // Configure wac and call its refresh method // This completes the initialization of the IOC container and the Application Context configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac); } } } if (wac == null) { // If it is not injected when the servlet is created, check to see if wac exists under the current servlet context. // If so, it means that initialization has been completed, with Parent context and contextId set wac = findWebApplicationContext(); } if (wac == null) { // If the servlet context does not have wac, create a // CongureAndRefreshWeb Application Context (cwac) is also called inside this method. wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext); } if (!this.refreshEventReceived) { // To determine whether refresh has passed, call the onRefresh method of Dispacher Servlet onRefresh(wac); } // If you need to publish wac as an attribute of servletContext if (this.publishContext) { String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName(); getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac); if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) { this.logger.debug("Published WebApplicationContext of servlet '" + getServletName() + "' as ServletContext attribute with name [" + attrName + "]"); } } return wac; }
The process of initialization of Application Context has been described in detail in Spring core source code analysis--IoC container initialization. After initialization of Web Application Context of the whole Web App, OnRefresh(wac), a key method of Dispacher Servlet, is called, which really starts the relevant initialization of Spring MVC.
DispatcherServlet:
@Override protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) { initStrategies(context); } // Initialize policy objects that all servlet s need to use // It may be overridden by subclasses protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) { // Initialize getBean("multipartResolver") // Supporting file upload, spring mvc only provides a Commons Fileupload initMultipartResolver(context); // Initialize getBean("localeResolver") // Used to support internationalization initLocaleResolver(context); // Initialize getBean("themeResolver") // Dealing with the Theme of web Pages initThemeResolver(context); // Initialize List < Handler Mapping > // Key processes, mapping requests to handlers and a series of pre-and post-processors initHandlerMappings(context); // Initialize List < Handler Adapter > // Help servlet call handler directly initHandlerAdapters(context); // Initialize List < Handler Exception Resolver > // Processing all unexpected exception s, you can specify modelandView // Standard exceptions can also be captured initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context); // Initialize getBean("viewNameTranslator") // If there is no viewName, the logically matched viewName, such as localhost/register.html, is register. // Then the ViewResolver might become localhost/register.jsp initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context); // Initialize List < ViewResolver > // viewResolver resolves the real relationship between viewName and view, such as suffix=".jsp" configured in this example initViewResolvers(context); // Initialize getBean ("Flash Map Manager") // FlashMap for storing and retrieving input and output // Usually attributes are passed to another request during redirection initFlashMapManager(context); }
The implementations of initMultipartResolver, initLocaleResolver, initThemeResolver and initRequestToViewNameTranslator are simple getBean("**"). If an exception is thrown, the default trategy is selected according to Dispatcher Servlet. properties.
So let's take a closer look at the initHandler Mappings (context) method and the initHandler Adapters (which are also key initialization methods for subsequent request processing).
// Initialize handlers Mappings used by this class // If BeanFactory does not have Handler Mapping, we use BeanNameUrlHandler Mapping by default. private void initHandlerMappings(ApplicationContext context) { this.handlerMappings = null; if (this.detectAllHandlerMappings) { // Find all Handler Mappings for Application Context, including ancestor Context Map<String, HandlerMapping> matchingBeans = BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerMapping.class, true, false); if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) { this.handlerMappings = new ArrayList<HandlerMapping>(matchingBeans.values()); // Sort handler Mappings AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.handlerMappings); } } else { try { HandlerMapping hm = context.getBean(HANDLER_MAPPING_BEAN_NAME, HandlerMapping.class); this.handlerMappings = Collections.singletonList(hm); } catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) { // A default Andler Mapping will be added later } } // If initialization handler Mappings is empty, add a default Handler Mapping if (this.handlerMappings == null) { // Dispatcher Servlet has a Dispatcher Servlet. properties file in the same package, and is created from this file // Default Handler Mapping -- Bean NameUrlHandler Mapping and Default Annotation Handler Mapping this.handlerMappings = getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerMapping.class); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("No HandlerMappings found in servlet '" + getServletName() + "': using default"); } } }
Dispatcher Servlet.properties are as follows:
# Default implementation classes for DispatcherServlet's strategy interfaces. # Used as fallback when no matching beans are found in the DispatcherServlet context. # Not meant to be customized by application developers. org.springframework.web.servlet.LocaleResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver org.springframework.web.servlet.ThemeResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.theme.FixedThemeResolver org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerMapping=org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping,\ org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerAdapter=org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.HttpRequestHandlerAdapter,\ org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter,\ org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapter org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerExceptionResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.AnnotationMethodHandlerExceptionResolver,\ org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.ResponseStatusExceptionResolver,\ org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.support.DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver org.springframework.web.servlet.RequestToViewNameTranslator=org.springframework.web.servlet.view.DefaultRequestToViewNameTranslator org.springframework.web.servlet.ViewResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver org.springframework.web.servlet.FlashMapManager=org.springframework.web.servlet.support.SessionFlashMapManager
InitHandler Adapters, initHandler Exception Resolvers, initViewResolvers and initHandler Mapping have the same logic.
At this point, the Web Application Context has been initialized.