Spring transaction management
1. Business
-
What is a transaction
A set of operations either succeeded or failed
-
Characteristics of transactions
ACID
- Atomicity, a group of operations is a whole, either all successful or all failed, and cannot be separated
- Consistency: the data is consistent before and after the transaction
- Isolation: multiple transactions access the database concurrently, and concurrent transactions are isolated from each other
- Persistence: once a transaction is committed, it cannot be modified
-
Isolation problem?
- Dirty read: one transaction reads uncommitted data from another transaction
- Non repeatable reading: one transaction reads another data (update) whose number is already committed
- Phantom read: one transaction reads another data (insert) whose number is already committed
Non repeatable reading refers to the modification of data
Unreal reading refers to adding a piece of data
-
Isolation level
- Read uncommitted: a transaction reads uncommitted data from another transaction
- Read committed: one transaction reads the committed data of another transaction, which solves a problem (dirty reading)
- Repeatable read: repeated data read in a transaction. Solve 2 problems (dirty reading, non repeatable reading)
- Serializable: single transaction to solve three problems (dirty reading, non repeatable reading and phantom reading)
-
contrast
- Performance: read uncommitted > read committed > repeatable read > serializable
- Security: read uncommitted < read committed < repeatable read < serializable
2. Transaction management
2.1 dissemination of affairs
There are seven kinds of transaction propagation behaviors
| Communication behavior | describe |
|---|---|
| propagation_required | If there is no current transaction, create one. If there is, use the current one |
| propagation_supports | The current transaction is supported. If there is no transaction, it will be executed as a non transaction |
| propagation_mandatory | Use the current transaction. If there is no transaction, throw an exception |
| propagation_requires_new | Create a new transaction. If there is a transaction, suspend it |
| propagation_not_supported | Non transaction execution. If there is a transaction currently, it will be suspended |
| propagation_never | Execute as a non transaction, and throw an exception if there is one currently |
| propagation_nested | The current transaction exists and is executed in a nested transaction. If not, use propagation_required |
2.2 isolation level of transactions
Isolation level
| Isolation level | describe |
|---|---|
| ISOLATION_DEFAULT | Use the default isolation level of the back-end database |
| ISOLATION_READ_UNCOMMITTED | Read uncommitted |
| ISOLATION_READ_COMMITTED | Read committed |
| ISOLATION_REPEATABLE_READ | Read repeatable |
| ISOLATION_SERIALIZABLE | Traversing |
2.3 read only
It means that you can only read the database, and cannot add, delete or modify the database
2.4 basic operation (note)
2.4.1 requirements
Complete transfer
2.4.2 realization
Table structure
CREATE TABLE account( id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT, money FLOAT );
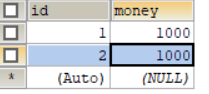
Table data
configuration file
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ssm_db1 jdbc.username=root jdbc.password=root
Configuration class
package com.czxy.demo11_transaction.config;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement;
import tk.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
@Configuration // Indicates the configuration class
@ComponentScan("com.czxy.demo11_transaction") // Set component scan path
@PropertySource("classpath:db.properties") //Load profile
@MapperScan("com.czxy.demo11_transaction.mapper") //The general mapper used for mapper scanning path needs to be imported under tk.mybatis. Package
@EnableTransactionManagement //Open transaction
public class SpringConfig {
@Value("${jdbc.driver}")
private String driver; //drive
@Value("${jdbc.url}")
private String url; //route
@Value("${jdbc.username}")
private String username;
@Value("${jdbc.password}")
private String password;
//Configure connection pool
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource(){
DruidDataSource source = new DruidDataSource();
source.setDriverClassName(driver);
source.setUrl(url);
source.setUsername(username);
source.setPassword(password);
return source;
}
@Bean
public DataSourceTransactionManager transactionManager(DataSource dataSource){
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource);
}
@Bean
public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory(DataSource dataSource) throws Exception {
//1 create factory
// 1. Create the object through the factory bean. Finally, you need to call getObject() to obtain the specific object
SqlSessionFactoryBean factoryBean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
// 1.1 setting data source
factoryBean.setDataSource(dataSource);
// 1.2 set alias package scanning
factoryBean.setTypeAliasesPackage("com.czxy.sm.domain");
// 1.3 global configuration: hump mapping
org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration config = new org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration();
config.setMapUnderscoreToCamelCase(true);
factoryBean.setConfiguration(config);
// Return SqlSessionFactory
return factoryBean.getObject();
}
}
service interface
public interface UserService {
/**
*
* @param outId Output account
* @param intId
* @param money
*/
void change(Integer outId, Integer intId, float money);
}
service implementation class
@Service
@Transactional //Open transaction
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Resource
private AccountMappper mapper;
public void change(Integer outId, Integer intId, float money) {
Account intAccount = mapper.selectByPrimaryKey(intId);
intAccount.setMoney(intAccount.getMoney() + money);
mapper.updateByPrimaryKey(intAccount);
Account outAccount = mapper.selectByPrimaryKey(outId);
outAccount.setMoney(outAccount.getMoney() - money);
mapper.updateByPrimaryKey(outAccount);
}
}
javaBean
//The database table name does not account
public class Account {
@Id
private Integer id;
private Float money;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public Float getMoney() {
return money;
}
public void setMoney(Float money) {
this.money = money;
}
}
Test class
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(classes = SpringConfig.class)
public class DemoTest {
@Resource
private UserService service;
@Test
public void test01(){
service.change(1,2,100);
System.out.println("success");
}
}
After operation
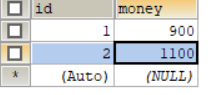
In case of error
Add an exception to the service method
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Resource
private AccountMappper mapper;
public void change(Integer outId, Integer intId, float money) {
Account intAccount = mapper.selectByPrimaryKey(intId);
intAccount.setMoney(intAccount.getMoney() + money);
mapper.updateByPrimaryKey(intAccount);
int i =1/0;
Account outAccount = mapper.selectByPrimaryKey(outId);
outAccount.setMoney(outAccount.getMoney() - money);
mapper.updateByPrimaryKey(outAccount);
}
}
After operation
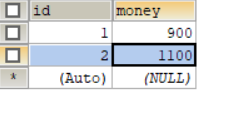
The data in the database has not changed.
2.5 summary
-
Add @ EnableTransactionManagement to the configuration class
- And add a bean of DataSourceTransactionManager
-
Add @ Transactional to the implementation class that requires transactions
-
@Parameters for Transactional
-
@Transactional( readOnly = false, //read-only timeout = -1, //overtime isolation = Isolation.DEFAULT, //Isolation level propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED) //Communication behavior
-
A bean of DataSourceTransactionManager
-
Add @ Transactional to the implementation class that requires transactions
-
@Parameters for Transactional
-
@Transactional( readOnly = false, //read-only timeout = -1, //overtime isolation = Isolation.DEFAULT, //Isolation level propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED) //Communication behavior
-