In spring webmvc, all requests start with a class called dispatcher servlet. It is the hub of request dispatch, often referred to as the front-end controller, also known as the request dispatcher.
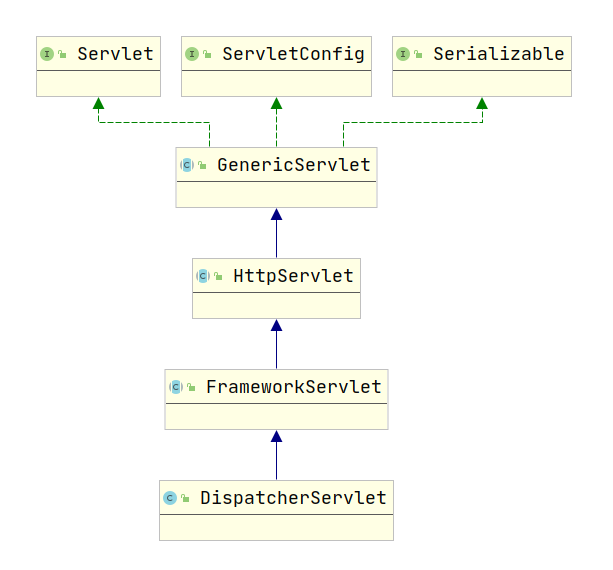
From the derived relationship, we can see that the dispatcher Servlet is also a Servlet. When we map the / path to the dsiaaptcherservlet, all requests received by the web container will be processed by it. Just like we used to use Servlet to write web, only dispatcher Servlet is a Servlet now, and it receives all requests and responds to all requests.
The main function that needs to be focused on is the doDispatch function, which, like the name, literally "do scheduling" to process requests.
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request; HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null; boolean multipartRequestParsed = false; WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request); try { ModelAndView mv = null; //Model and View after request processing Exception dispatchException = null; //Exception in request try { processedRequest = checkMultipart(request); // Check if it is a multipart request multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request); // Set identity to true if multipartRequest mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest); // Traverse the processor mapper to find the handler (including interceptors and processors) // 404 if the handler is found or not included in the handler if (mappedHandler == null || mappedHandler.getHandler() == null) { noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response); return; } // To get the adapter of the processor, you need to call the processor through the adapter. HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler()); String method = request.getMethod(); // get?post?delete boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method); if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) { long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler()); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Last-Modified value for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "] is: " + lastModified); } if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) { return; } } // Here we get the interceptor in the handler, and execute the prehandle (preprocessing). If one of the interceptor chains returns false, it will directly return // Note here that after completion will still execute when pre fails. Not if it passes. if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) { return; } // Call the processor through the adapter, which is the processing function we wrote in the controller. // You can see that in the end, no matter what we return is string, model, view or ModelAndView, it is the returned ModelAndView mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler()); if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { return; } // If mv is null or does not contain a view. Use the default view applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv); // Call the postprocessor that intercepts it mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv); } catch (Exception ex) { dispatchException = ex; } catch (Throwable err) { // As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well, // making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios. dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err); } // Handle the result of the call. Our program has finished processing here, and the rest is the view processing. processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException); } catch (Exception ex) { triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex); } catch (Throwable err) { triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err)); } finally { if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { // Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion if (mappedHandler != null) { mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response); } } else { // Clean up any resources used by a multipart request. if (multipartRequestParsed) { cleanupMultipart(processedRequest); } } } }
checkMultipart
Whether it is a multipart request, such as when the file is uploaded.
protected HttpServletRequest checkMultipart(HttpServletRequest request) throws MultipartException { // If multipartResolver is not configured and is not a multipart request, use the existing request resolver if (this.multipartResolver != null && this.multipartResolver.isMultipart(request)) { // The code here doesn't need attention } return request; }
getHandler
Get handler handlerexecutionchain, which contains the handler and interceptor corresponding to the request
private final Object handler; // Processor object private HandlerInterceptor[] interceptors; // Stop them protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { for (HandlerMapping hm : this.handlerMappings) { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace( "Testing handler map [" + hm + "] in DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'"); } HandlerExecutionChain handler = hm.getHandler(request); if (handler != null) { return handler; } } return null; }
applyPreHandle
Literally, perform preprocessing. Call the preprocessing of all interceptors in the handler. It should be noted here that when calling the preprocessor, if one of the interceptors returns false, it will interrupt the execution of the preprocessor and turn to the final processing.
boolean applyPreHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { HandlerInterceptor[] interceptors = getInterceptors(); // Get interceptor if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(interceptors)) { for (int i = 0; i < interceptors.length; i++) { HandlerInterceptor interceptor = interceptors[i]; // If one of the interceptors fails to pass when processing the PreHandle, it will be interrupted. Execute afterCompletion instead if (!interceptor.preHandle(request, response, this.handler)) { triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, null); // Execute afterCompletion return false; } this.interceptorIndex = i; } } return true; }
processDispatcherResult
After the execution of the processor, you can see the ModelAndView in the parameter. All our processing results are of the ModelAndView type.
private void processDispatchResult(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler, ModelAndView mv, Exception exception) throws Exception { boolean errorView = false; // Is there any exception if (exception != null) { if (exception instanceof ModelAndViewDefiningException) { logger.debug("ModelAndViewDefiningException encountered", exception); mv = ((ModelAndViewDefiningException) exception).getModelAndView(); } else { Object handler = (mappedHandler != null ? mappedHandler.getHandler() : null); mv = processHandlerException(request, response, handler, exception); errorView = (mv != null); } } // Render if (mv != null && !mv.wasCleared()) { // Rendering render(mv, request, response); if (errorView) { // Processing an error response attribute in the request WebUtils.clearErrorRequestAttributes(request); } } else { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Null ModelAndView returned to DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "': assuming HandlerAdapter completed request handling"); } } if (WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { // Concurrent handling started during a forward return; } if (mappedHandler != null) { // Perform the final processing of the interceptor mappedHandler.triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, null); } }
The summary process is that after the dispatcher receives the request, if it is a multipart request, it will call the configured multipart resolver (multipart resolver) to process the request. Then the handler is obtained through the handler mapping, which contains the handler and several interceptor arrays configured. After getting the processor through the handler, you need to call the handler through the processor adapter, and then return a ModelAndView. Before calling the processor through the adapter, you need to call several interceptor preprocessing in the handler. After getting ModelAndView, several interceptors are called for post-processing. After processing, prepare to learn the rendering of the View. The rendering of the View needs to be processed through the viewResolver. The logical View name in mv needs to be converted to the actual View object through the viewResolver, and then rendered and returned through the View object. After the response, you need to call the final processing of several interceptors.