We used two examples, document and Mvc, and now we use annotations to reconstruct:
document:
//Class document
@Component("document")
public interface Document {
public void read();
public void write();
}
//Management category
@Component("documentManager")
public class DocumentManager {
//Applying resource to attribute assignment
@Resource(name="wordDocument")
private Document document;
public void read(){
document.read();
}
public void write(){
document.write();
}
}
//Class excel:
@Component("excelDocument")
public class ExcelDocument implements Document {
@Override
public void read() {
System.out.println("excelRead");
}
@Override
public void write() {
System.out.println("excelWrite");
}
}
//Class pdf:
@Component("pdfDocument")
public class PDFDocument implements Document {
@Override
public void read() {
System.out.println("pdfRead");
}
@Override
public void write() {
System.out.println("pdfWrite");
}
}
//Class word:
@Component("wordDocument")
public class WordDocument implements Document {
@Override
public void read() {
System.out.println("wordRead");
}
@Override
public void write() {
System.out.println("wordWrite");
}
}
//Configuration file:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-2.5.xsd">
<!--
//Registered Scan Class
-->
<context:component-scan base-package="cn.ansel.annotation_document"></context:component-scan>
</beans>
//Test class:
public class testAnnotationDocument {
@Test
public void testAnnotationDocument(){
//Start the spring container.
ApplicationContext applicationContext=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("cn/ansel/annotation_document/applicationContext-annotation-document.xml");
//Get the object of the management class
DocumentManager documentManager=(DocumentManager) applicationContext.getBean("documentManager");
//Call the method in it
documentManager.read();
documentManager.write();
}
}
As I said in the previous post, I will not elaborate on the specific ideas.
Operation results: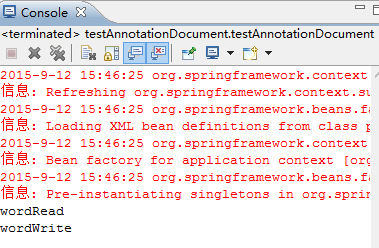
document summary:
From the above code and the configuration file, we can see that there is no getter & setter method in the class, nor does it place the class in the configuration file. spring On containers, including assigning values to attributes, we also use annotations to see that the amount of code is actually down.
Refactoring the Mvc example:
Our Mvc example is just a super simple Mvc example.
spring's annotations provide us with more detailed annotations on Mvc. You can see spring's help documentation:
So here we can apply: @Controller, @Service, @Repository.
Here is the code:
//Control layer
@Controller("studentAction")
public class StudentAction {
//Call the service layer
@Resource(name="studentServiceImpl")
private StudentService service;
public void saveStudent(){
service.saveStudent();
}
}
//Logical Business Layer Implementation Layer
@Service("studentServiceImpl")
public class StudentServiceImpl implements StudentService {
@Resource(name="studentDAOImpl")
private StudentDAO dao;
@Override
public void saveStudent() {
dao.saveStudent();
}
}
//dao layer implementation layer
@Repository("studentDAOImpl")
public class StudentDAOImpl implements StudentDAO {
@Override
public void saveStudent() {
System.out.println("save student dao");
}
}
//Configuration file:
<context:component-scan base-package="cn.ansel.annotation.mvc"></context:component-scan>
//Test class:
public class testAnnotationMVC {
@Test
public void testAnnotation_MVC(){
//Start the spring container
ApplicationContext applicationContext=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("cn/ansel/annotation/mvc/applicationContext-annotation-MVC.xml");
//Get the Control Layer Object
StudentAction action=(StudentAction) applicationContext.getBean("studentAction");
//operation
action.saveStudent();
}
}
Operation results: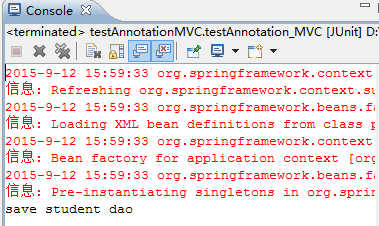
mvc summary:
It's much easier to use annotations than calling new objects from the top and putting classes into spring containers to use xml configuration files. It feels like we've done very little, but spring containers have done a lot for us.
Conclusion:
So far, five annotations have been learned:
The annotations for attribute assignment are as follows:
@Resource
@Autowired
@Qualifier
The annotation to load the class into the spring container is:
@ Component
@ Controller (Control Layer/Presentation Layer)
@ Service (Logical Business Layer)
@ Repository (persistence layer)