Dependency injection in spring
IOC role: reduce the coupling between programs (dependency)
Dependency management: to be maintained by spring (objects of other classes are needed in the current class, provided by spring, we only need to explain in the configuration file)
Dependency maintenance: dependency injection
Dependency injection:
Data that can be injected:
- Basic types and strings
- Other bean types (beans configured in configuration files or annotations)
- Complex type / set type
How to inject bean objects:
- Using constructors
- Using the set function
- Use annotations
Using constructors
Constructor entry:|
Label used: constructor- arg
Where the tag appears: inside the bean tag
Properties in Tags
Type: Specifies the data type of the data to be injected, which is also the type of one or some parameters in the constructor
Index: used to specify the data to be injected to assign a value to the parameter in the constructor that specifies the index position. Index position starts from e
Name: commonly used for parameter assignment to the specified name in the constructor
=========The three above are used to specify which parameter assignment in the constructor
value: used to provide data of basic type and String type
ref: used to specify other bean type data. It refers to the core containers of Ioc in spring
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="accountService" class="com.ay.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl"> <constructor-arg name="name" value="Flying"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg name="age" value="20"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg name="birthday" ref="now"></constructor-arg> </bean> <bean id="now" class="java.util.Date" ></bean> </beans>
package com.ay.service; public interface AccountService { public void saveAccount(); }
package com.ay.service.impl; import com.ay.service.AccountService; import java.util.Date; public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService { private String name; private Integer age; private Date birthday; @Override public void saveAccount() { System.out.println("Method created successfully"); } public AccountServiceImpl(String name, Integer age, Date birthday) { this.name = name; this.age = age; this.birthday = birthday; } @Override public String toString() { return "AccountServiceImpl{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + ", birthday=" + birthday + '}'; } }
package com.ay.ui; import com.ay.service.AccountService; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class Client { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml"); AccountService as = (AccountService)ac.getBean("accountService"); as.saveAccount(); System.out.println(as.toString()); } }
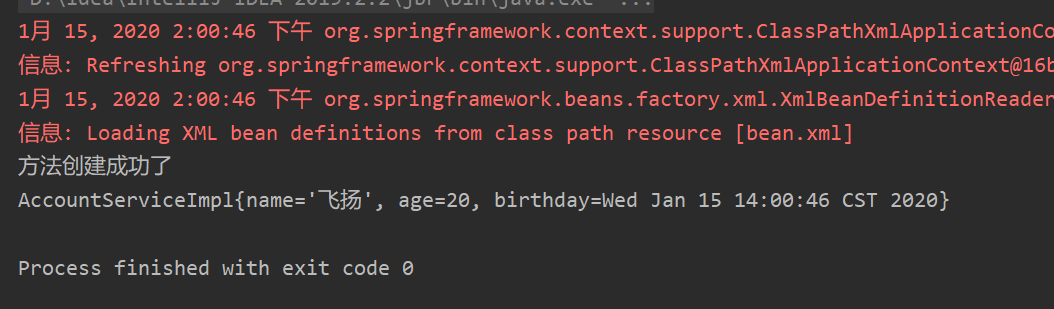
Conclusion:
Advantage: when getting the bean object, injecting data is a necessary operation, otherwise the object cannot be created successfully.
Disadvantage: it changes the instantiation method of bean objects, so that when we create objects, if we can't use these data, we must also provide them.
Using the set function
Tags involved: property
Where it appears: inside the bean tag
Properties of the label
Name: used to specify the set method name called in
value: used to provide data of basic type and String type
ref: used to specify other bean type data. It refers to the bean objects that have appeared in the Ioc core container of spring
package com.ay.service; public interface AccountService { public void saveAccount(); }
package com.ay.service.impl; import com.ay.service.AccountService; import java.util.Date; public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService { private String name; private Integer age; private Date birthday; @Override public void saveAccount() { System.out.println("Method created successfully"); } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } public void setBirthday(Date birthday) { this.birthday = birthday; } @Override public String toString() { return "AccountServiceImpl{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + ", birthday=" + birthday + '}'; } }
package com.ay.ui; import com.ay.service.AccountService; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class Client { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml"); AccountService as = (AccountService)ac.getBean("accountService"); as.saveAccount(); System.out.println(as.toString()); } }
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="accountService" class="com.ay.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl"> <property name="name" value="Flying"></property> <property name="age" value="20"></property> <property name="birthday" ref="now"></property> </bean> <bean id="now" class="java.util.Date" ></bean> </beans>
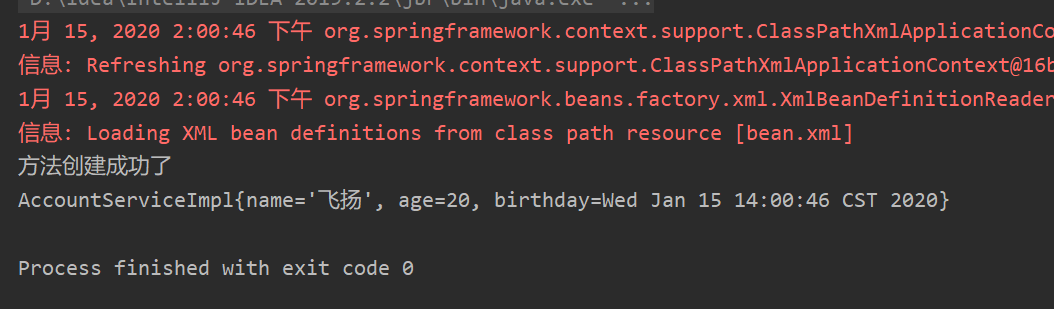
Conclusion:
Advantage: there is no explicit restriction when creating objects, and you can directly use the default constructor
Disadvantage: if a member must have a value, it is possible that the set method is not executed.

