1. Introduction to spring cloud
Spring cloud provides developers with tools to quickly build distributed systems, including configuration management, service discovery, circuit breakers, routing, micro-agents, event bus, global locks, decision campaigns, distributed sessions, and so on.It runs in a simple environment and can run on a developer's computer.Additionally, spring cloud is based on springboot, so you need to know something about springboot in development. If you don't, you can read this article: Learn springboot in 2 hours .In addition, if you are not familiar with the "Micro Service Architecture", you can learn about it through search engine search for "Micro Service Architecture".
2. Creating a Service Registration Center
Here, on the components we need to use, Spring Cloud Netflix's Eureka, Eureka is a service registration and discovery module.
2.1 First create a maven master project.
2.2 Then create two model projects: one as the service registry, Eureka Server, and the other as the Eureka Client.
The following is an example of creating a server to illustrate the creation process in detail:
Right-click Project - > Create Model - > Select spring initialir as follows:

Next - > Select cloud discovery - > Eureka server, and then proceed to the next step.

The pom.xml file for the created project is as follows:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.1.8.RELEASE</version> <relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository --> </parent> <groupId>com.free</groupId> <artifactId>eurekaserver</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <name>eurekaserver</name> <description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description> <properties> <java.version>1.8</java.version> <spring-cloud.version>Greenwich.SR3</spring-cloud.version> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-server</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> <dependencyManagement> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId> <version>${spring-cloud.version}</version> <type>pom</type> <scope>import</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> </dependencyManagement> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project>
2.3 Starting a service registry requires only a comment @EnableEurekaServer, which needs to be added to the startup application class of the springboot project:
package com.free.eurekaserver; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.server.EnableEurekaServer; @EnableEurekaServer @SpringBootApplication public class EurekaserverApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(EurekaserverApplication.class, args); } }
**2.4 **eureka is a highly available component that does not have a backend cache, and after each instance is registered it needs to send a heartbeat to the registry (so it can be done in memory), and by default erureka server is also a eureka client, and a server must be specified.The configuration file appication.yml for eureka server:
server: port: 8761 eureka: instance: hostname: localhost client: registerWithEureka: false fetchRegistry: false serviceUrl: defaultZone: http://${eureka.instance.hostname}:${server.port}/eureka/
Indicate yourself as a eureka server by eureka.client.registerWithEureka:false and fetchRegistry:false.
2.5 Ereka server has an interface, start the project, open the browser access: http://localhost:8761, the interface is as follows:
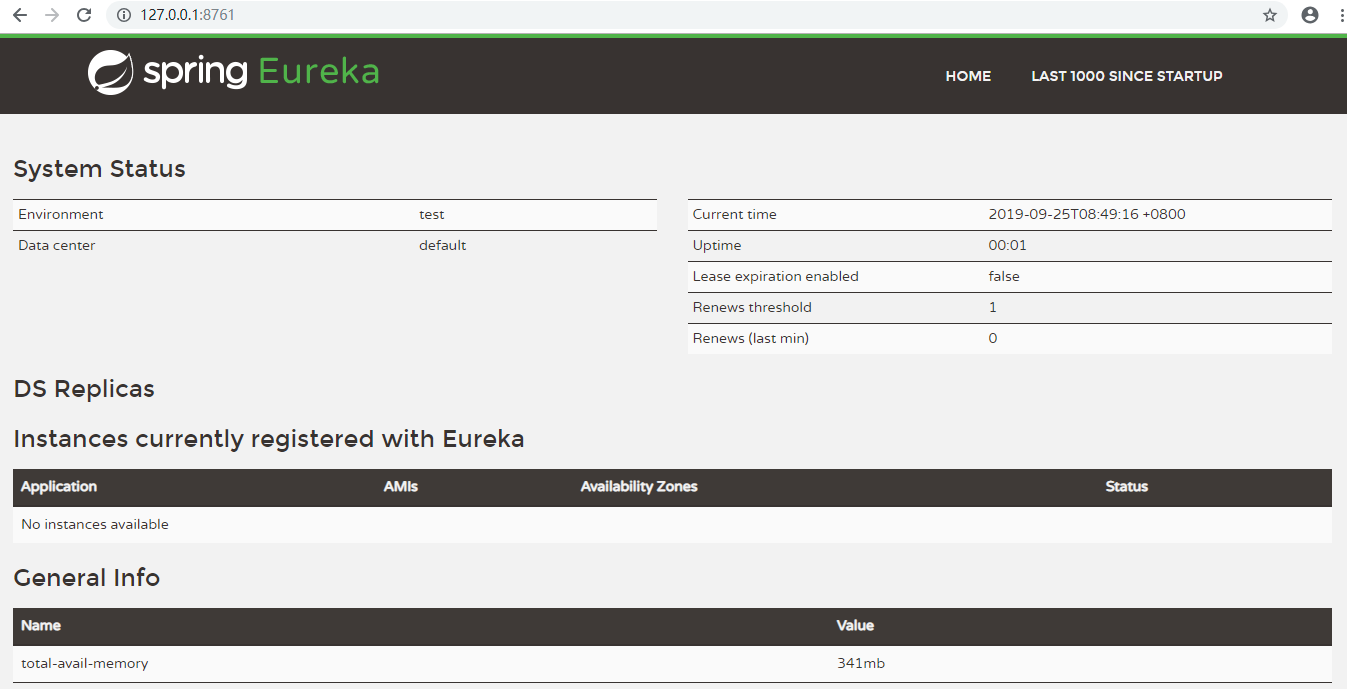
No application available No service found...^^ Because of the fact that no service can be discovered without a registered service.
3. Create a service provider (eureka client)
When a client registers with a server, it provides some metadata, such as host and port, URL, home page, and so on.Eureka server receives a heartbeat message from each client instance.If the heartbeat times out, the instance is usually removed from the registered server.
The creation process is similar to that of a server, where the pom.xml is created as follows:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.1.8.RELEASE</version> <relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository --> </parent> <groupId>com.free</groupId> <artifactId>eurekaserver</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <name>eurekaserver</name> <description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description> <properties> <java.version>1.8</java.version> <spring-cloud.version>Greenwich.SR3</spring-cloud.version> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-server</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> <dependencyManagement> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId> <version>${spring-cloud.version}</version> <type>pom</type> <scope>import</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> </dependencyManagement> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project>
Indicate yourself as a eurekaclient by commenting @EnableEurekaClient.
package com.free.servicehi; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EnableEurekaClient; @EnableEurekaClient @SpringBootApplication public class ServiceHiApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(ServiceHiApplication.class, args); } }
package com.free.servicehi.web; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; /** * @program: SpringCloudDemo * @description: * @author: Mr.Zhou * @create: 2019-09-25 08:2019:26 **/ @RestController public class HelloController { @Value("${server.port}") String port; @RequestMapping("/hi") public String home(@RequestParam String name) { return "hi "+name+",i am from port:" +port; } }
It is not enough to just @EnableEurekaClient. You also need to specify the address of your service registry in the configuration file, which is as follows:
server: port: 8762 spring: application: name: service-hi eureka: client: serviceUrl: defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka/
It is important to specify spring.application.name, which is the basis for subsequent calls between services.Start the project and open http://localhost:8761, the address of eureka server:
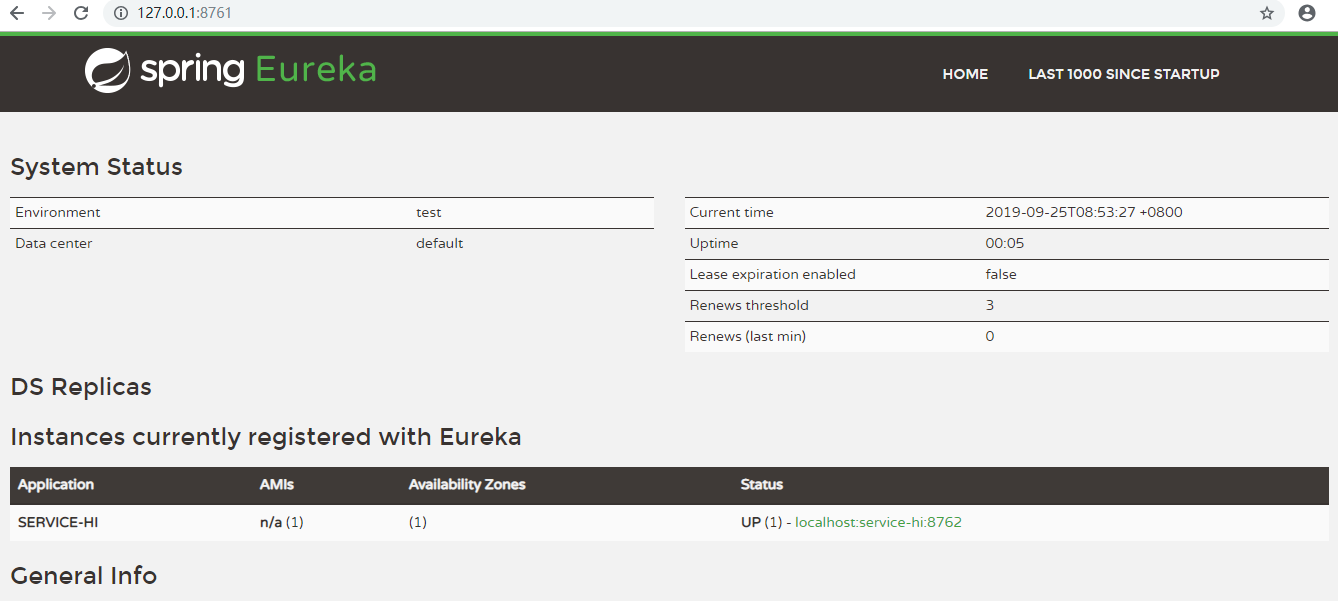
You will find a service registered with the service, named SERVICE-HI, with port 7862
Open http://localhost:8762/hi?name=zz and you will see:
hi zz,i am from port:8762
Source download: https://github.com/forezp/SpringCloudLearning/tree/master/chapter1
4. References
Official document for springcloud eureka server
Official document for springcloud eureka client
Good articles recommend:
-
[The simplest SpringCloud tutorial ever Final Chapter] (http://blog.csdn.net/forezp/article/details/70148833) -
[The simplest SpringCloud tutorial ever Article 1: Registration and Discovery of Services (Eureka)] (http://blog.csdn.net/forezp/article/details/696915) -
[The simplest SpringCloud tutorial ever Article 7: Highly Available Distributed Config (http://blog.csdn.net/forezp/article/details/70037513)