1, Overview
1.1 process

1.2 architecture
-
Eureka
-
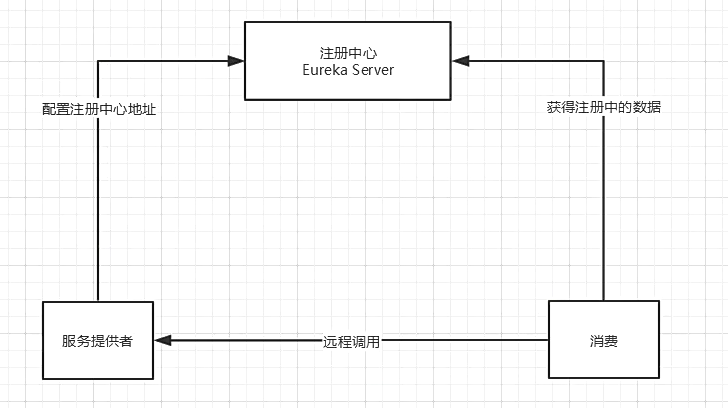
Spring cloud encapsulates the eureka module developed by netfix company to realize service registration and discovery
-
The C-S architecture design is adopted, and EurakaServer is used as the service registry
-
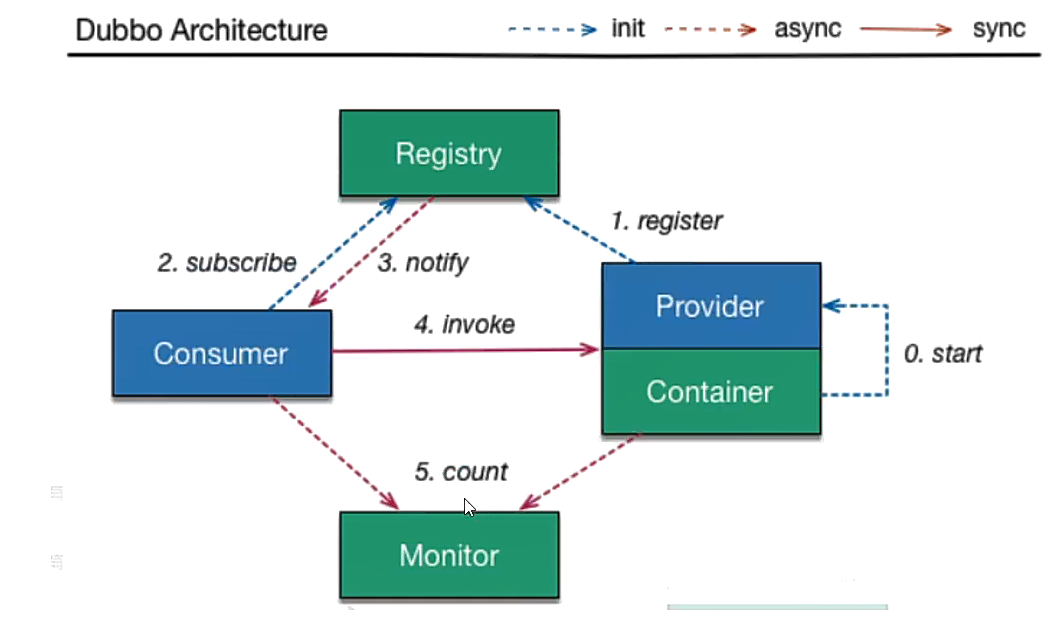
Other services in the system use the client to connect to EurakaServer and maintain heartbeat connection. Other modules in spring, such as Zuul, can find other micro services in the system and compare with Dubbo architecture through EurakaServer
-
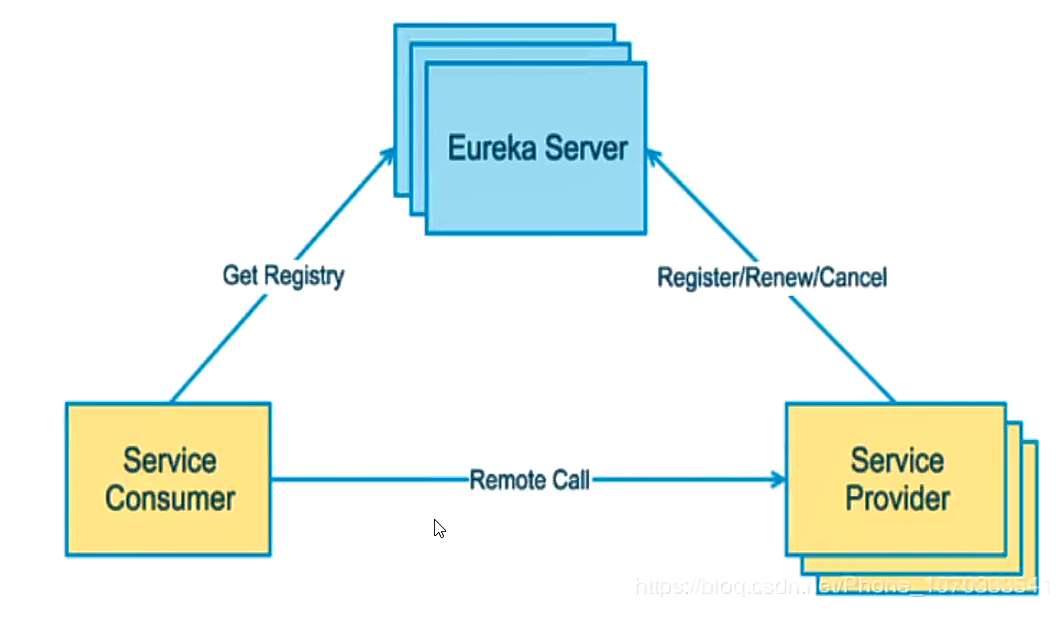
- Eureka consists of two components: Eureka server and Eureka Clinet
- EurakaServer is responsible for registering the service. After each node is started, it will register. The service registry will store the information of all available service nodes. The information of service nodes can be seen intuitively in the interface
- Eureka Clinet is a java client, which is used to simplify the operation of Eureka Server. At the same time, the client has built-in load balancer for polling load algorithm. After startup, it will send heartbeat to the server 30 seconds. If the server does not receive the heartbeat of a node within multiple heartbeat cycles, the server will remove the node from the registry. The default cycle is 90 seconds
- Three roles
- Eureka Server: the server that provides services is registered at discovery
- Service Provider: registers itself in the service so that consumers can call
- Service consumer: the service consumer obtains the service registration service list from Eureka to find the consumer service
2, Step 1: create Eureka

2.1 create springcloud-eureka-7001
2.1.1 step 1: import dependency
<!--Guide Package~-->
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-eureka-server</artifactId>
<version>1.4.7.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!--Hot deployment tool-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
2.1.2 step 2: Configuration
2.1.2.1 application.yml
server:
port: 7001
servlet:
context-path: /eureka
#Eureka configuration
eureka:
instance:
hostname: localhost # Name of Eureka server instance
client:
register-with-eureka: false # Indicates whether to register yourself with the Eureka registry
fetch-registry: false #If false, you are the registry
service-url: # Monitoring page address
defaultZone: http://${eureka.instance.hostname}:${server.port}/eureka/
2.1.2.2 main configuration class
Finally, add the annotation @ EnableEurekaServer //EnableEurekaServer server startup class on the main startup class, which can accept others to register~
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaServer //EnableEurekaServer represents the startup class of the server, which can receive others to register
public class EurekaServer_7001 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ConfigEurekaServer_7001.class, args);
}
}
Access after startup http://localhost:7001/
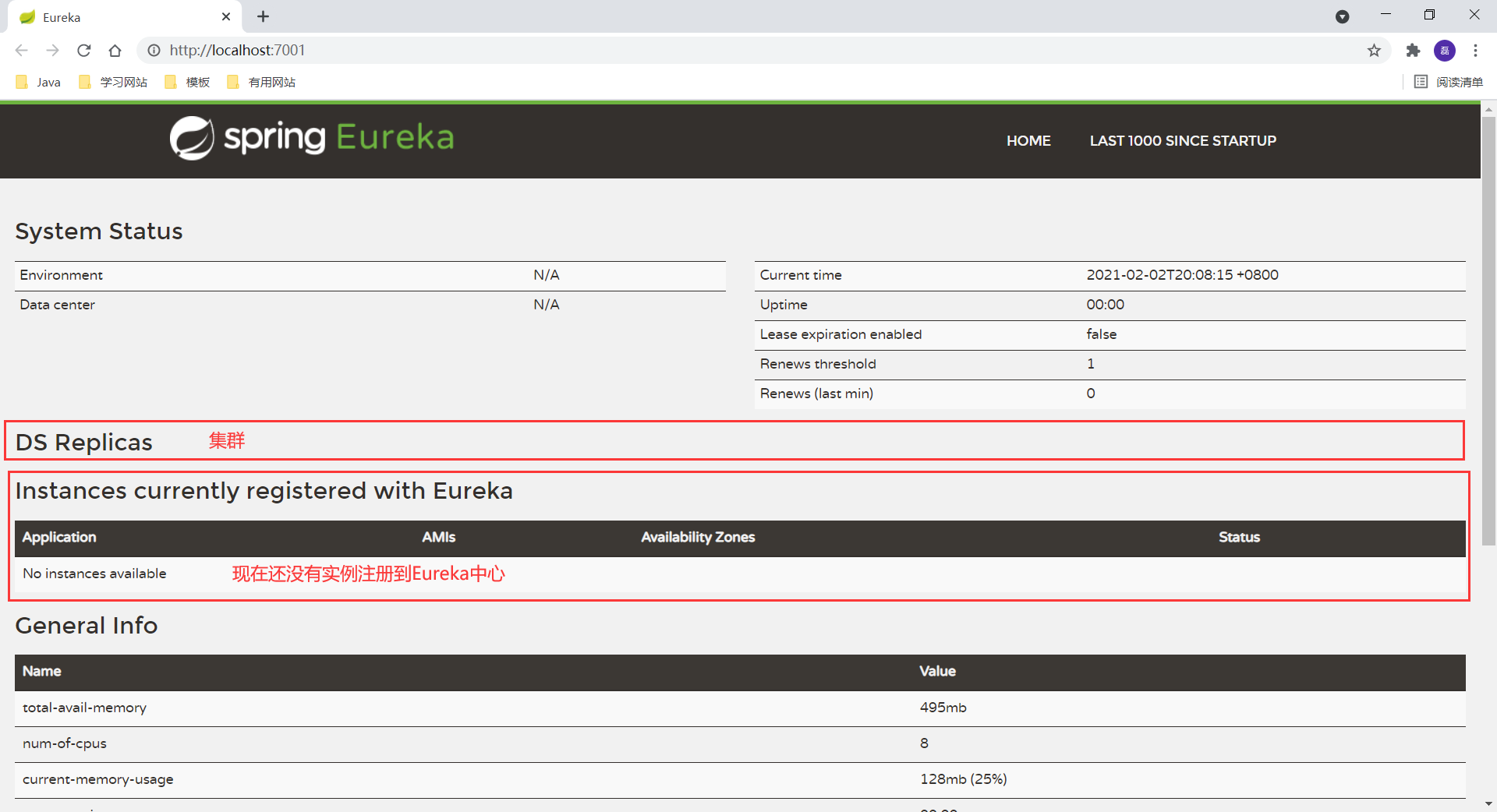
2.2 Eureka's self-protection mechanism


3, Step 2: let the service provider register with Eureka
3.1 step 1: import dependency
springcloud-provider-dept-8001
First, you must import the corresponding dependencies
<!--Eureka-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-eureka</artifactId>
<version>1.4.7.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
3.2 step 2: Configuration
Then add the corresponding Eureka registration configuration in the configuration file
application.yml
#The configuration of eureka, where is the service registered
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:7001/eureka/
Add annotation on the configuration main startup class
@EnableEurekaClient / / automatically register with Eureka after the service is started
Step 3: start
Start springcloud-config-eureka-7001, and then start the following services
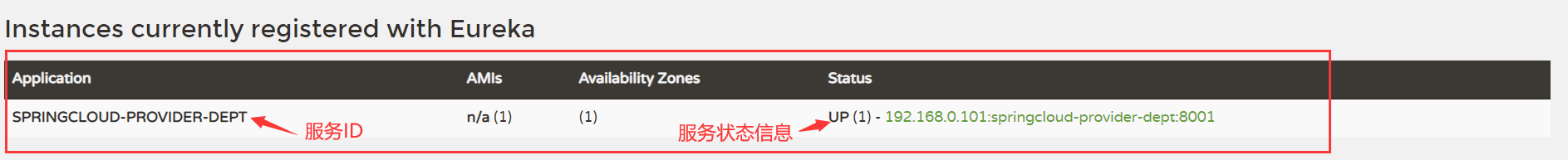
Start springcloud-provider-dept-8001 and visit again later http://localhost:7001/
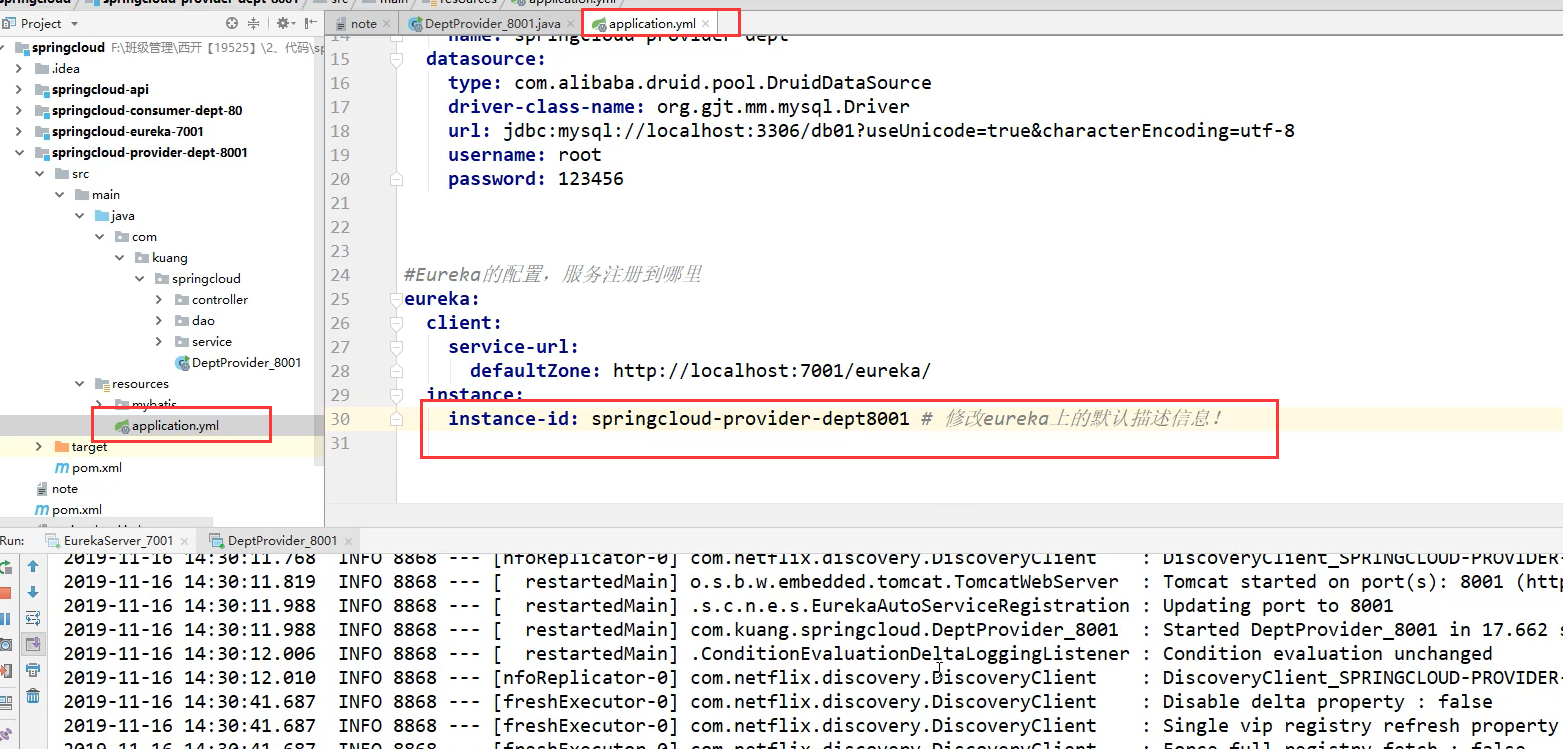
Modify default description information
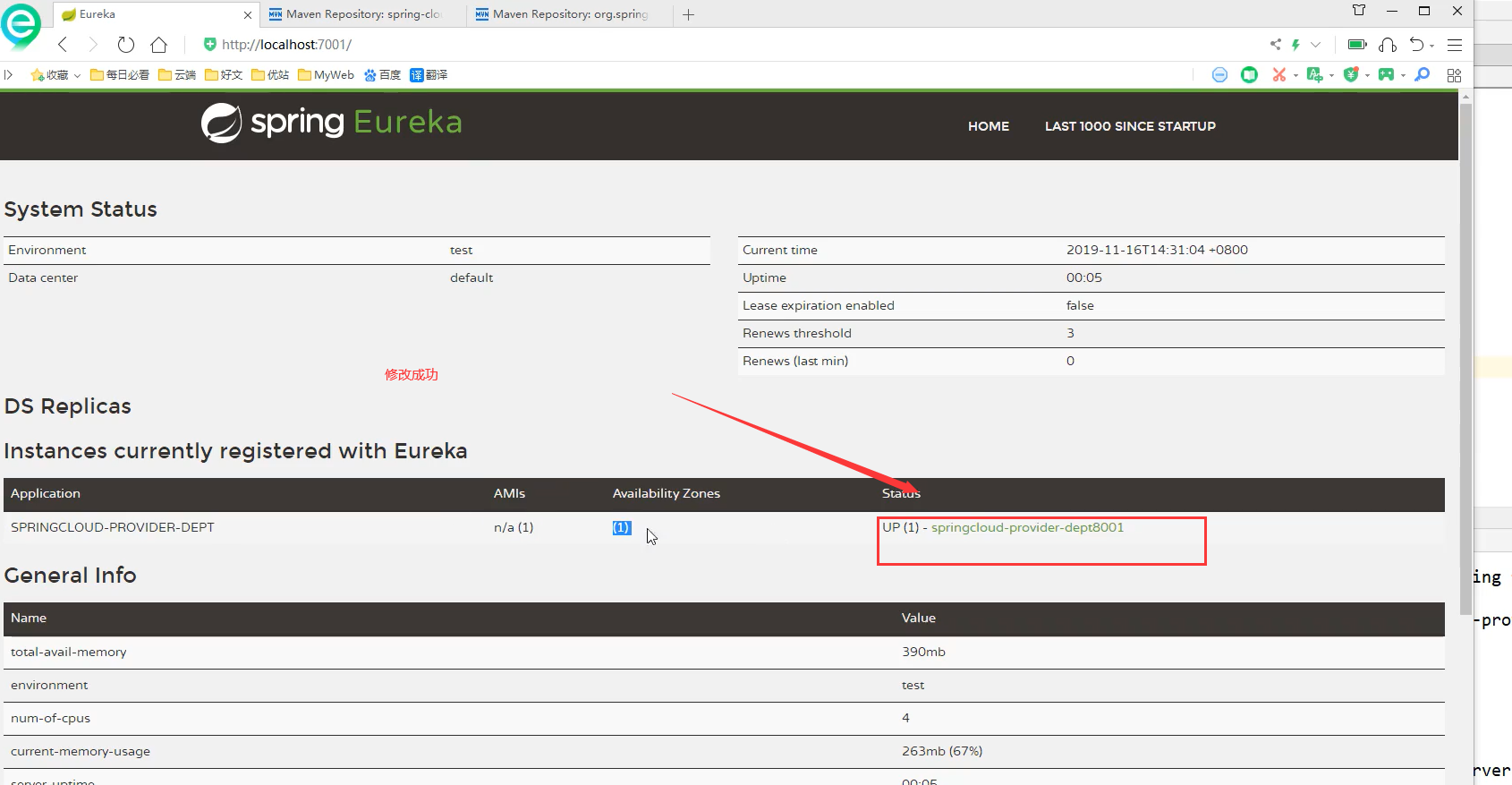
But when you click on the service status information, you will jump to a page
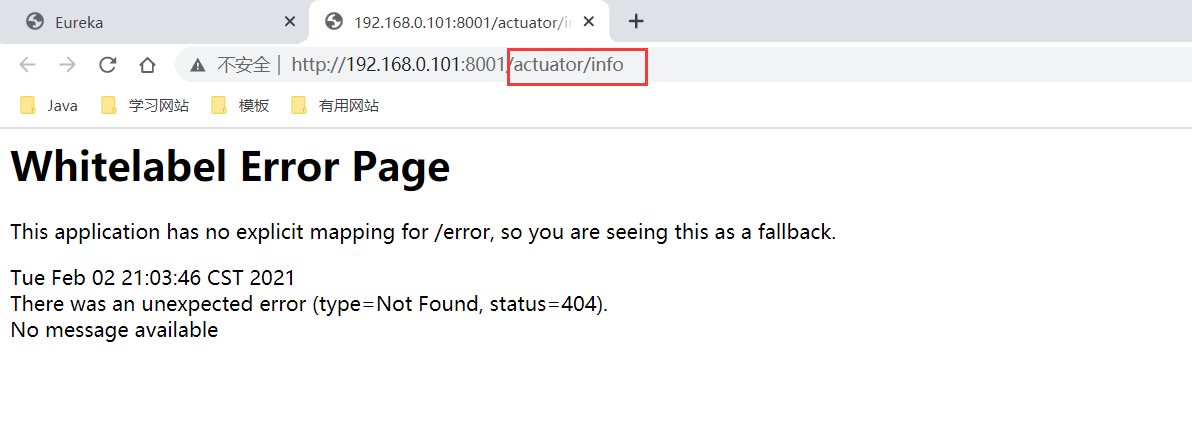
Step 4: configure the actor to improve the monitoring information
Step 1: import dependencies
<!--actuator Improve monitoring information-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
Step 2: configure yml
#The configuration of eureka, where is the service registered
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:7001/eureka/
instance:
instance-id: springcloud-provider-dept8001 #Modify the default state name on Eureka
#info configuration (click the status information to return something, which can be Baidu)
info:
app.name: name
company.name: corporate name
Step 3: Information
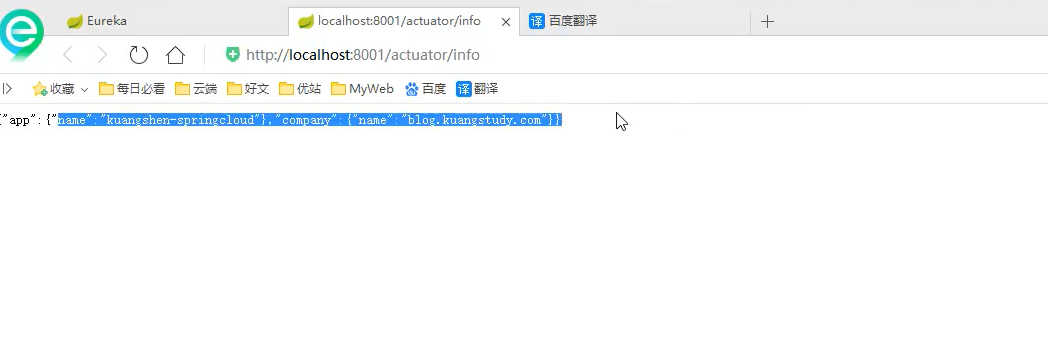
Step 5: expose your services
Step 1: add in the controller of 8001 project
import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.DiscoveryClient;
//Get some configuration information and get some specific micro services
@Autowired
private DiscoveryClient client;
//Register the micro Service ~, and get some information
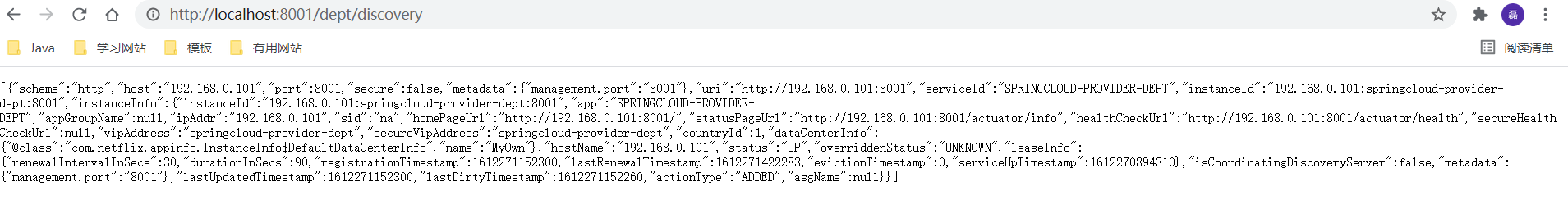
@GetMapping("/dept/discovery")
public Object discovery() {
//Get the list of micro services
List<String> services = client.getServices();
System.out.println("discovery=>services:" + services);
//Get a specific microservice information through the specific microservice ID applicationName
List<ServiceInstance> instances = client.getInstances("SPRINGCLOUD-PROVIDER-DEPT");
for (ServiceInstance instance : instances) {
System.out.println(
instance.getHost() + "\t" +
instance.getPort() + "\t" +
instance.getUri() + "\t" +
instance.getServiceId()
);
}
return instances;
}
Step 2: configure annotations
Then add the service discovery annotation on the main startup class of 8001 project I tried this annotation. You can access the above interface and return information without adding it @EnableDiscoveryClient //Service discovery
Step 3: restart access
Restart 8001 project and access http://localhost:8001/dept/discovery