Gateway introduction
What is it?
There is a very important component in the Spring Cloud family bucket: gateway. In the 1.x version, Zuul gateway is used, but in the 2.x version, Spring Cloud has developed a set of gateway components: Spring Cloud Gateway because Zuul's upgrade keeps skipping tickets.
Based on Spring Boot 2.x, Spring WebFlux and Project Reactor, Spring Cloud Gateway uses the reactor Netty responsive programming component in Webflux, and the underlying layer uses the Netty communication framework.
See: Official website
What can I do?
Reverse proxy
authentication
flow control
Fuse
Log monitoring
......
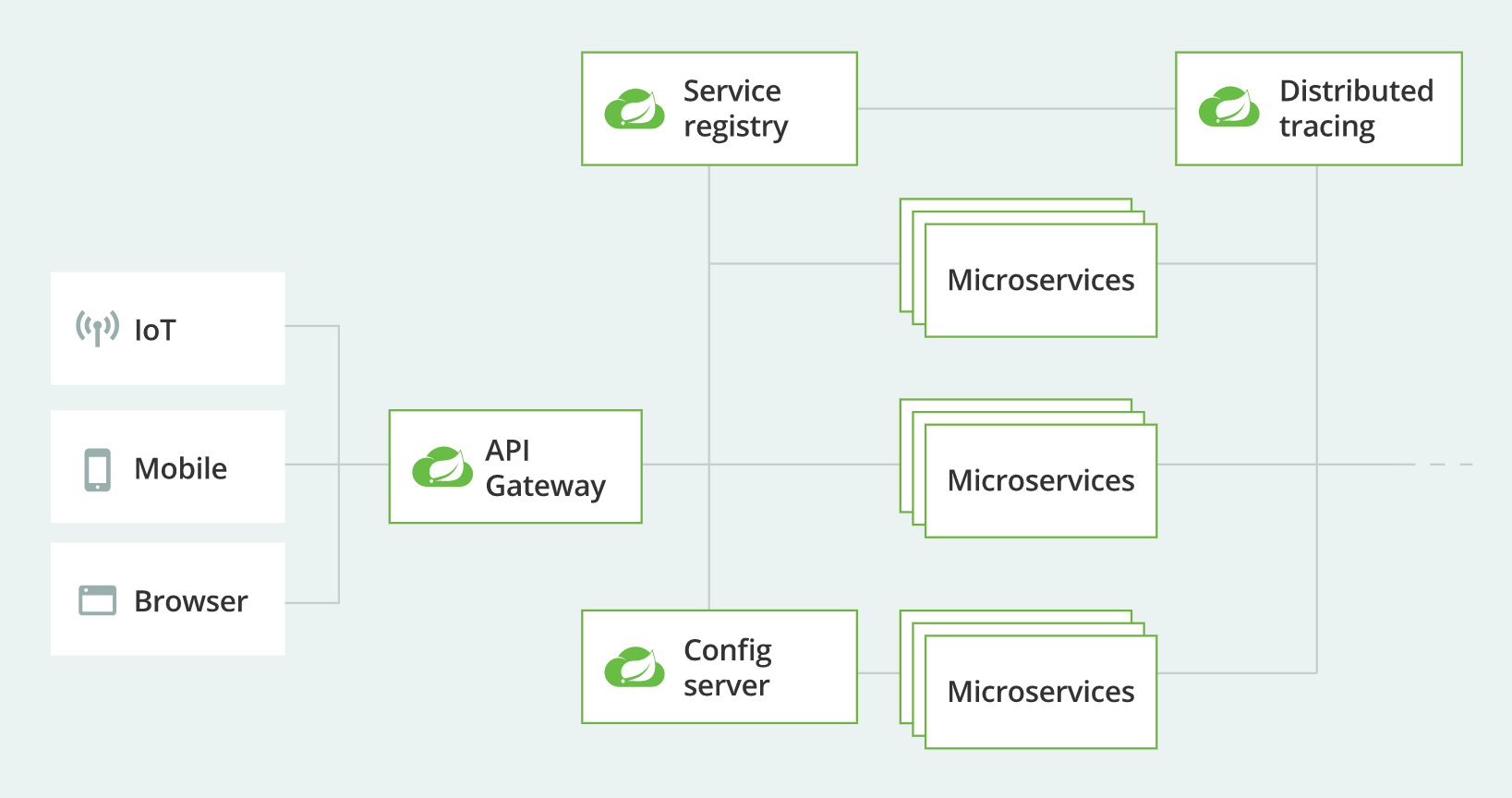
The location of gateway in microservice architecture
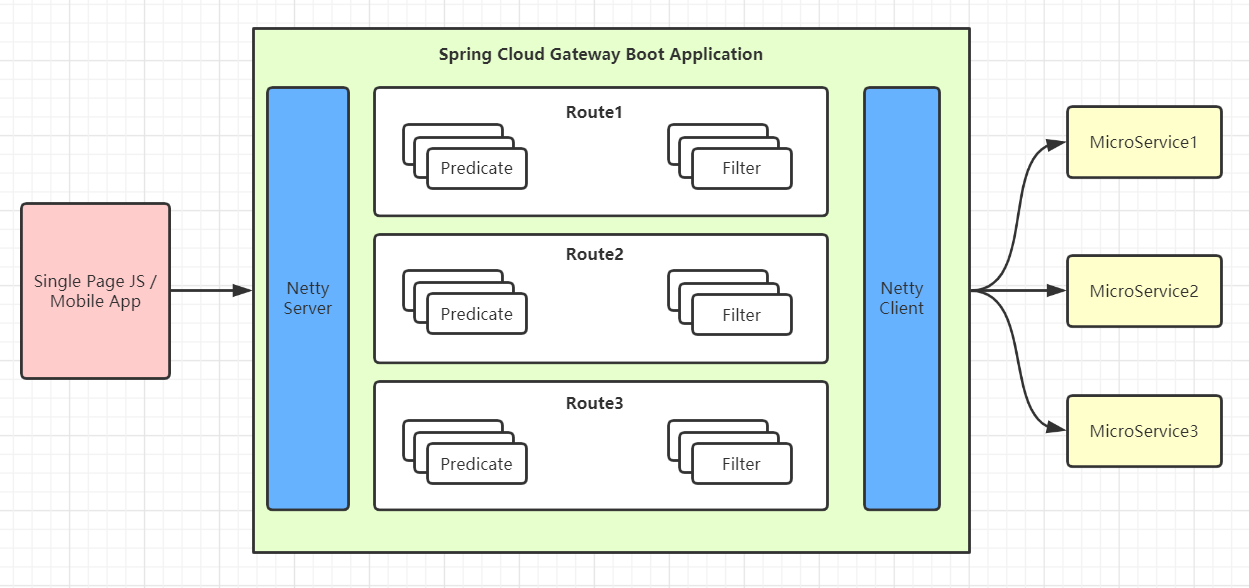
Three concepts of Gateway
Route: route is the basic module of building gateway. It consists of ID, target URI, a series of assertions and filters. If the assertion is true, the route will be matched
Predicate: refer to java.util.function.Predicate in Java 8. Developers can match everything in an HTTP request (such as a request header or a request parameter) and route if the request matches an assertion
Filter: refers to the instance of GatewayFilter in the Spring framework. Using the filter, you can modify the request before or after it is routed
Workflow
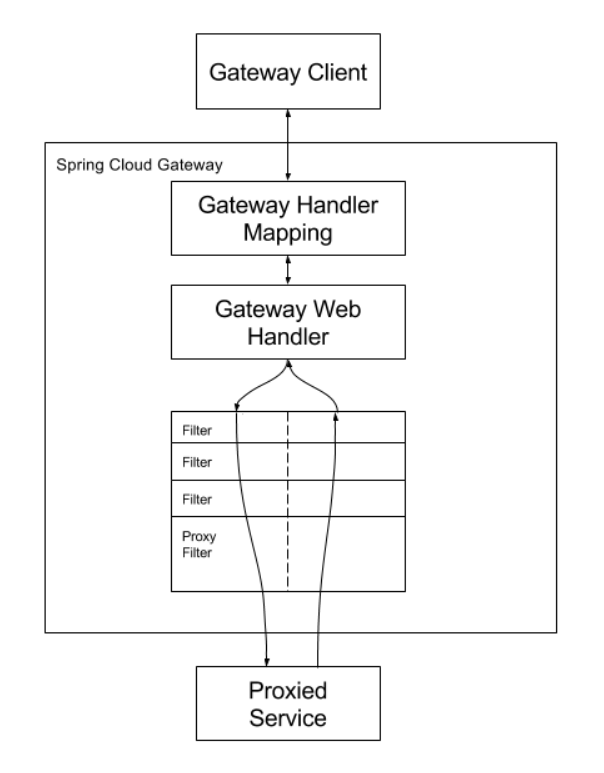
Clients make requests to Spring Cloud Gateway. If the Gateway Handler Mapping determines that a request matches a route, it is sent to the Gateway Web Handler. This handler runs the request through a filter chain that is specific to the request. The reason the filters are divided by the dotted line is that filters can run logic both before and after the proxy request is sent. All "pre" filter logic is executed. Then the proxy request is made. After the proxy request is made, the "post" filter logic is run.
The client sends a request to the Spring Cloud Gateway. If the gateway handler mapping determines that the request matches the route, it is sent to the gateway Web handler. The handler runs the request through a request specific filter chain. The reason filters are separated by dashed lines is that they can run logic before and after sending proxy requests. All "pre" filter logic is executed, and then a proxy request is issued. After the proxy request is issued, the "post" filter logic will run.
Summary: route forwarding + execution filter chain
Two configurations
Profile mode
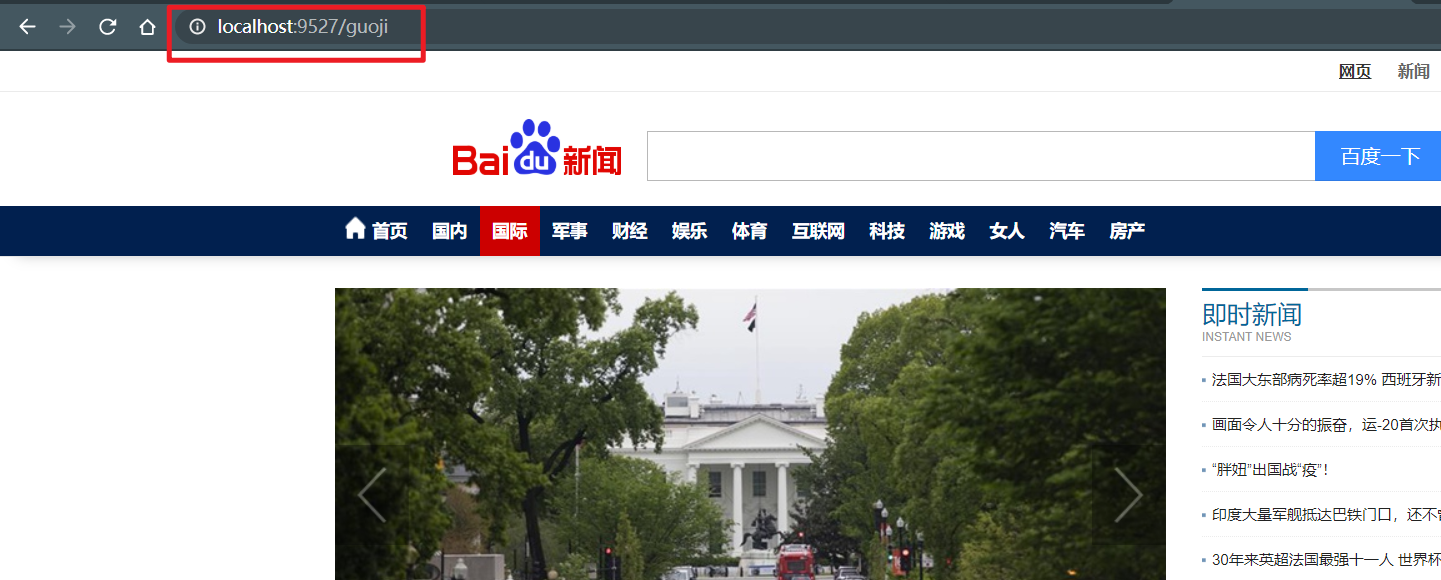
Take Baidu news for example, add the following configuration
server: port: 9527 spring: application: name: cloud-gateway9527 cloud: gateway: routes: - id: news # Routing id uri: http://news.baidu.com ා real call address predicates: - Path=/guonei # Assertion, routing according to rules
Although the browser enters localhost: 9527 / GUI, it will forward it to the specified address

Coding method
New profile
@Configuration public class GatewayConfig { @Bean public RouteLocator routes(RouteLocatorBuilder builder) { return builder.routes() .route("news2", r -> r.path("/guoji").uri("http://news.baidu.com")) .build(); } }
effect:
Dynamic routing
When enabled, by default, the Gateway will create a dynamic route based on the service list registered by the registry and the path of the microservice name on the registry, so as to realize the function of dynamic route
spring: cloud: gateway: discovery: locator: enabled: true #Enable the function of dynamically creating routes from the registry, and use the microservice name to route routes: - id: payment_routh1 #uri: http://localhost:8001 ා static, address is written dead, only one service can be called uri: lb://Group-payment-service ා dynamic, lb: / / microservice name predicates: - Path=/payment/get/** - id: payment_routh2 #uri: http://localhost:8001 uri: lb://CLOUD-PAYMENT-SERVICE predicates: - Path=/payment/lb/**
Use of Predicate
Time related configuration
After: route after the specified time
Before: route before the specified time
Between: route between specified times
predicates: - Path=/payment/lb/** #- After=2020-04-25T16:30:58.215+08:00[Asia/Shanghai] #- Before=2020-04-25T16:40:58.215+08:00[Asia/Shanghai] - Between=2020-04-25T16:35:58.215+08:00[Asia/Shanghai],2020-04-25T16:40:58.215+08:00[Asia/Shanghai]
The time format of the above configuration can be obtained through the following code
@Test public void test(){ ZonedDateTime now = ZonedDateTime.now(); System.out.println(now); }
Request related configuration
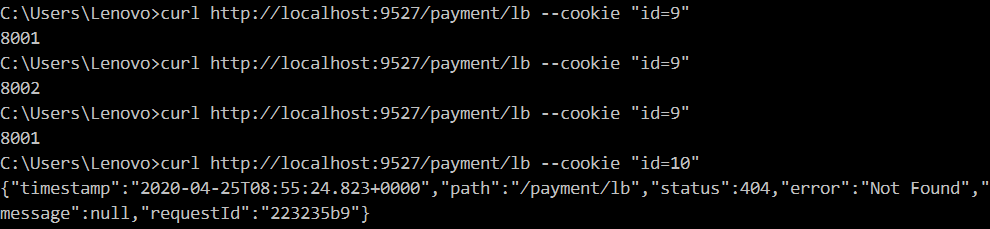
Cookie
Configuration Description: [Cookie=cookie name, regular expression rule of cookie value]
predicates: - Path=/payment/lb/** - Cookie=id, [0-9]
Using curl tool to simulate sending requests with cookie s
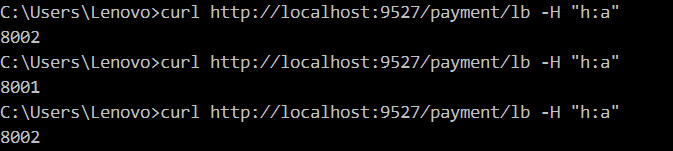
Header
Configuration Description: [Header=header name, regular expression rule of header value]
predicates: - Path=/payment/lb/** - Header=h, [a-h]
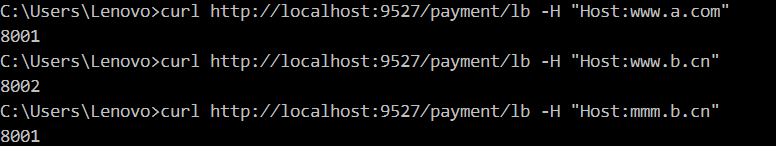
Host
Configuration Description: [Host = Host name (multiple can be configured or wildcard can be used)]
predicates: - Path=/payment/lb/** - Host=**.a.com,**.b.cn
Method
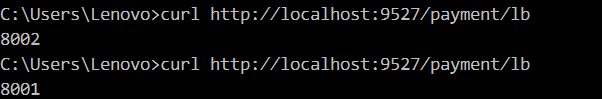
Configuration Description: [Method = request type]
predicates: - Path=/payment/lb/** - Method=GET
Path
Configuration Description: [Path = request Path]
predicates: - Path=/payment/lb/**

Query
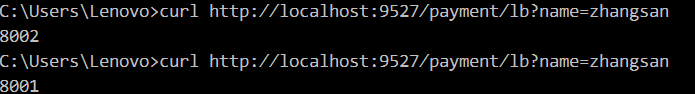
Configuration Description: [Query = parameter name, parameter value]
predicates: - Path=/payment/lb/** - Query=name, zhangsan
See: Official website
Use of Filter
- Life cycle: pre, post
- Category: GatewayFilter, GlobalFilter
GatewayFilter has dozens of official documents! For detailed configuration, please refer to Official website , which mainly introduces the custom global filter.
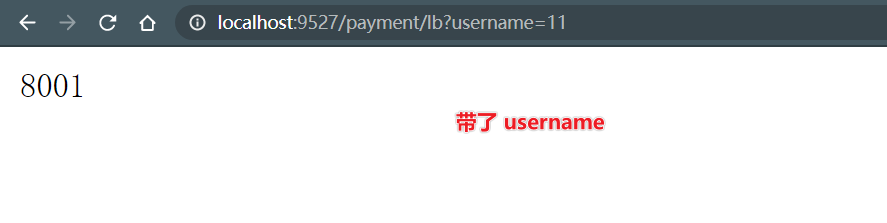
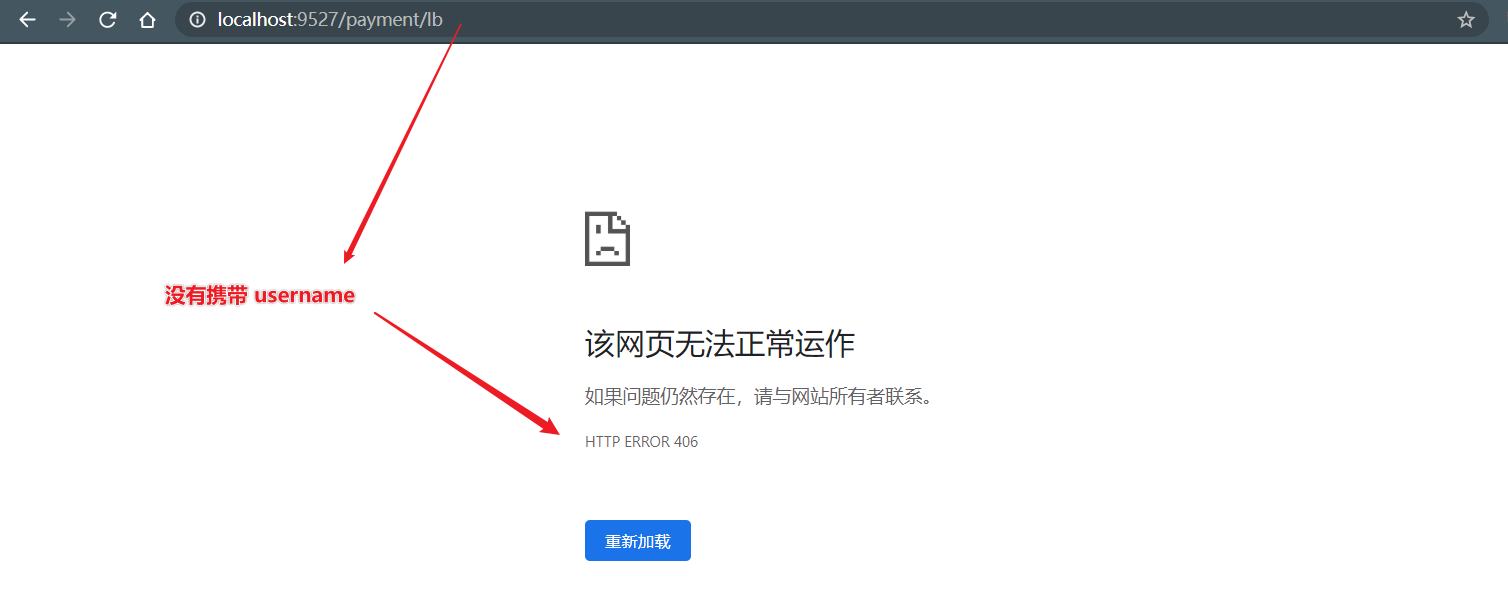
@Component @Slf4j public class MyGlobalFilter implements GlobalFilter, Ordered { @Override public Mono<Void> filter(ServerWebExchange exchange, GatewayFilterChain chain) { String username = exchange.getRequest().getQueryParams().getFirst("username"); //Error response when user name is empty if (username == null) { log.info("User name is empty, illegal login"); exchange.getResponse().setStatusCode(HttpStatus.NOT_ACCEPTABLE); return exchange.getResponse().setComplete(); } return chain.filter(exchange); } @Override public int getOrder() { return 0; } }