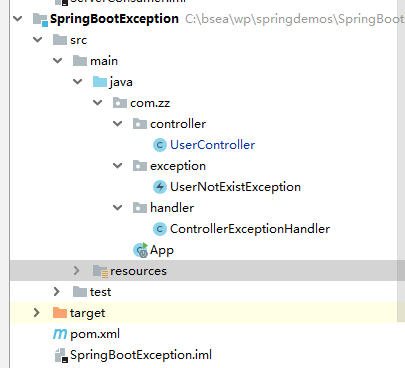
Code structure
Configure pom file
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>bsea</groupId>
<artifactId>SpringBootException</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>1.5.14.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
Startup class
package com.zz;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(App.class,args);
}
}
Custom exception class
package com.zz.exception;
public class UserNotExistException extends RuntimeException{
private static final long serialVersionUID = -1574716826948451793L;
private String id;
public UserNotExistException(String id){
super("user not exist");
this.id = id;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
}
Unified processing class
1. Add @ ControllerAdvice on the class to indicate the global exception handling class
2. Add @ ExceptionHandler(UserNotExistException.class) on the top of the method to indicate catch to this exception type, and handle it in the method. Different exceptions can be handled by different methods. Each method uses the exception class in the annotation bracket to set the exception type to be handled.
package com.zz.handler;
import com.zz.exception.UserNotExistException;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@ControllerAdvice
public class ControllerExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(UserNotExistException.class)
@ResponseBody
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR)
public Map<String, Object> handleUserNotExistsException(UserNotExistException e) {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("id", e.getId());
map.put("message", e.getMessage());
return map;
}
}
controller class
package com.zz.controller;
import com.zz.exception.UserNotExistException;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("user")
public class UserController {
@GetMapping("/{id:\\d+}")
public void get(@PathVariable String id) {
throw new UserNotExistException(id);
}
@GetMapping("error2")
public void get2() {
int a=1/0;
}
}
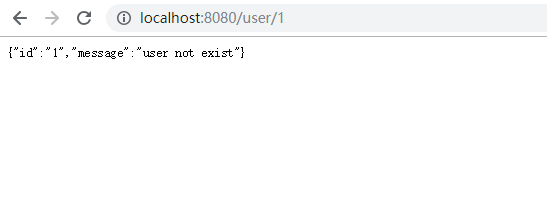
#Operation results