Next, we will show how spring boot integrates filters in two ways.
Mode 1: implement through @ WebFilter annotation
import org.slf4j.Logger; import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import javax.servlet.*; import javax.servlet.annotation.WebFilter; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import java.io.IOException; /** * @author wusy * Company: xxxxxx Technology Co., Ltd * Createtime : 2020/3/10 10:56 * Description : Custom filter */ @Component @WebFilter(urlPatterns = "/*", filterName = "CustomFilter") @Order(1) public class CustomFilter implements Filter { private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(CustomFilter.class); /** * Address to ignore */ private static String[] ignores = new String[]{ }; @Override public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException { HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) servletRequest; HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) servletResponse; //Determine whether the url needs to be blocked if (this.ignoring(request.getRequestURI())) { chain.doFilter(request, response); return; } logger.info("This is a custom interceptor"); chain.doFilter(request, response); } /** * Determine whether the url needs to be blocked * @param uri * @return */ private boolean ignoring(String uri) { for (String string : ignores) { if (uri.contains(string)) { return true; } } return false; } }
Next, we launch the project and enter http://127.0.0.1:8787/swagger-ui.html (last article introduced how to integrate swagger), observations
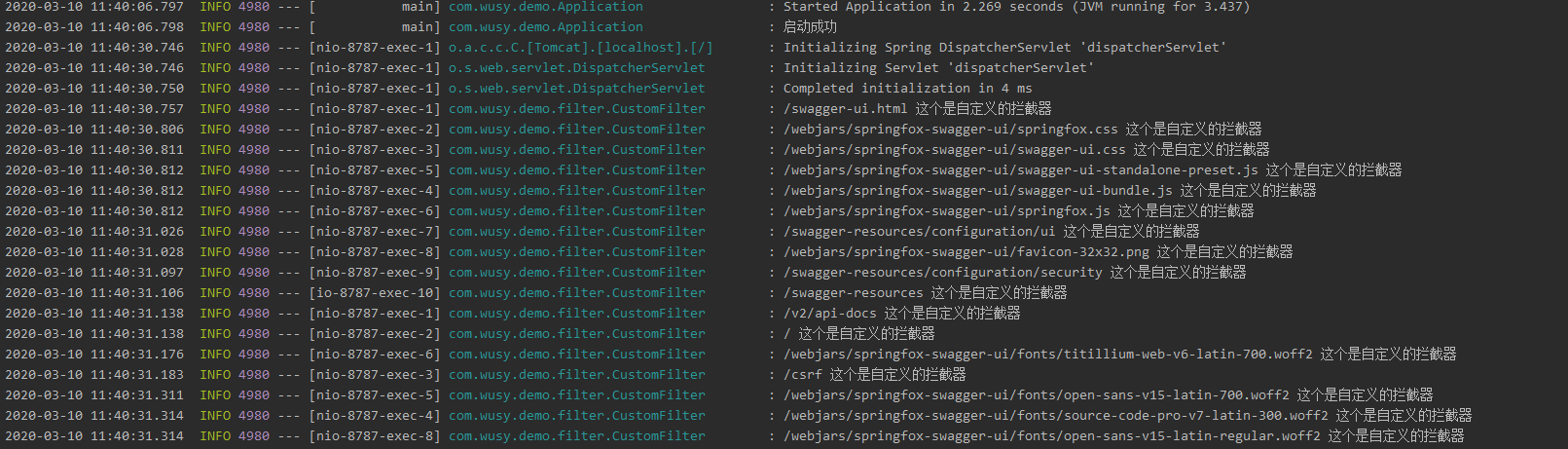
Method 2: register a FilterRegistrationBean class through @ Bean
First, you should delete the @ WebFilter and other annotations in the CustomFilter class in method 1, so that it becomes a normal class without any annotations
import org.slf4j.Logger; import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; import javax.servlet.*; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import java.io.IOException; /** * @author wusy * Company: xxxxxx Technology Co., Ltd * Createtime : 2020/3/10 10:56 * Description : Custom filter */ public class CustomFilter implements Filter { private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(CustomFilter.class); /** * Address to ignore */ private static String[] ignores = new String[]{ }; @Override public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException { HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) servletRequest; HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) servletResponse; //Determine whether the url needs to be blocked if (this.ignoring(request.getRequestURI())) { chain.doFilter(request, response); return; } logger.info(request.getRequestURI() +" This is a custom interceptor"); chain.doFilter(request, response); } /** * Determine whether the url needs to be blocked * @param uri * @return */ private boolean ignoring(String uri) { for (String string : ignores) { if (uri.contains(string)) { return true; } } return false; } }
Then add the configuration information of @ Bean
/** * Custom filter * @return */ @Bean public FilterRegistrationBean customFilterRegistration() { FilterRegistrationBean registration = new FilterRegistrationBean(); CustomFilter filter = new CustomFilter(); //Injection filter registration.setFilter(filter); //Interception rules registration.addUrlPatterns("/*"); //Filter name registration.setName("CustomFilter"); //Filter sequence registration.setOrder(1); return registration; }
Next, we launch the project and enter http://127.0.0.1:8787/swagger-ui.html (last article introduced how to integrate swagger), observations
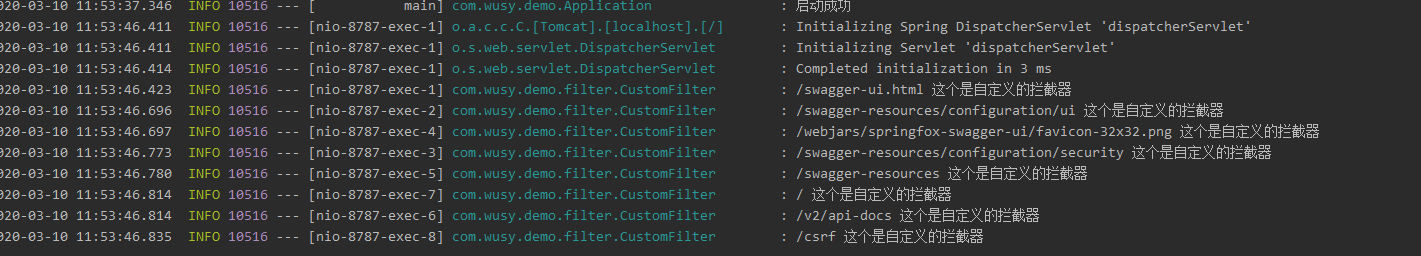
From the demonstration results of the two ways, we can see that the results of the two ways are the same. Generally, mode 1 is used more in projects.
Note: filtering will intercept all requests including front-end pages and scripts, so if you want to not intercept the relevant addresses of swagger in the future, you should add the relevant addresses of swagger to the filtered addresses
/** * Address to ignore */ private static String[] ignores = new String[]{ //Filter the interface of swagger related requests, otherwise swagger will prompt that base URL is blocked "/swagger-ui", "/swagger-resources", "/v2/api-docs" };