Spring Security
brief introduction
The core functions of spring security are Authentication and Authorization, that is, whether the authenticated user can access the system and what operations the authorized user can perform in the system.
Introducing spring security component
Add in pom.xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>Verify whether the component works. Now, do not change anything in the frame. Start the project and input it in the browser http://localhost:8080 , you can see the following interface. You can directly enter the initial interface of spring boot before. Now it is invisible. After importing spring security, authentication has been enabled by default. You must log in for authentication before you can access it.
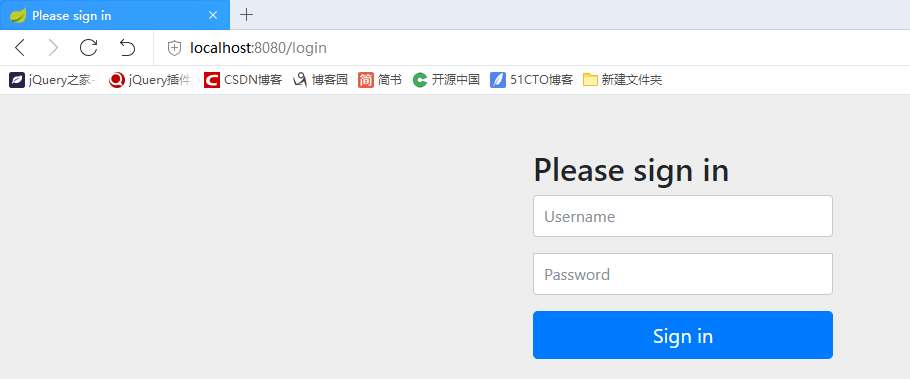
If no settings are made in the code, the default account is user, and the default password will be printed in the console as the project starts.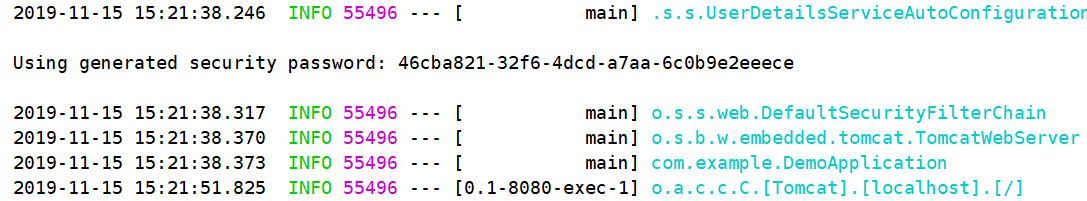
Enter the account password to enter the default initial interface.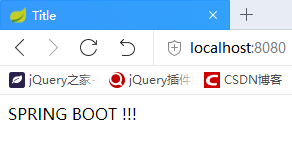
Code actual combat
In order to recognize this component quickly, simply and directly, write the user password into the memory directly, and the project will exist when it is started, so as to avoid the irrelevant contents such as table building, entity class, database operation, etc. Naming is the simplest and rudimentary way to eliminate all interferences and use the least effort to master the use of this component.
New code directory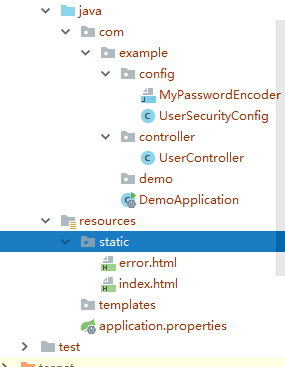
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
SPRING BOOT !!!
</body>
</html>error.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
//error
</body>
</html>UserController
package com.example.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("user")
public class UserController {
@RequestMapping("/addUser")
@ResponseBody
String addUser() {
return "This is add user!!!";
}
@RequestMapping("/deleteUser")
@ResponseBody
String deleteUser() {
return "This is to delete users!!!";
}
@RequestMapping("/updateUser")
@ResponseBody
String updateUser() {
return "This is to modify users!!!";
}
@RequestMapping("/findAllUsers")
@ResponseBody
String findAllUsers() {
return "This is the query user!!!";
}
}UserSecurityConfig
package com.example.config;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.builders.AuthenticationManagerBuilder;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter;
//Annotation enables Spring Security authentication and authorization
@EnableWebSecurity
public class UserSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
//User authentication
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
//In memory
auth.inMemoryAuthentication().passwordEncoder(new MyPasswordEncoder())
//Add user, password, role
.withUser("zs").password("123456").roles("AAA")
//Chain programming
.and()
.withUser("ls").password("123456").roles("BBB")
.and()
.withUser("ww").password("123456").roles("CCC", "primary")
.and()
.withUser("zl").password("123456").roles("primary");
}
//User authorization
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
/**
* permitAll(): Allow all users access
* hasRole(): url Roles that request access
* hasAnyRole() : url Multiple roles that are requested to be allowed access
* access(): The roles that can be accessed, permitAll, hasRole and hasAnyRole, are all called access methods at the bottom
* access("permitAll") Equivalent to permitAll()
*/
http.authorizeRequests().antMatchers("/").permitAll(); // "/": the application homepage so that users can access
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/user/addUser").hasRole("AAA") // The slash "/" indicates the application context, / user/addUser requests AAA role access
.antMatchers("/user/deleteUser/**").hasAnyRole("AAA", "BBB") //"/user/deleteUser/**"Allow "AAA", "BBB" role access, / * * match any
.antMatchers("/user/updateUser").hasAnyRole("AAA", "BBB", "CCC")//In addition to this chain programming, it can also be written separately
.antMatchers("/user/findAllUsers").access("permitAll");
http.authorizeRequests().anyRequest().authenticated();
/**
* formLogin: Specifies that form based authentication is supported
* When the user has no login or permission, he will automatically jump to the login page (default / login)
* When login fails, default to / error
* Release on successful login
*/
http.formLogin();
}
}MyPasswordEncoder
package com.example.config;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder;
//Password encoding. Spring Security higher version must be password encoded, otherwise an error will be reported
public class MyPasswordEncoder implements PasswordEncoder {
@Override
public String encode(CharSequence charSequence) {
return charSequence.toString();
}
@Override
public boolean matches(CharSequence charSequence, String s) {
return s.equals(charSequence.toString());
}
}The result is
Log in with the user name zs (the role permission is AAA), you can enter the system, the browser input address can be accessed, localhost:8080, localhost:8080/user/addUser, localhost:8080/user/deleteUser, localhost:8080/user/updateUser, localhost:8080/user/findAllUsers
Log in with the user name ls (the role permission is BBB), you can enter the system, the browser input address can be accessed, localhost:8080, localhost:8080/user/deleteUser, localhost:8080/user/updateUser, localhost:8080/user/findAllUsers
Log in with the user name ww (the role permission is CCC), you can enter the system, the browser input address can be accessed, localhost:8080, localhost:8080/user/deleteUser, localhost:8080/user/updateUser, localhost:8080/user/findAllUsers
Log in with the user name zl (the role permission is CCC), you can enter the system, the browser input address can be accessed, localhost:8080, localhost:8080/user/updateUser, localhost:8080/user/findAllUsers
Log in with the user name admin, and you cannot enter the system, because the user is not yet in the system.