On the introduction of Spring framework, there are many good and detailed articles on the Internet. My personal ability is limited. I can only use my blog to record my current knowledge! There are mistakes, welcome to correct!
This blog will briefly introduce the simple running process of the Spring framework.
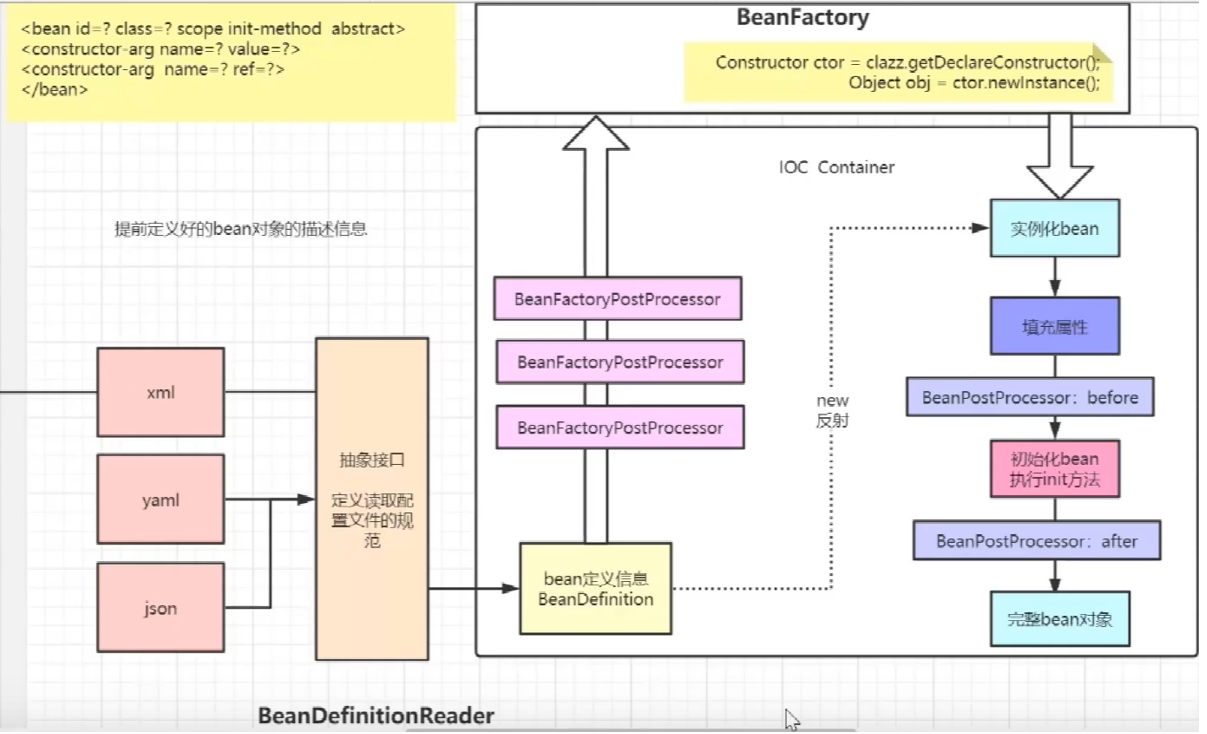
The process of SpringIOC is roughly as follows:
1. Create BeanFactory first
2. Read the information in xml into BeanDefinition through BeanDefinitionReader
3. After some processing
4. Instantiated by BeanFactory
5. Fill in attributes, such as Name and id
6. Initialization
7. Complete
Sample code
Users.java
package com.piao.pojo;
public class Users {
private int id;
private String name;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Users{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
public Users() {
}
public Users(int id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="user" class="com.piao.pojo.Users">
<property name="id" value="12"/>
<property name="name" value="mike"/>
</bean>
</beans>Test code
@Test
public void test(){
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext con = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Users user = con.getBean("user", Users.class);
System.out.println(user);
}Process analysis
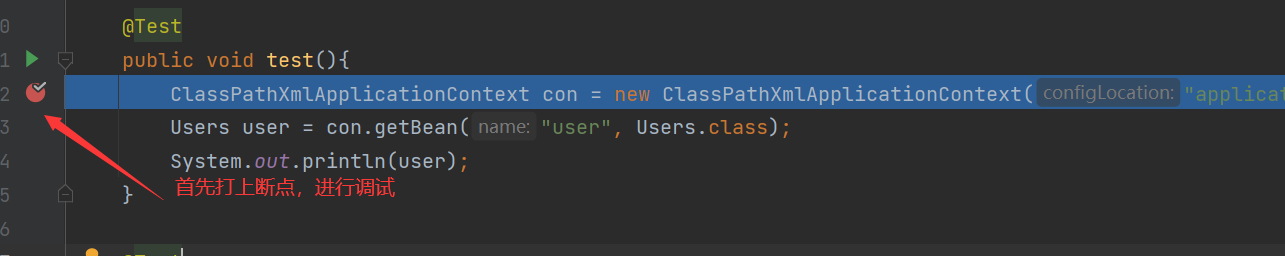
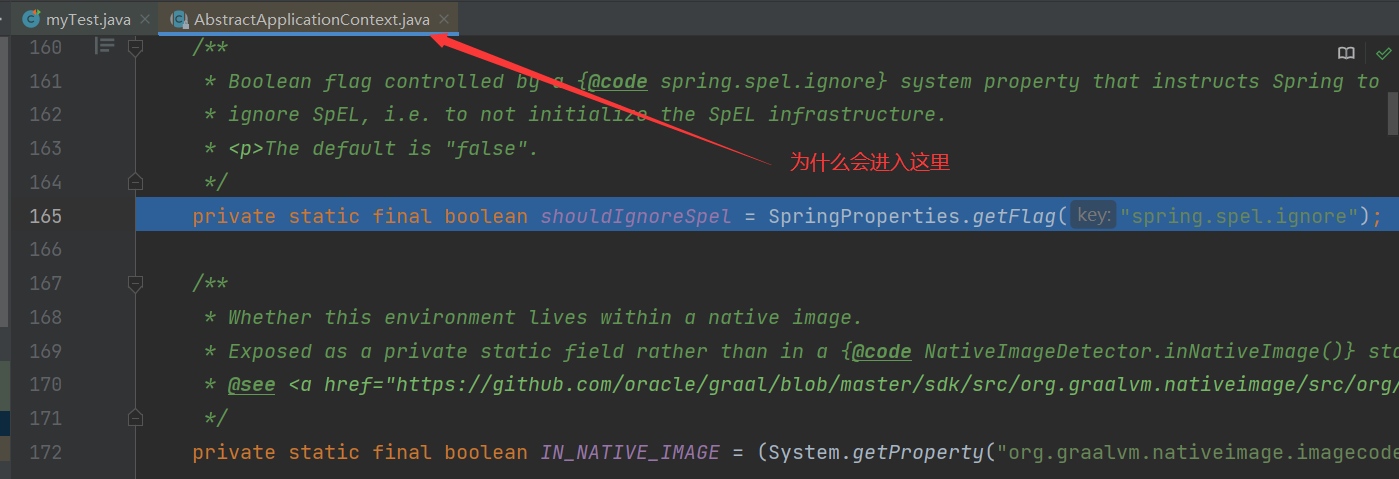
Why didn't you enter the ClassPathXmlApplicationContext class? The reasons are as follows:
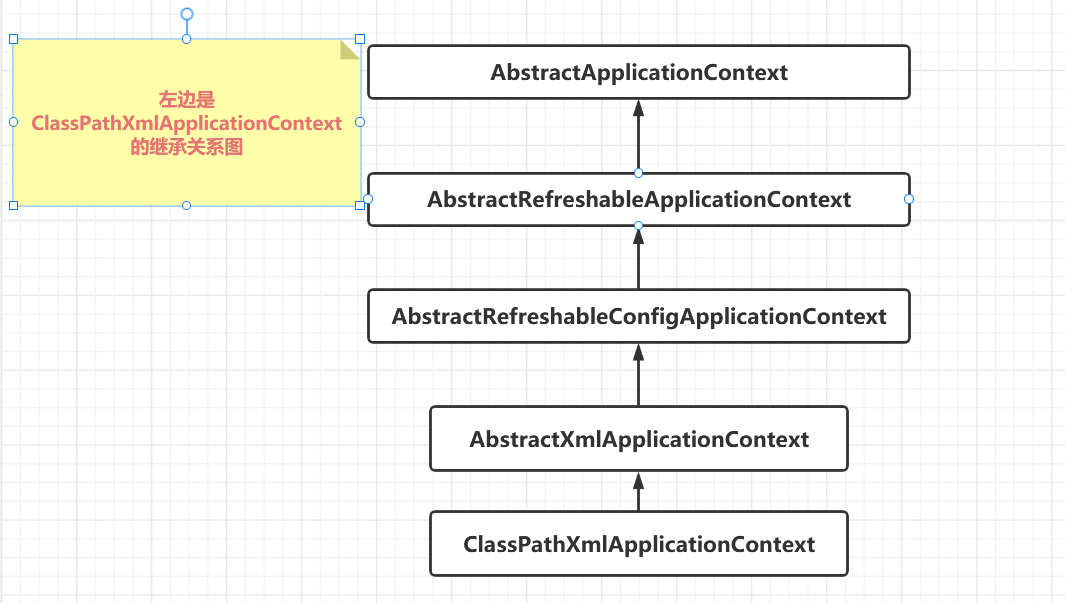
Because of the inheritance relationship in the above figure, before implementing ClassPathXmlApplicationContext, the static method block identified by static in its parent class and the static attribute of initializing the parent class will be implemented first;
After that, it will enter the construction method of ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
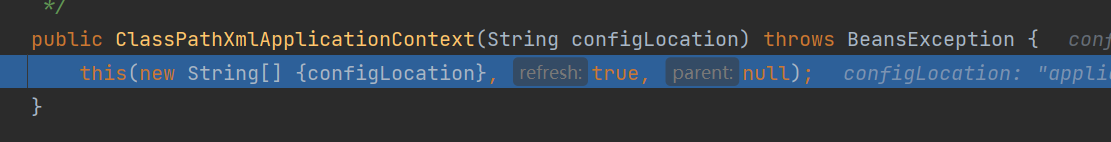
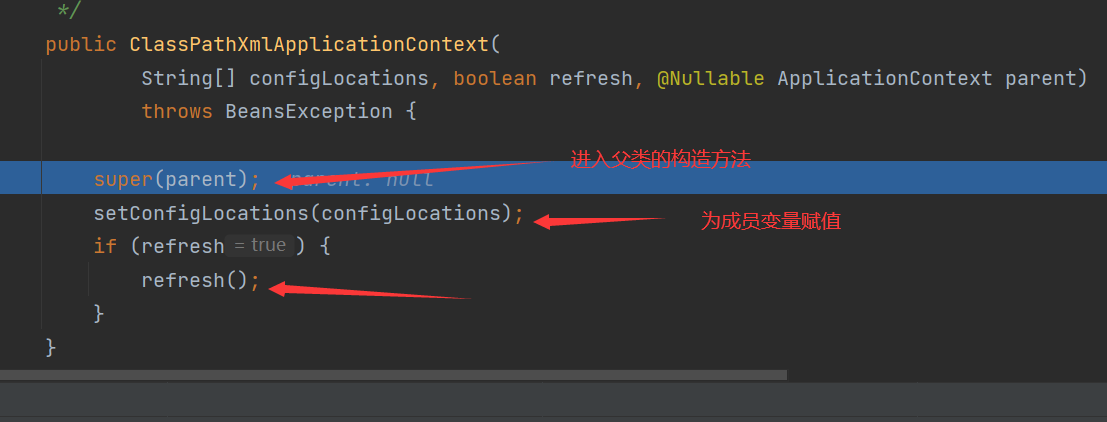
The refresh method in the figure above is the most critical step, because many attribute initialization, BeanFactory construction and preliminary preparations are called from this method.
Back to business, let's explore it step by step,
super(parent) will call the constructor of the parent class. If there is no operation in the middle, we won't show them one by one. Go directly to
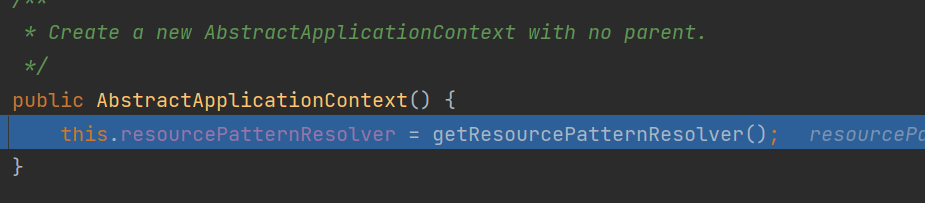
All member variables are initialized before calling the null parameter constructor.
And then
setConfigLocations(configLocations)
In fact, it can be understood as an initialization. It is understood that it is only necessary to assign values to the member variables of this class. The contents have no impact on the whole process. At the beginning, it is not necessary to study too much, otherwise it will be very confused. We have to learn to first breadth and then depth, and there is no more explanation,
And then
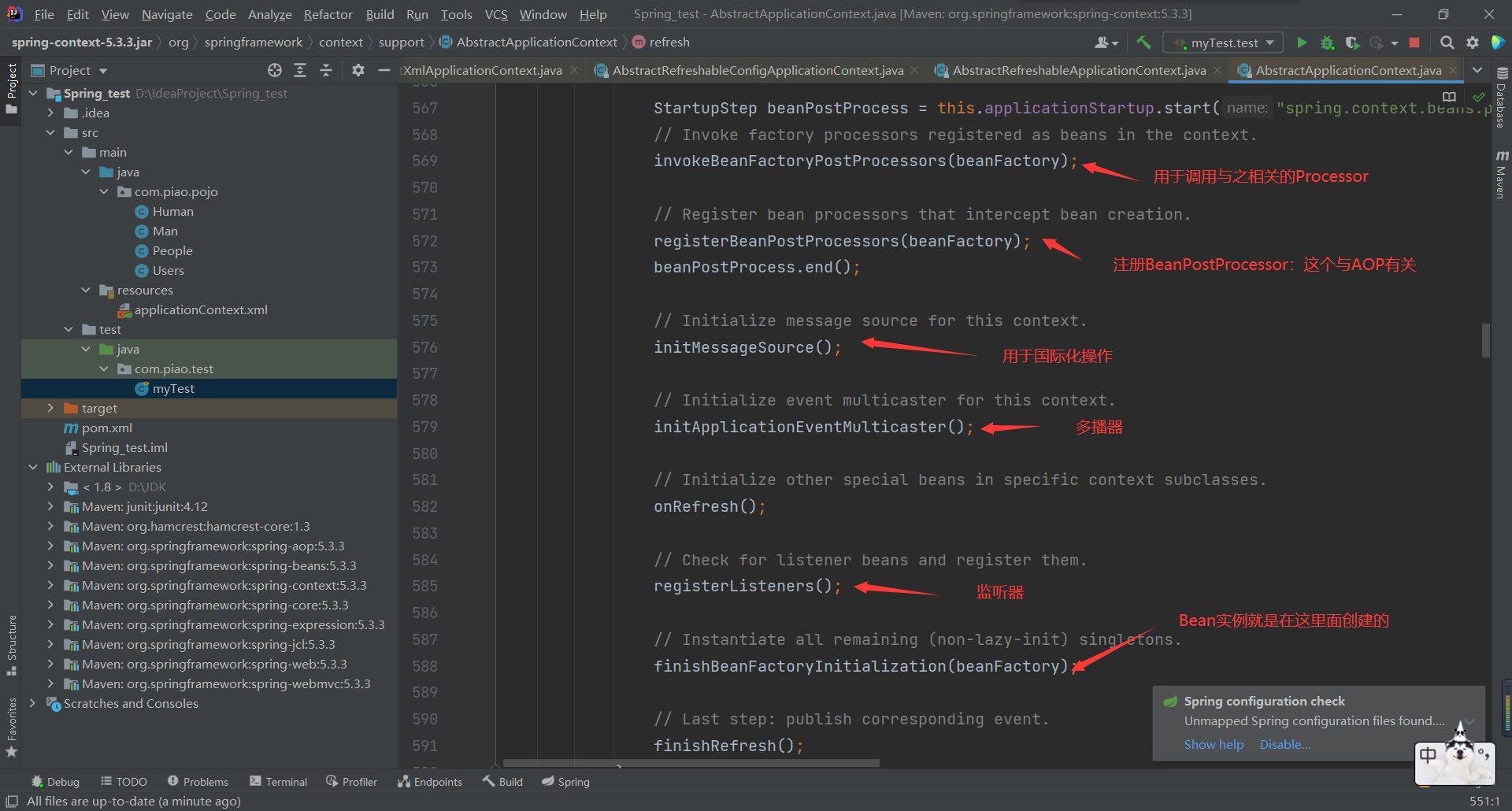
refresh(): focus
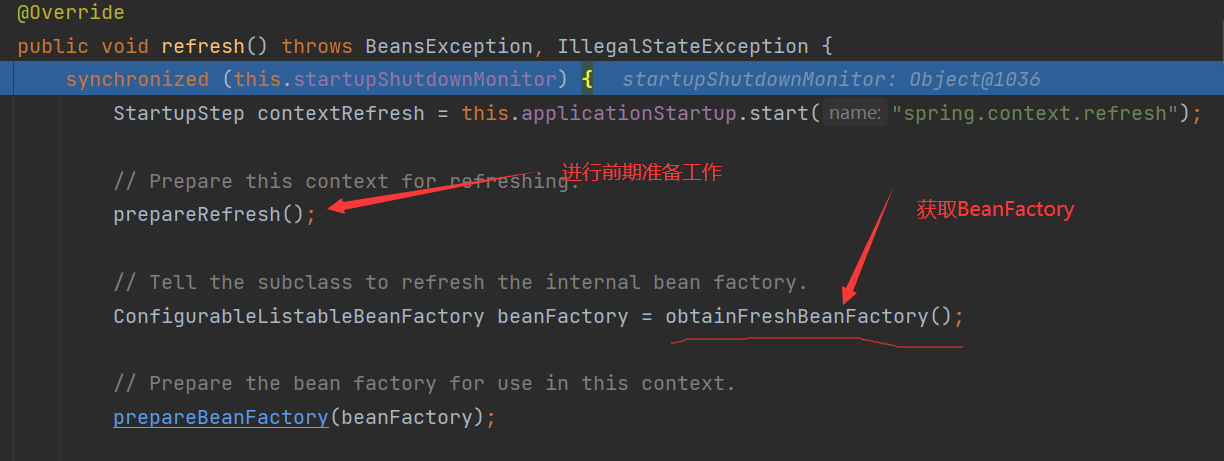
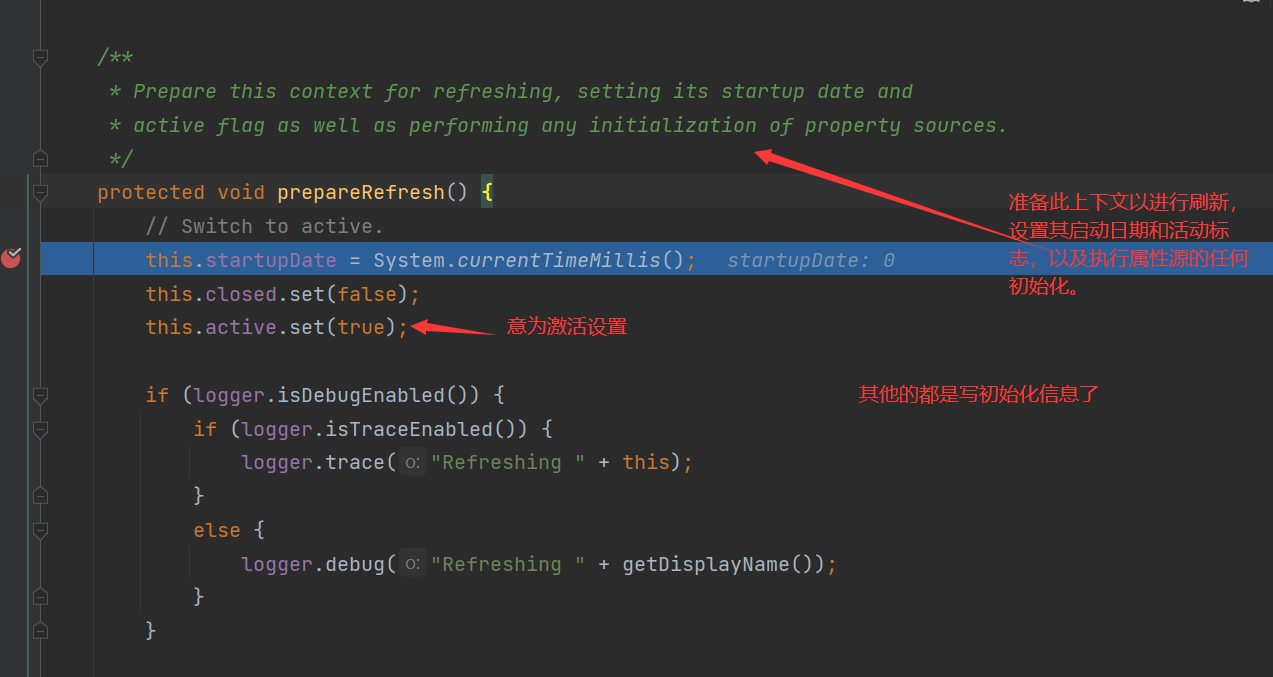
prepareRefresh()
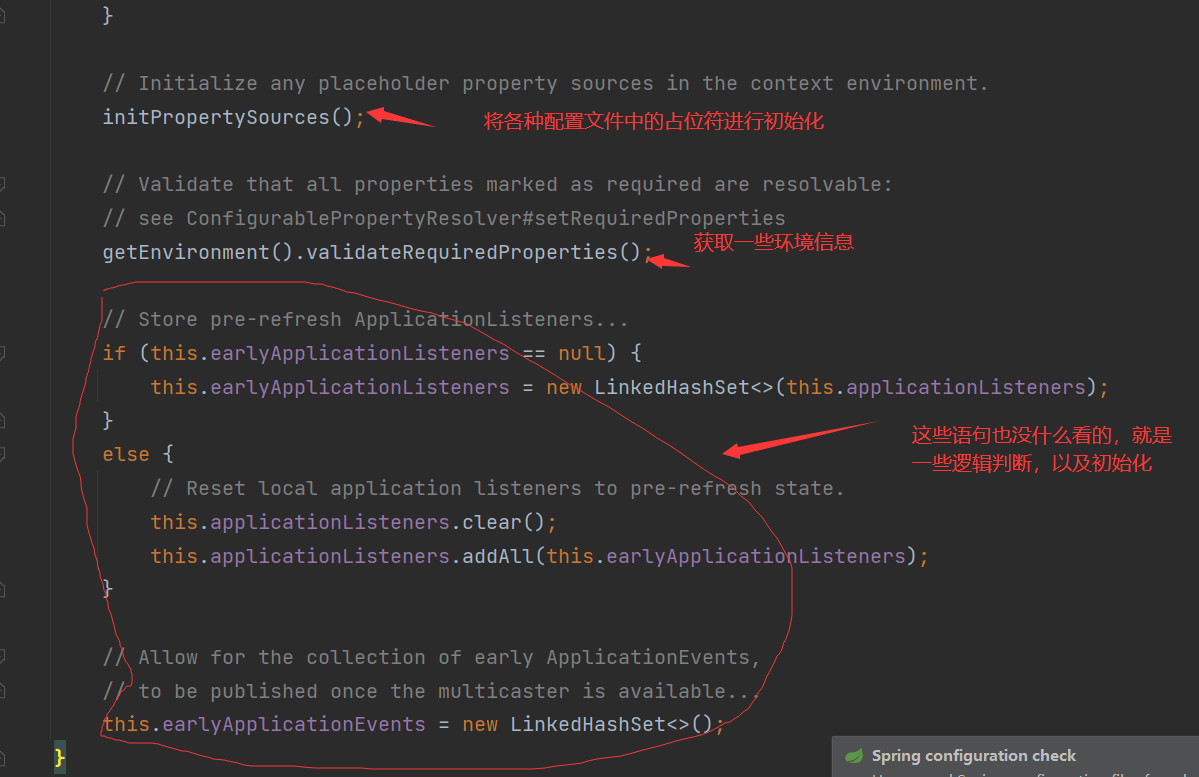
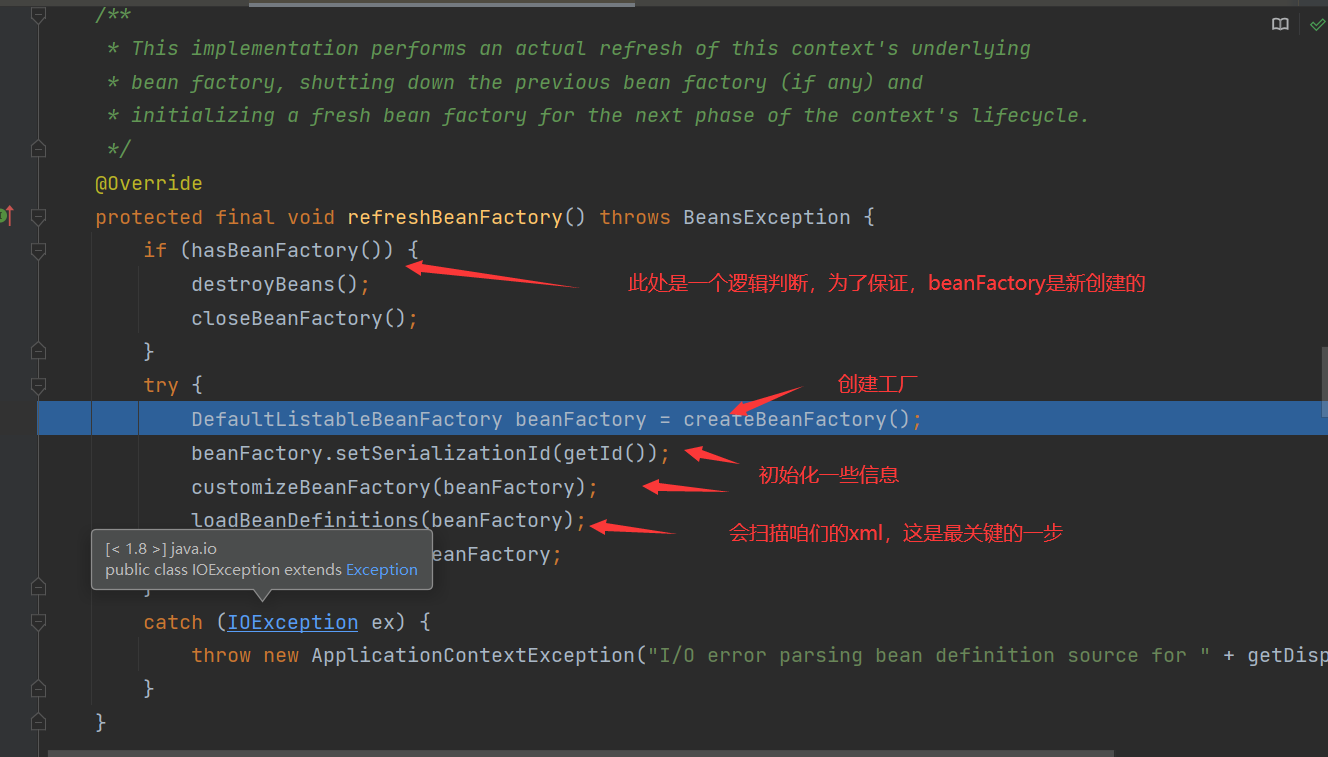
obtainFreshBeanFactory()
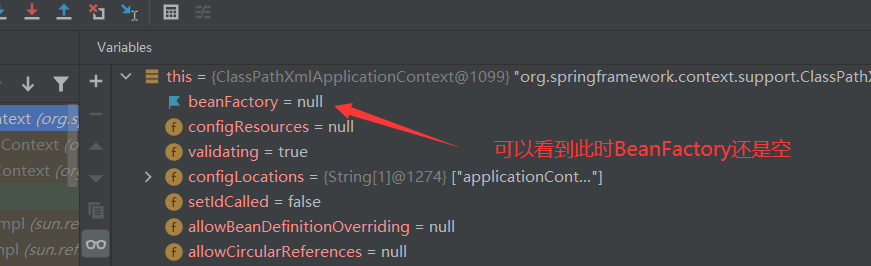
When this method is not run, BeanFactory is still null
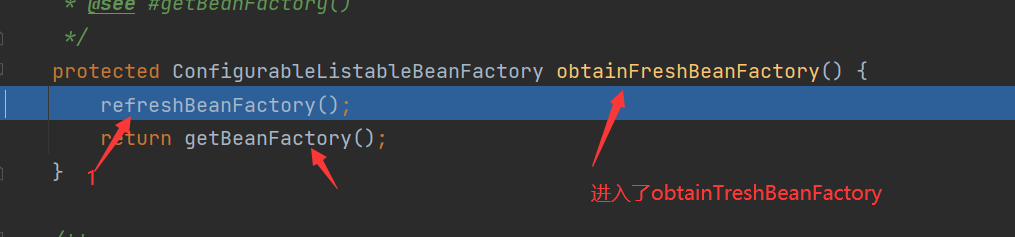
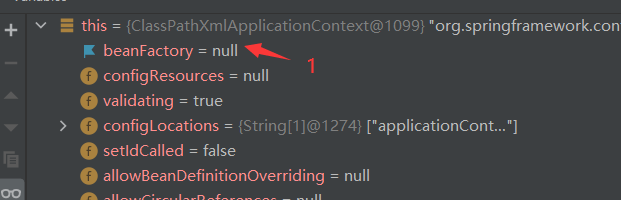
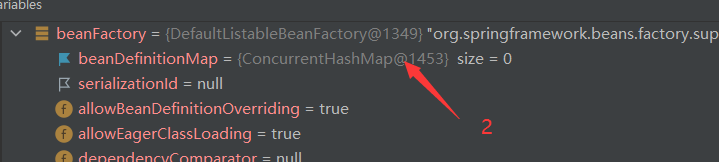
1 and 2 represent our bean information. The following ideas focus on this exhibition to see when it will be injected
Continue running
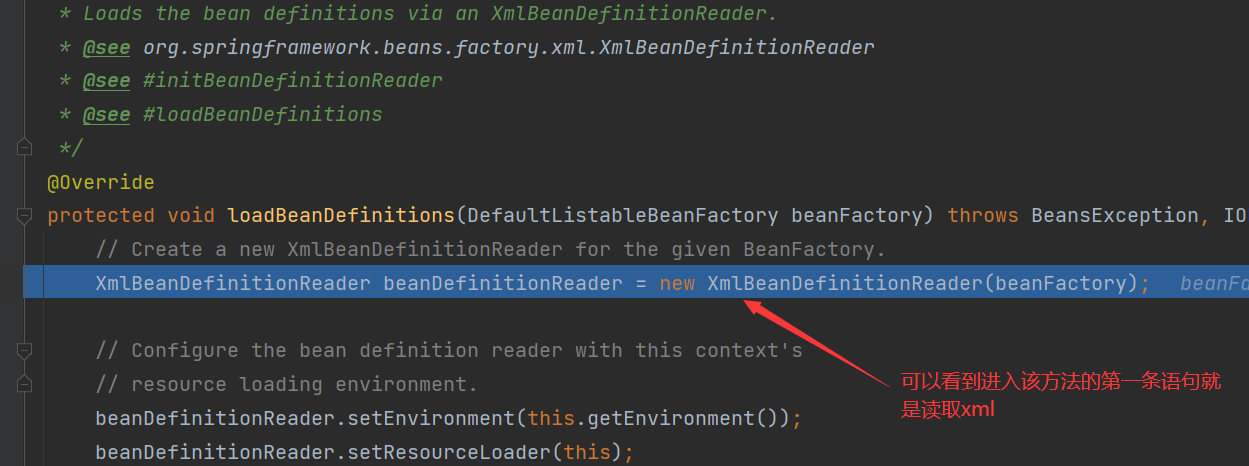
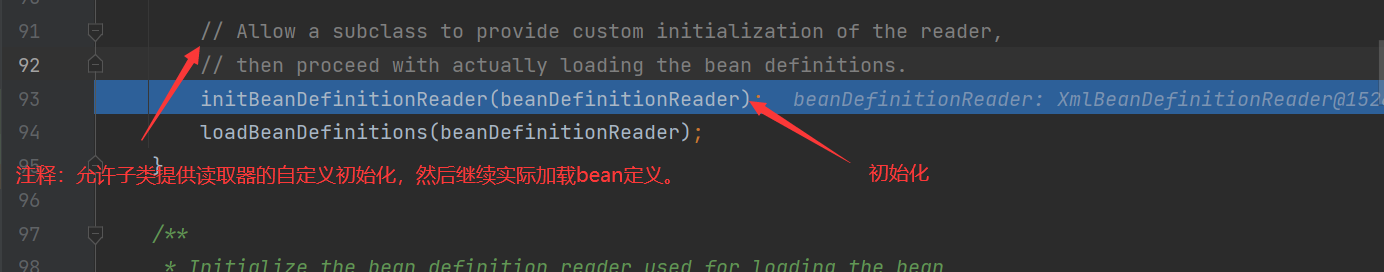 After loadbean definitions () is executed, we will get the contents in the bean tag
After loadbean definitions () is executed, we will get the contents in the bean tag
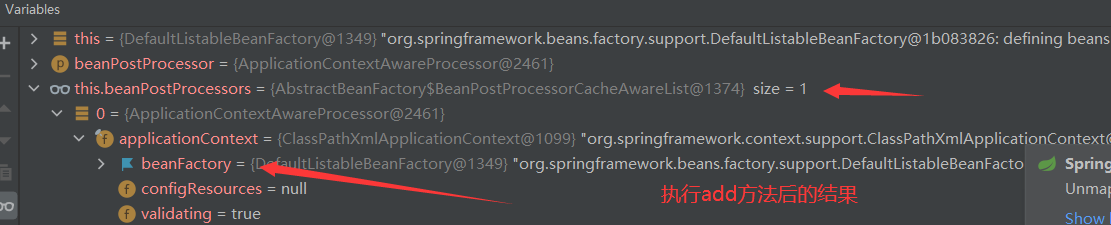
prepareBeanFactory(): configure the standard context features of the factory, such as the class loader and post processor of the context.
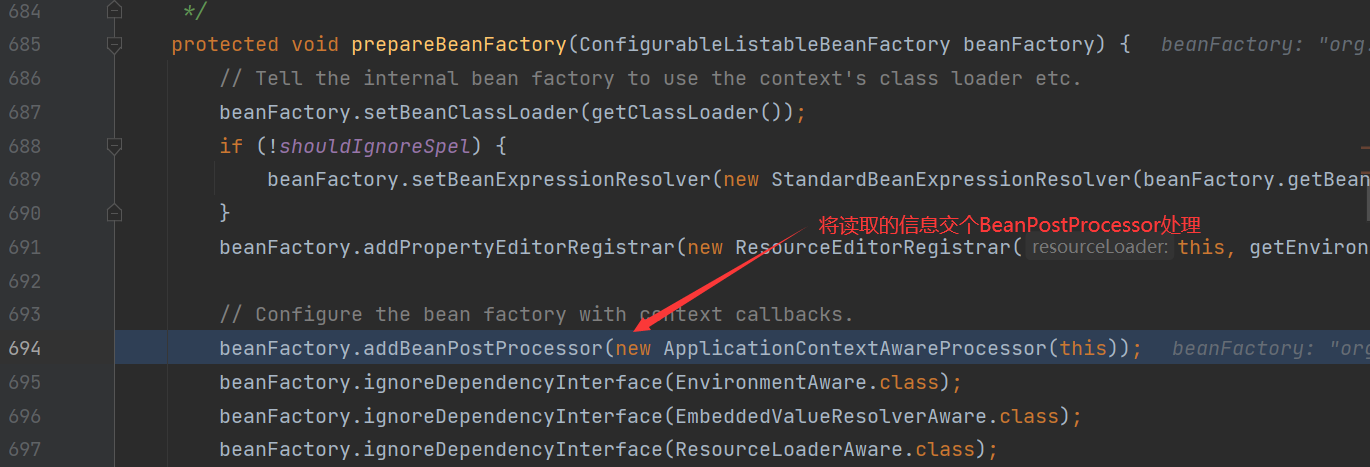

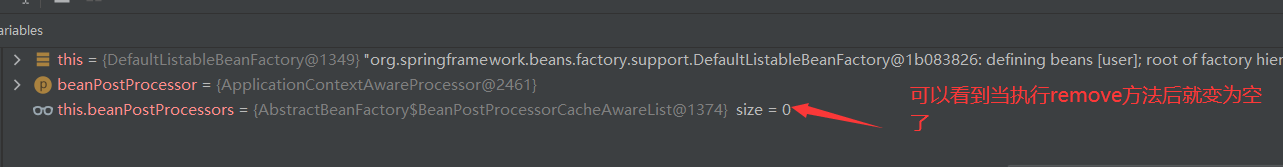
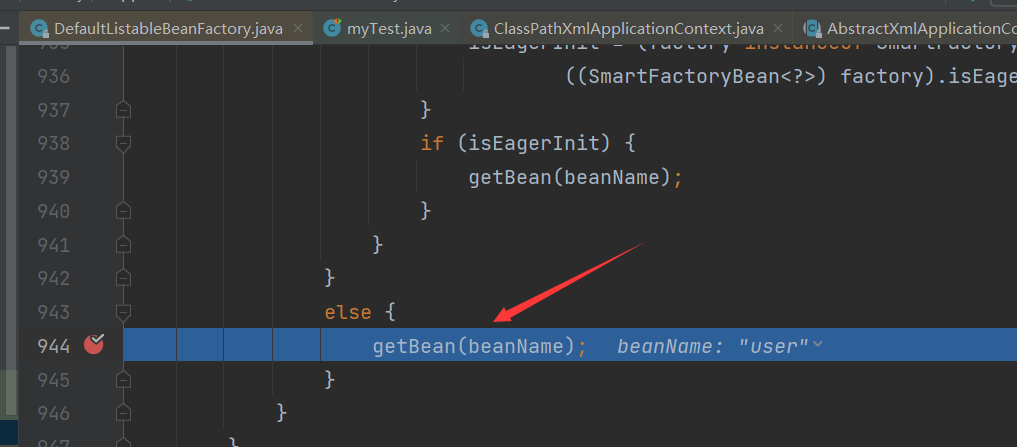
Bean instance creation
Because we know that Bean instances are created by BeanFactory through the reflection mechanism, other details will not be explored
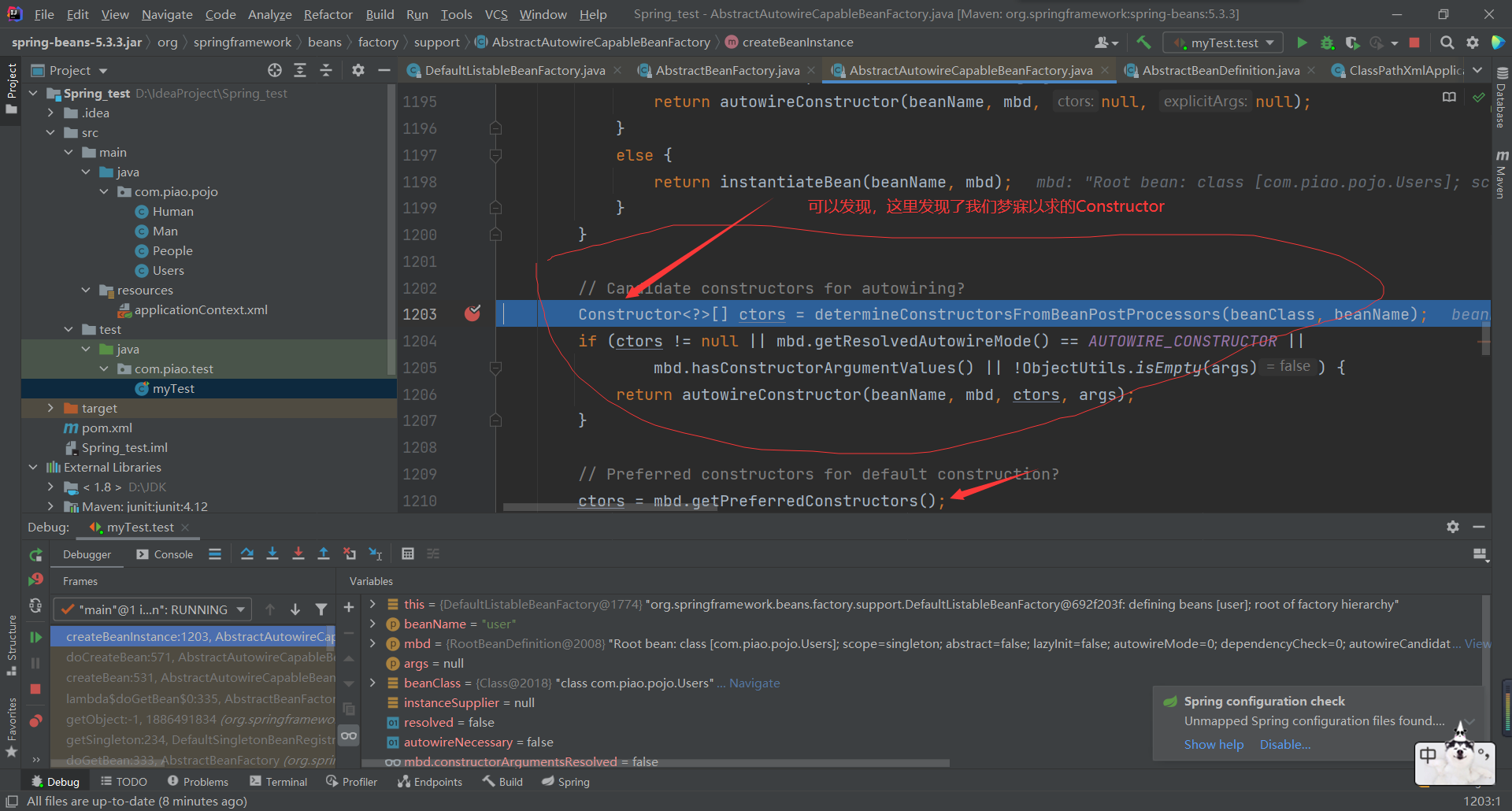
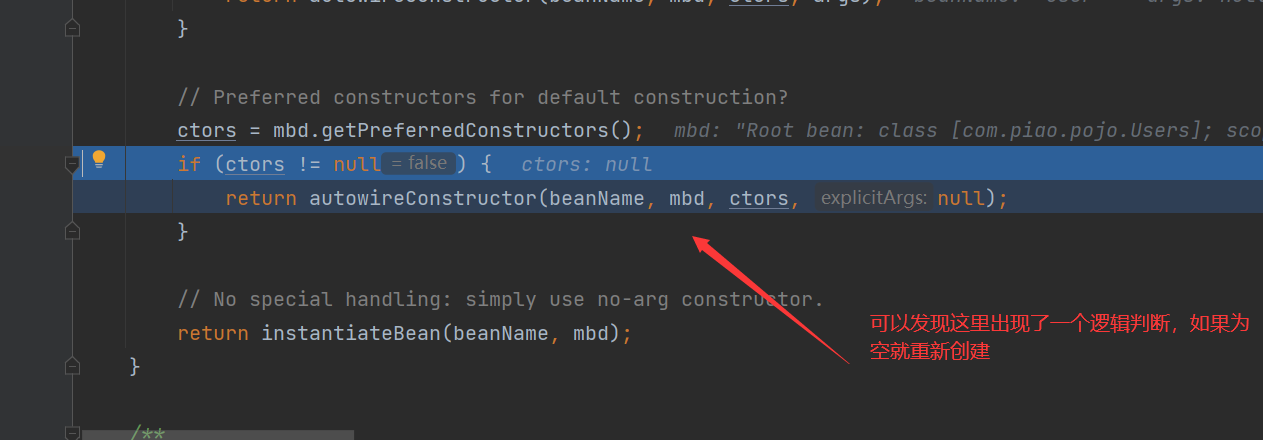
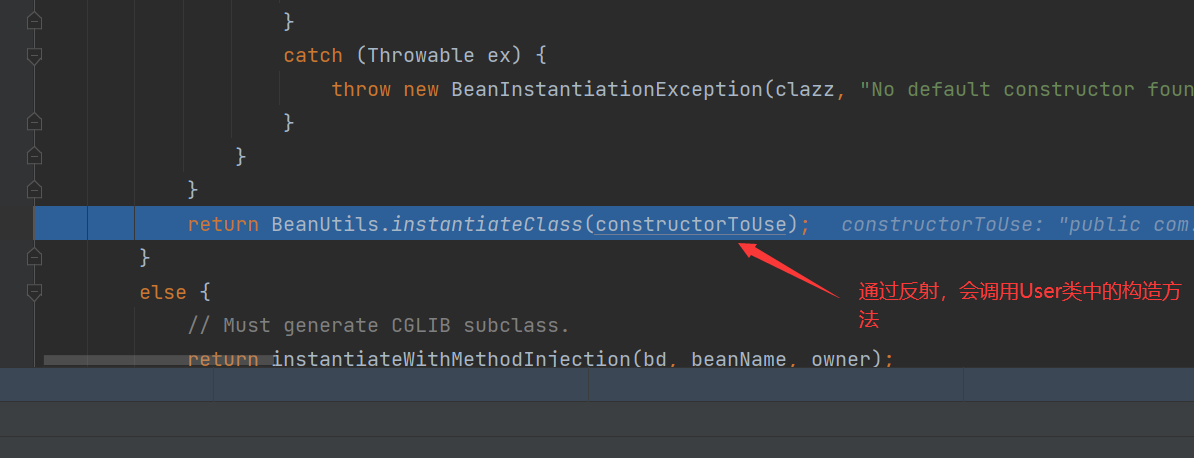
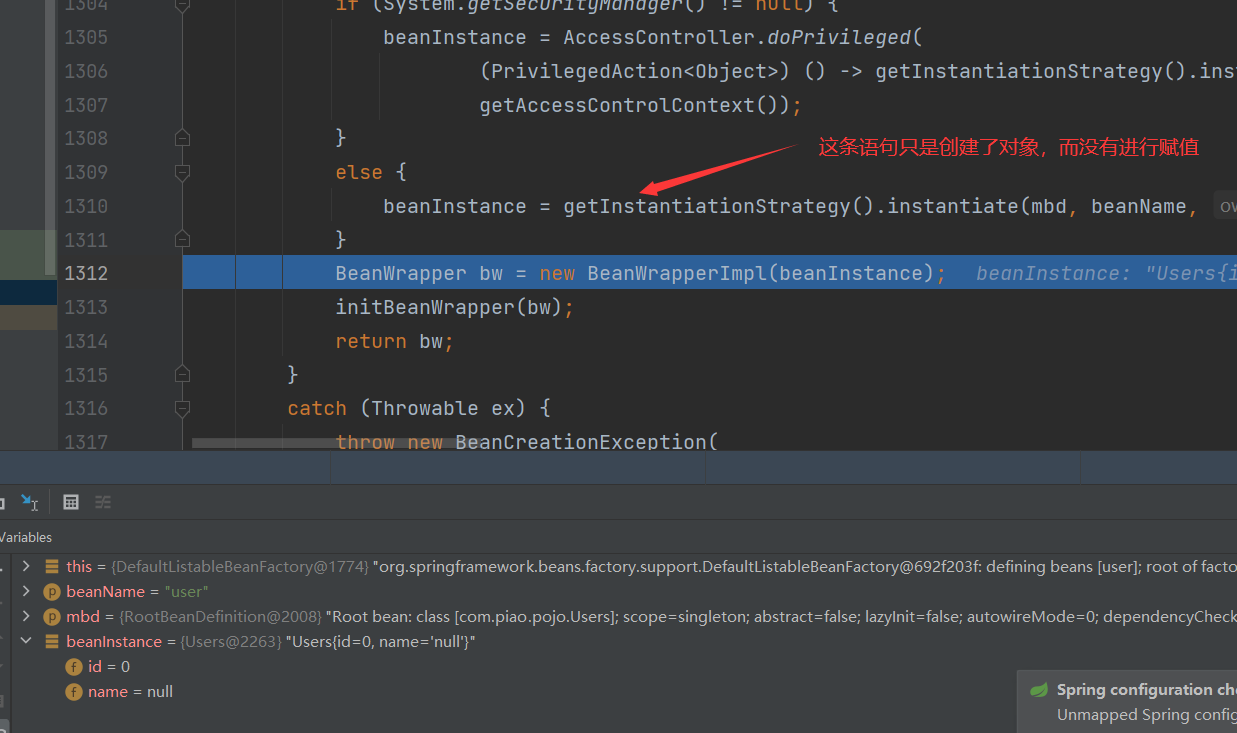
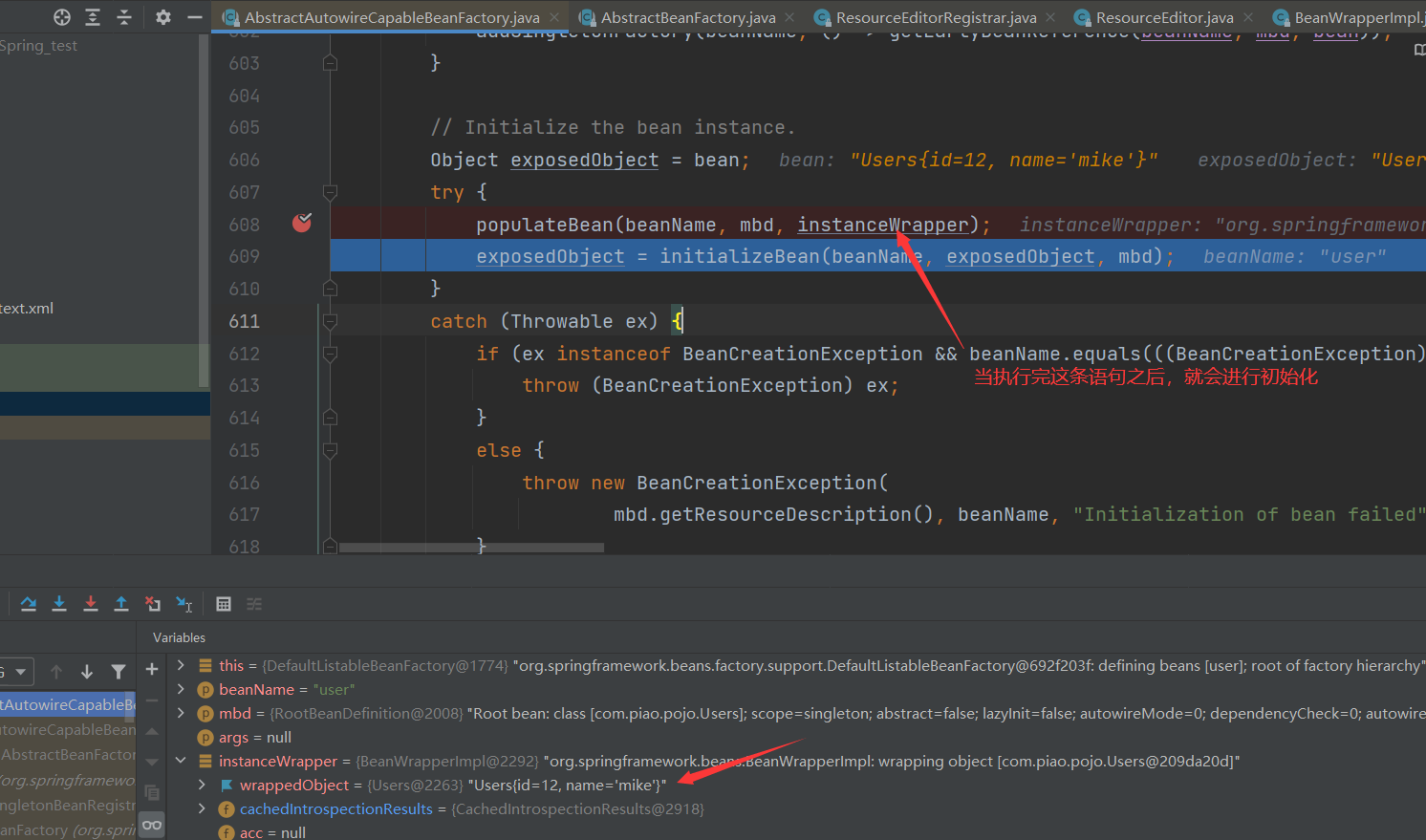
This Bean has been instantiated successfully
IOC is almost like this
Worry is also a day, bitter is also a day, why not learn every day