proxy pattern
- The proxy pattern is the bottom layer of spring AOP
- Agent mode classification: static agent and dynamic agent
1. Static proxy
- Role analysis
Abstract role: it is usually solved by using interfaces or abstract classes
Real role: the role represented
Proxy role: represents a real role. After representing a real role, there will be some ancillary operations
Client: the person who accesses the proxy object
1. Example 1
Interface
//Rental / rental
public interface Rent {
public void rent();
}
Real role
//landlord or landlady
public class Host implements Rent {
@Override
public void rent() {
System.out.println("The landlord wants to rent the house!");
}
}
delegable role
//agent
public class Proxy implements Rent{
private Host host;
public Proxy(Host host) {
this.host = host;
}
@Override
public void rent() {
seeHouse();
host.rent();
hetong();
fare();
}
//House viewing
public void seeHouse(){
System.out.println("The agent will show you the house!");
}
//sign a contract
public void hetong(){
System.out.println("Sign the lease contract!");
}
//Intermediary fee
public void fare(){
System.out.println("Charge intermediary fee!");
}
}
Customer access agent role
//customer
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//The landlord rented the house
Host host = new Host();
//Agent rental
Proxy proxy = new Proxy(host);
//You can rent a house without facing the landlord
proxy.rent();
}
}
result
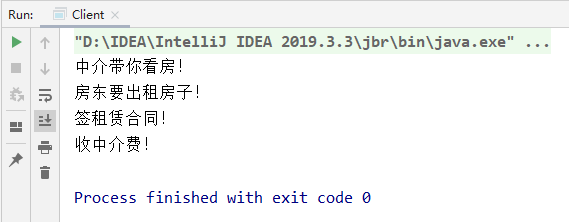
2. Example 2
Interface
public interface UserService {
public void add();
public void delete();
public void update();
public void query();
}
Real role
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Override
public void add() {
System.out.println("Added a user!");
}
@Override
public void delete() {
System.out.println("Deleted a user!");
}
@Override
public void update() {
System.out.println("Modified a user!");
}
@Override
public void query() {
System.out.println("Queried a user!");
}
}
delegable role
public class UserServiceProxy implements UserService {
private UserService userService;
public void setUserService(UserService userService) {
this.userService = userService;
}
@Override
public void add() {
log("add");
userService.add();
}
@Override
public void delete() {
log("delete");
userService.delete();
}
@Override
public void update() {
log("update");
userService.update();
}
@Override
public void query() {
log("query");
userService.query();
}
//Log method
public void log(String msg){
System.out.println("Used"+msg+"method");
}
}
Customer access agent role
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
UserServiceImpl userService = new UserServiceImpl();
UserServiceProxy proxy = new UserServiceProxy();
proxy.setUserService(userService);
proxy.query();
proxy.add();
}
}
result
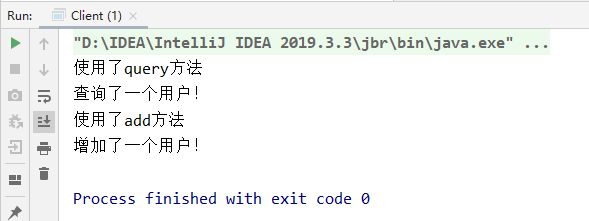
- Benefits of agent mode:
It can make the operation of real roles more pure without paying attention to some public businesses
The public business is handed over to the agent role to realize the division of business
When the public business is expanded, it is convenient for centralized management - Disadvantages:
A real role will produce a proxy role, the amount of code will double, and the development efficiency will be low.
2. Dynamic agent
- Dynamic agents have the same role as static agents
- The proxy class of dynamic proxy is generated dynamically, not written directly
- Dynamic agents are divided into two categories: dynamic agents that give interfaces and class based dynamic agents
Interface based: jdk dynamic agent [learning]
Class based: cglib - Classes to understand: Proxy: Proxy, InvocationHandler: calling handler
1. Example 1
Interface
//Rental / rental
public interface Rent {
public void rent();
}
Real role
//landlord or landlady
public class Host implements Rent {
@Override
public void rent() {
System.out.println("The landlord wants to rent the house!");
}
}
Class used to generate proxy roles
//Use this class to automatically generate proxy classes.
public class ProxyInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {
//Proxy interface
private Rent rent;
public void setRent(Rent rent) {
this.rent = rent;
}
//Generated proxy class
public Object getProxy(){
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(this.getClass().getClassLoader(),rent.getClass().getInterfaces(),this);
}
//Process the proxy instance and return the result
@Override
public Object invoke(Object o, Method method, Object[] objects) throws Throwable {
//The essence of dynamic agent is to use reflection mechanism.
seeHouse();
Object result = method.invoke(rent);
fare();
return result;
}
public void seeHouse(){
System.out.println("Show me the house");
}
public void fare(){
System.out.println("Intermediary fee");
}
}
Automatically generate proxy roles and access
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Real role
Host host = new Host();
//Agent role: not yet
ProxyInvocationHandler pih = new ProxyInvocationHandler();
//Handle the interface object we want to call by calling the program processing role.
pih.setRent(host);
//The agent role is dynamically generated here
Rent proxy = (Rent) pih.getProxy();
proxy.rent();
}
}
result
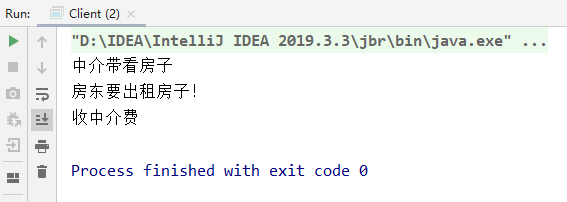
2. Example 2
Interface
public interface UserService {
public void add();
public void delete();
public void update();
public void query();
}
Real role
//Real role
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Override
public void add() {
System.out.println("Added a user!");
}
@Override
public void delete() {
System.out.println("Deleted a user!");
}
@Override
public void update() {
System.out.println("Modified a user!");
}
@Override
public void query() {
System.out.println("Queried a user!");
}
}
Class used to generate proxy roles
//Use this class to automatically generate proxy classes. Agent demo02 (at this time, this class is equivalent to a tool class)
public class ProxyInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {
//Proxy interface
private Object target;
public void setTarget(Object target) {
this.target = target;
}
//Generated proxy class
public Object getProxy(){
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(this.getClass().getClassLoader(),target.getClass().getInterfaces(),this);
}
//Process the proxy instance and return the result
@Override
public Object invoke(Object o, Method method, Object[] objects) throws Throwable {
//The essence of dynamic agent is to use reflection mechanism.
log(method.getName());
Object result = method.invoke(target);
return result;
}
public void log(String msg){
System.out.println("Yes"+msg+"method");
}
}
Automatically generate proxy roles and access
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Real role
UserServiceImpl userService = new UserServiceImpl();
//Agent role: currently exists
ProxyInvocationHandler pih = new ProxyInvocationHandler();
//Sets the object of the proxy
pih.setTarget(userService);
//Dynamically generate proxy classes
UserService proxy = (UserService) pih.getProxy();
proxy.query();
}
}
result
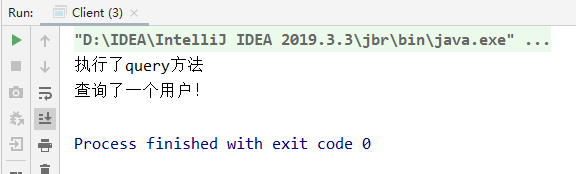
Related resources: Learning address of learning crazy God (the above is only a note)