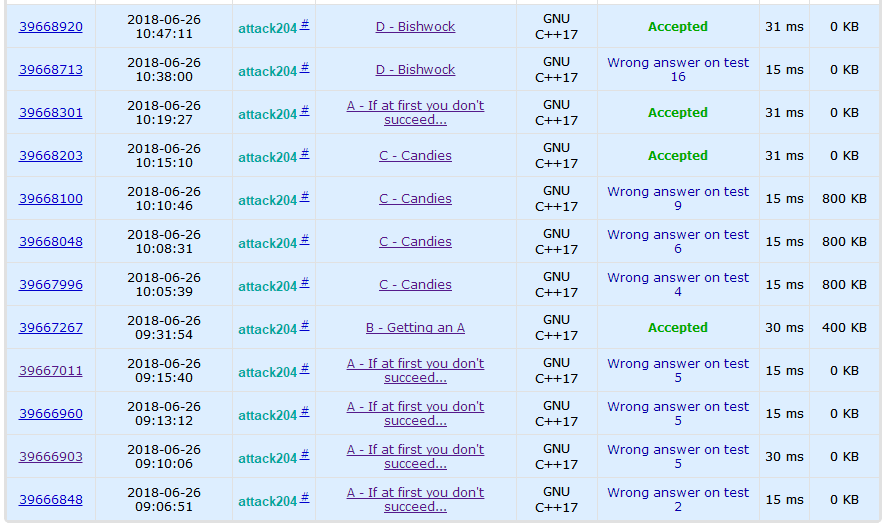
This game is a good ghost and beast. A question has broken down wa four times. The mentality has exploded directly. I wanted to give up treatment, but I found that BCD is a silly question.
A. If at first you don't succeed... (Principle of inclusion and exclusion)
Main idea of the title:
Some $N individuals took the exam. Among those who passed the exam, some $A individuals went to the first hotel party, some $B individuals went to the second hotel party, and some $C individuals went to two hotel parties at the same time.
Ask how many people failed the exam (the protagonist failed the exam)
Sol
The pupils scolded it. There must be $A+B-C $individuals at the party. If you subtract the amount from $N, it's unqualified.
At first wa exploded four times and then added a special sentence A.
#include<cstdio> using namespace std; int main() { int A, B, C, N; scanf("%d %d %d %d", &A, &B, &C, &N); int no = N - (A + B - C); if(A >= N || B >= N || C >= N || (C > A) || (C > B)) {printf("-1"); return 0;} if(no <= 0 || no > N) {printf("-1"); return 0;} printf("%d", N - (A + B - C)); return 0; }
B. Getting an A (Tan Xin)
Main idea of the title:
Vasya did the $n $door experiment and scored between $2 and $5. He wanted to round his average score (total score divided by the number of experiments) to $5. He asked for at least a few more experiments.
Sol
Directly greedy, it must be done a little again first, first sorting, enumeration to determine whether it has been qualified on the line.
#include<cstdio> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; const int MAXN = 1e5 + 10; inline int read() { char c = getchar(); int x = 0, f = 1; while(c < '0' || c > '9') {if(c == '-') f = -1; c = getchar();} while(c >= '0' && c <= '9') x = x * 10 + c - '0', c = getchar(); return x * f; } int a[MAXN]; int main() { double N = read(), S = 0; int x = N; for(int i = 1; i <= N; i++) a[i] = read(), S += a[i]; sort(a + 1, a + x + 1); if(S / N >= 4.5) {printf("0"); return 0;} for(int i = 1; i <= N; i++) { S -= a[i]; S += 5; if(S / N >= 4.5) { printf("%d", i); return 0; } } return 0; }
C. Candies (two points)
Main idea of the title:
Vasya had $n $candy, and at the beginning Vasya chose an integer of $k $to indicate that he would eat $k $candy a day. Petya wanted to steal some candy, and he would eat the current amount of $10\$(down to the whole) candy every day.
Note: If Vasya should eat candy and is not satisfied with $k, Vasya will eat it all. If Petya eats less than $10 candy, then Petya won't eat candy.
Output the smallest $k $so that $Vasya $eats at least half of the candy
Sol
Obviously, $k $is monotonous. Divide it directly.
Because $Petya $eats $10\\\\ candy at a time, the process of eating candy is fast and can be simulated directly.
#include<cstdio> #include<algorithm> #define int long long using namespace std; inline int read() { char c = getchar(); int x = 0, f = 1; while(c < '0' || c > '9') {if(c == '-') f = -1; c = getchar();} while(c >= '0' && c <= '9') x = x * 10 + c - '0', c = getchar(); return x * f; } int N; bool check(int k) { int cur = 1, Ansa = 0, Ansb = 0, now = N; while(now > 0) { if(cur & 1) Ansa += min(k, now), now -= min(k, now); else Ansb += now / 10, now -= now / 10; cur ^= 1; } return Ansa >= Ansb; } main() { N = read(); int l = 1, r = N, ans = 0; check(3); while(l <= r) { int mid = l + r >> 1; if(check(mid)) r = mid - 1, ans = mid; else l = mid + 1; } printf("%I64d", ans); }
D. Bishwock(dp)
Main idea of the title:
Bishwock is a special kind of chess. Its placement rules are as follows (similar to Tetris)
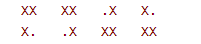
Give an initial scenario of $2*n $and ask how many chess pieces you can play at most (X means you can't play them here, 0 means you can play them several times)
Sol
Ran1's code is amazing. You can't learn it.
I only violence dp, let $f[i][j] $denote to the line of $i $and the state is the maximum of $j $(four states), $g[i] $denotes the maximum of all States of the line of $i $(max for f[i][1/2/3/4).)
Judge where you can move from when you move.
#include<cstdio> #include<algorithm> #include<cstring> using namespace std; const int MAXN = 1001; char s1[MAXN], s2[MAXN]; int f[MAXN][5], g[MAXN]; int getg(int x) { int ans = 0; for(int i = 1; i <= x; i++) ans = max(ans, g[i]); return ans; } int main() { scanf("%s %s", s1 + 1, s2 + 1); int N = strlen(s1 + 1), ans = 0; for(int i = 2; i <= N; i++) { for(int k = 1; k <= 4; k++) f[i][k] = getg(i - 1); if(s1[i] == '0' && s2[i] == '0') { if(s1[i - 1] == '0') { f[i][2] = max(f[i][2], g[i - 2] + 1); if(s2[i - 1] == '0') f[i][2] = max(f[i][2], f[i - 1][1] + 1); } if(s2[i - 1] == '0') { f[i][3] = max(f[i][3], g[i - 2] + 1); if(s1[i - 1] == '0') f[i][3] = max(f[i][3], f[i - 1][4] + 1); } } if(s1[i] == '0') { if(s1[i - 1] == '0' && s2[i - 1] == '0') f[i][4] = max(f[i][4], g[i - 2] + 1); } if(s2[i] == '0') { if(s1[i - 1] == '0' && s2[i - 1] == '0') f[i][1] = max(f[i][1], g[i - 2] + 1); } for(int k = 1; k <= 4; k++) g[i] = max(f[i][k], g[i]); ans = max(ans, g[i]); } printf("%d", ans); return 0; }
summary
The war was terrible.