Steps to introduce VirtualApk:
I. Introduction of virtual APK to host application
1. Add dependency in the build.gradle file of the project:
dependencies {
classpath 'com.didi.virtualapk:gradle:0.9.8.6'
}The complete gradle file is as follows:
// Top-level build file where you can add configuration options common to all sub-projects/modules.
buildscript {
repositories {
google()
jcenter()
}
dependencies {
classpath 'com.android.tools.build:gradle:3.1.4'
classpath 'com.didi.virtualapk:gradle:0.9.8.6'
// NOTE: Do not place your application dependencies here; they belong
// in the individual module build.gradle files
}
}
allprojects {
repositories {
google()
jcenter()
}
}
task clean(type: Delete) {
delete rootProject.buildDir
}2. Add dependency in the build.gradle file of app:
apply plugin: 'com.didi.virtualapk.host'
dependencies {
implementation 'com.didi.virtualapk:core:0.9.8'
}The complete gradle file is as follows:
apply plugin: 'com.android.application'
apply plugin: 'com.didi.virtualapk.host'
android {
compileSdkVersion 28
defaultConfig {
applicationId "com.wangyz.virtualapk.host"
minSdkVersion 21
targetSdkVersion 28
versionCode 1
versionName "1.0"
testInstrumentationRunner "android.support.test.runner.AndroidJUnitRunner"
}
buildTypes {
release {
minifyEnabled false
proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile('proguard-android.txt'), 'proguard-rules.pro'
}
}
}
dependencies {
implementation fileTree(dir: 'libs', include: ['*.jar'])
implementation 'com.android.support:appcompat-v7:28.+'
implementation 'com.android.support.constraint:constraint-layout:1.0.2'
testImplementation 'junit:junit:4.12'
androidTestImplementation 'com.android.support.test:runner:1.0.1'
androidTestImplementation 'com.android.support.test.espresso:espresso-core:3.0.1'
implementation 'com.didi.virtualapk:core:0.9.8'
}3. The Application of the new project is inherited from Application and initialized in attachBaseContext method
public class App extends Application{
@Override
protected void attachBaseContext(Context base) {
super.attachBaseContext(base);
PluginManager.getInstance(base).init();
}
}4. Introduce custom Application in Android manifest.xml
<application
android:name=".App"
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme">
<activity android:name=".MainActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application>5. Declaration of authority
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" /> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" />
II. Introducing VirtualApk into Plugin
1. Add dependency in the build.gradle file of the project:
dependencies {
classpath 'com.didi.virtualapk:gradle:0.9.8.6'
}The complete gradle file is as follows:
// Top-level build file where you can add configuration options common to all sub-projects/modules.
buildscript {
repositories {
google()
jcenter()
}
dependencies {
classpath 'com.android.tools.build:gradle:3.1.4'
classpath 'com.didi.virtualapk:gradle:0.9.8.6'
// NOTE: Do not place your application dependencies here; they belong
// in the individual module build.gradle files
}
}
allprojects {
repositories {
google()
jcenter()
}
}
task clean(type: Delete) {
delete rootProject.buildDir
}2. Add dependency in the build.gradle file of app:
apply plugin: 'com.didi.virtualapk.plugin'
virtualApk{
packageId = 0x6f
targetHost = '../../VirtualAPKHost/app'//app module path of host application
applyHostMapping = true
}3. Add signature configuration to build.gradle file of app
signingConfigs{
release{
storeFile file('../../android.keystore')
storePassword "android"
keyAlias "android"
keyPassword "android"
}
}
buildTypes {
release {
minifyEnabled false
signingConfig signingConfigs.release
proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile('proguard-android.txt'), 'proguard-rules.pro'
}
}The complete gradle file is as follows:
apply plugin: 'com.android.application'
apply plugin: 'com.didi.virtualapk.plugin'
android {
compileSdkVersion 28
defaultConfig {
applicationId "com.wangyz.virtualapk.plugin"
minSdkVersion 21
targetSdkVersion 28
versionCode 1
versionName "1.0"
testInstrumentationRunner "android.support.test.runner.AndroidJUnitRunner"
}
signingConfigs{
release{
storeFile file('../../android.keystore')
storePassword "android"
keyAlias "android"
keyPassword "android"
}
}
buildTypes {
release {
minifyEnabled false
signingConfig signingConfigs.release
proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile('proguard-android.txt'), 'proguard-rules.pro'
}
}
}
dependencies {
implementation fileTree(dir: 'libs', include: ['*.jar'])
implementation 'com.android.support:appcompat-v7:28.+'
implementation 'com.android.support.constraint:constraint-layout:1.0.2'
testImplementation 'junit:junit:4.12'
androidTestImplementation 'com.android.support.test:runner:1.0.1'
androidTestImplementation 'com.android.support.test.espresso:espresso-core:3.0.1'
}
virtualApk{
packageId = 0x6f
targetHost = '../../VirtualAPKHost/app'
applyHostMapping = true
}Note: the resource file of Plugin application cannot have the same name as the resource file of host, otherwise an error will be reported when generating plug-in APK:
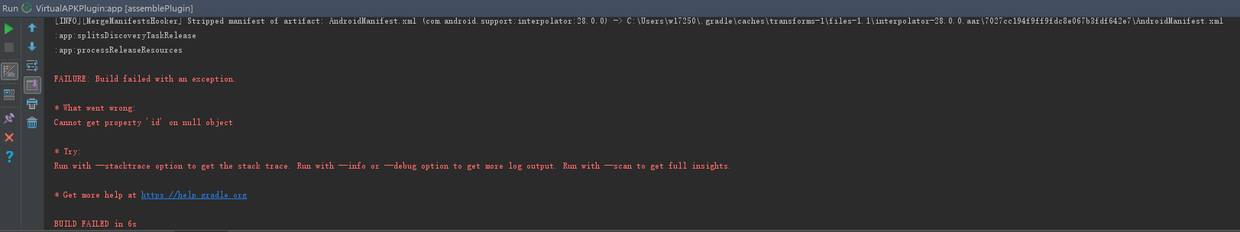
It is recommended that module resource names begin with module names.
4. Generate plug-in APK
Open gradle window, double-click assemblyplugin to generate APK
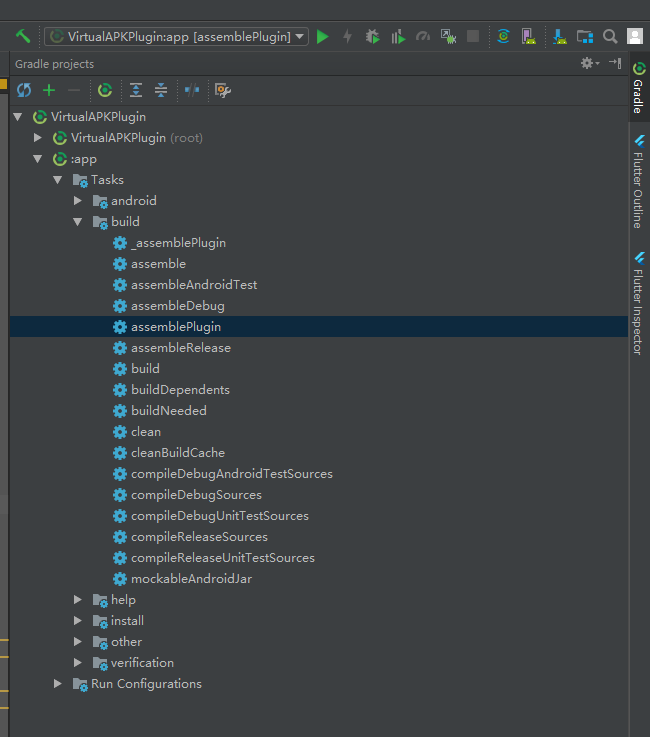
File generation Directory: app/build/outputs/plugin/release/
3. Load the plug-in APK in the host application
1. Push the generated plug-in APK (through the network or adb, etc.) to the specified path of the mobile phone, such as / sdcard/Plugin.apk.
2. Load APK in the host application
private static final String PLUGIN_PACKAGE_NAME = "com.wangyz.virtualapk.plugin";
private static final String PLUGIN_NAME = "com.wangyz.virtualapk.plugin.MainActivity";
private void loadPlugin() {
try {
String pluginPath = Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory().getAbsolutePath().concat("/Plugin.apk");
File plugin = new File(pluginPath);
PluginManager.getInstance(this).loadPlugin(plugin);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}3. Call the Activity in APK
public void loadPlugin(View view) {
if (PluginManager.getInstance(this).getLoadedPlugin(PLUGIN_PACKAGE_NAME) == null) {
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "Plug in not loaded", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
return;
}
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setComponent(new ComponentName(PLUGIN_PACKAGE_NAME, PLUGIN_NAME));
startActivity(intent);
}Source address: https://github.com/miloveting/samples/tree/master/virtuaapk