1. Background
Full text according to Algorithms - Fourth Edition, Dijkstra (Dijkstra) algorithm, a single source shortest path algorithm.We abstract the problem into two steps: 1. Data structure abstraction 2. Implementation.They correspond to Chapter Two and Chapter Three respectively.
2. Algorithmic Analysis
2.1 Data Structure
Vertex+Edge->Graph.Note: The limitations of the Dijkstra algorithm:
- 1. Edges have weight and are not negative
- 2. Edge Directed
2.1.1 Weighted Directed Edges
DirectedEdge, API abstracted as follows:
| Method | describe |
| DirectedEdge(int v, int w, double weight) | Construct Edges |
| double weight() | Edge weight |
| int from() | The starting point of the edge |
| int to() | End point of edge |
2.1.2 Weighted Directed Graph
EdgeWeightedDigraph, API abstracted as follows:
| Method | describe |
| EdgeWeightedDigraph(In in) | Construct a graph from an input stream |
| int V() | Total number of vertices |
| int E() | Total Edges |
| void addEdge(DirectedEdge e) | Add Edge e to the diagram |
| Iterable<DirectedEdge> adj(int v) | Edges indicated from vertex v (contiguity table, a hash list, key=vertex, value=vertex-indicated edge chain list) |
| Iterable<DirectedEdge> edges() | All edges in the graph |
2.1.3 Shortest Path
DijkstraSP, API abstracted as follows:
| Method | describe |
| DijkstraSP(EdgeWeightedDigraph G, int s) | Construct Shortest Path Tree |
| double distTo(int v) | Distance from vertex s->v to initialize infinity |
| boolean hasPathTo(int v) | Is there a path to vertex s->v |
| Iterable<DirectedEdge> pathTo(int v) | S->v path, does not exist as null |
Elements:
Edges in the shortest path tree (DirectedEdge[] edgeTo):
The edgeTo[v] represents the edge in the tree that connects V to the parent node (the last array of edges of the shortest path). Each vertex has such an edge that makes up the shortest path tree.
Distance from origin to vertex: array double[] distTo indexed by vertices:
distTo[v] represents the shortest distance from the origin to vertex v.
Index Minimum Priority Queue: IndexMinPQ<Double> pq:
int[] pq: index binary heap (element=vertex v, corresponding to keys[v]): array is inserted from pq[0] on behalf of origin and other vertices from pq[1]
Key[] keys: The shortest distance an ordered array of elements (assigned as a subscript according to the pq value) is stored to a vertex
2.2 algorithm core
Calculate the shortest path in three steps:
- 1. Select the minimum node vertex at a time: If so?Use the minimum heap sorting, each time you pick up the top element of the heap.
- 2. Traverse all edges emitted from vertices
- 3. Relax
3. Specific implementation
3.1 Construction
3.1.1 Element Iterator
Because of traversal requirements, the Bag<Item>class is defined here to implement the Iterable<Item>iterator interface, where Item is an element.Is the basic implementation of an iterator for a simple element.
1 package study.algorithm.base; 2 3 import java.util.Iterator; 4 import java.util.NoSuchElementException; 5 6 /** 7 * The {@code Bag} class represents a bag (or multiset) of 8 * generic items. It supports insertion and iterating over the 9 * items in arbitrary order. 10 * <p> 11 * This implementation uses a singly linked list with a static nested class Node. 12 * See {@link LinkedBag} for the version from the 13 * textbook that uses a non-static nested class. 14 * See {@link ResizingArrayBag} for a version that uses a resizing array. 15 * The <em>add</em>, <em>isEmpty</em>, and <em>size</em> operations 16 * take constant time. Iteration takes time proportional to the number of items. 17 * <p> 18 * For additional documentation, see <a href="https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/13stacks">Section 1.3</a> of 19 * <i>Algorithms, 4th Edition</i> by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne. 20 * 21 * @author Robert Sedgewick 22 * @author Kevin Wayne 23 * 24 * @param <Item> the generic type of an item in this bag 25 */ 26 public class Bag<Item> implements Iterable<Item> { 27 /** 28 * First Node 29 */ 30 private Node<Item> first; 31 /** 32 * Number of elements 33 */ 34 private int n; 35 36 /** 37 * Linked Table 38 * @param <Item> 39 */ 40 private static class Node<Item> { 41 private Item item; 42 private Node<Item> next; 43 } 44 45 /** 46 * Initialize an empty package 47 */ 48 public Bag() { 49 first = null; 50 n = 0; 51 } 52 53 /** 54 * Returns true if this bag is empty. 55 * 56 * @return {@code true} if this bag is empty; 57 * {@code false} otherwise 58 */ 59 public boolean isEmpty() { 60 return first == null; 61 } 62 63 /** 64 * Returns the number of items in this bag. 65 * 66 * @return the number of items in this bag 67 */ 68 public int size() { 69 return n; 70 } 71 72 /** 73 * Adds the item to this bag. 74 * 75 * @param item the item to add to this bag 76 */ 77 public void add(Item item) { 78 // Keep the old first node 79 Node<Item> oldfirst = first; 80 // Construct a new first node 81 first = new Node<Item>(); 82 // item Is New First Node item 83 first.item = item; 84 // New Node's next Node Points to Old First Node 85 first.next = oldfirst; 86 n++; 87 } 88 89 90 /** 91 * Returns an iterator that iterates over the items in this bag in arbitrary order. 92 * 93 * @return an iterator that iterates over the items in this bag in arbitrary order 94 */ 95 @Override 96 public Iterator<Item> iterator() { 97 return new LinkedIterator(first); 98 } 99 100 /** 101 * Link iterator, remove not supported 102 */ 103 private class LinkedIterator implements Iterator<Item> { 104 private Node<Item> current; 105 106 public LinkedIterator(Node<Item> first) { 107 current = first; 108 } 109 110 @Override 111 public boolean hasNext() { return current != null; } 112 @Override 113 public void remove() { throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); } 114 115 @Override 116 public Item next() { 117 if (!hasNext()) { 118 throw new NoSuchElementException(); 119 } 120 Item item = current.item; 121 // Next Node 122 current = current.next; 123 return item; 124 } 125 } 126 127 /** 128 * Unit tests the {@code Bag} data type. 129 * 130 * @param args the command-line arguments 131 */ 132 public static void main(String[] args) { 133 Bag<String> bag = new Bag<String>(); 134 while (!StdIn.isEmpty()) { 135 String item = StdIn.readString(); 136 bag.add(item); 137 } 138 139 StdOut.println("size of bag = " + bag.size()); 140 for (String s : bag) { 141 StdOut.println(s); 142 } 143 } 144 145 }
3.1.2 Specific Constructions
1. Initialize the diagram from the input stream in the format of the input stream (comments in parentheses, not in the actual file):
8 (Number of vertices)
15 (Number of Edges)
45 0.35 (edge 4->5 weight=0.35)
5 4 0.35
4 7 0.37
5 7 0.28
7 5 0.28
5 1 0.32
0 4 0.38
0 2 0.26
7 3 0.39
1 3 0.29
2 7 0.34
6 2 0.40
3 6 0.52
6 0 0.58
6 4 0.93
In the following figure, the public EdgeWeightedDigraph (In) construction method, core:
Adds weighted edges to the adjacency table where vertices are array subscripts.
1 package study.algorithm.graph; 2 3 import study.algorithm.base.*; 4 5 import java.util.NoSuchElementException; 6 7 /*** 8 * @Description Edge Weighted Directed Graph 9 * @author denny.zhang 10 * @date 2020/4/24 9:58 morning 11 */ 12 public class EdgeWeightedDigraph { 13 private static final String NEWLINE = System.getProperty("line.separator"); 14 15 /** 16 * Total number of vertices 17 */ 18 private final int V; 19 /** 20 * Total Edges 21 */ 22 private int E; 23 /** 24 * adjacency list 25 */ 26 private Bag<DirectedEdge>[] adj; 27 28 /** 29 * Initialize the diagram from the input stream format: 30 * 8(Number of vertices) 31 * 15(Total Edges) 32 * 4 5 0.35(4->5 weights 0.35 per edge) 33 * 5 4 0.35 34 * 4 7 0.37 35 * ... 36 * 37 * @param in the input stream 38 * @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code in} is {@code null} 39 * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the endpoints of any edge are not in prescribed range 40 * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the number of vertices or edges is negative 41 */ 42 public EdgeWeightedDigraph(In in) { 43 if (in == null) { 44 throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument is null"); 45 } 46 try { 47 // 1.Number of read vertices 48 this.V = in.readInt(); 52 // Initialize adjacency table 53 adj = (Bag<DirectedEdge>[]) new Bag[V]; 54 for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) { 55 adj[v] = new Bag<DirectedEdge>(); 56 } 57 // 2.Number of read edges 58 int E = in.readInt(); 59 62 for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) { 63 int v = in.readInt(); 64 int w = in.readInt(); 67 // 3.Reading Edge Weights 68 double weight = in.readDouble(); 69 // Add Weight Edge 70 addEdge(new DirectedEdge(v, w, weight)); 71 } 72 } 73 catch (NoSuchElementException e) { 74 throw new IllegalArgumentException("invalid input format in EdgeWeightedDigraph constructor", e); 75 } 76 } 77 78 /** 79 * Number of vertices 80 * 81 * @return the number of vertices in this edge-weighted digraph 82 */ 83 public int V() { 84 return V; 85 } 86 87 /** 88 * Number of Edges 89 * 90 * @return the number of edges in this edge-weighted digraph 91 */ 92 public int E() { 93 return E; 94 } 95 106 /** 107 * Add an edge to the diagram 108 * 109 * @param e the edge 110 * @throws IllegalArgumentException unless endpoints of edge are between {@code 0} 111 * and {@code V-1} 112 */ 113 public void addEdge(DirectedEdge e) { 114 // Starting point of edge 115 int v = e.from(); 116 // End point of edge 117 int w = e.to();120 // Starting point v Add an edge to the adjacency table of 121 adj[v].add(e); 122 // Total Edges+1 123 E++; 124 } 125 126 127 /** 128 * Returns all iterative edges indicated from vertex V (adjacency table) 129 * 130 * @param v the vertex 131 * @return the directed edges incident from vertex {@code v} as an Iterable 132 * @throws IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= v < V} 133 */ 134 public Iterable<DirectedEdge> adj(int v) { 135 validateVertex(v); 136 return adj[v]; 137 } 138 139 /** 140 * Return all directed edges 141 * 142 * @return all edges in this edge-weighted digraph, as an iterable 143 */ 144 public Iterable<DirectedEdge> edges() { 145 Bag<DirectedEdge> list = new Bag<DirectedEdge>(); 146 // Traverse all vertices 147 for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) { 148 // Contiguity table for each vertex (pointing out edges) 149 for (DirectedEdge e : adj(v)) { 150 // Point out edges list 151 list.add(e); 152 } 153 } 154 return list; 155 } 156 157 /** 158 * Returns a string representation of this edge-weighted digraph. 159 * 160 * @return the number of vertices <em>V</em>, followed by the number of edges <em>E</em>, 161 * followed by the <em>V</em> adjacency lists of edges 162 */ 163 @Override 164 public String toString() { 165 StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder(); 166 s.append(V + " " + E + NEWLINE); 167 for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) { 168 s.append(v + ": "); 169 for (DirectedEdge e : adj[v]) { 170 s.append(e + " "); 171 } 172 s.append(NEWLINE); 173 } 174 return s.toString(); 175 } 176 177 /** 178 * Unit tests the {@code EdgeWeightedDigraph} data type. 179 * 180 * @param args the command-line arguments 181 */ 182 public static void main(String[] args) { 183 In in = new In(args[0]); 184 EdgeWeightedDigraph G = new EdgeWeightedDigraph(in); 185 StdOut.println(G); 186 } 187 188 }
3.2 Calculate Shortest Path
3.2.1 Index Priority Queue
1 package study.algorithm.base; 2 3 import java.util.Iterator; 4 import java.util.NoSuchElementException; 5 6 /** 7 * Index Minimum Priority Queue 8 * 9 * @param <Key> 10 */ 11 public class IndexMinPQ<Key extends Comparable<Key>> implements Iterable<Integer> { 12 /** 13 * Maximum number of elements 14 */ 15 private int maxN; 16 /** 17 * Number of elements 18 */ 19 private int n; 20 /** 21 * Index binary heap (element = vertex v, corresponding to keys[v]): pq[0] represents the origin, other vertices are inserted from pq[1] 22 */ 23 private int[] pq; 24 /** 25 * The position of the element marked with index I in the binary heap.Inverted array of PQ (qp[index]=i): qp[pq[i] = pq[qp[i]] = I 26 */ 27 private int[] qp; 28 29 /** 30 * Ordered array of elements (assigned by index of pq) 31 */ 32 private Key[] keys; 33 34 /** 35 * Initialize an empty index priority queue, index range: 0 ~ maxN-1 36 * 37 * @param maxN the keys on this priority queue are index from {@code 0} 38 * {@code maxN - 1} 39 * @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code maxN < 0} 40 */ 41 public IndexMinPQ(int maxN) { 42 if (maxN < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException(); 43 this.maxN = maxN; 44 // Initially there are 0 elements 45 n = 0; 46 // Initialization key array length is maxN + 1 47 keys = (Key[]) new Comparable[maxN + 1]; 48 // Initialization"Key-Value Pairs"Array length is maxN + 1 49 pq = new int[maxN + 1]; 50 // Initialization"Value Key Pair"Array length is maxN + 1 51 qp = new int[maxN + 1]; 52 // Traverse to"Value Key Pair"Array assignment-1,Follow-up as long as!=-1,That is, contains i 53 for (int i = 0; i <= maxN; i++) 54 qp[i] = -1; 55 } 56 57 /** 58 * Returns true if this priority queue is empty. 59 * 60 * @return {@code true} if this priority queue is empty; 61 * {@code false} otherwise 62 */ 63 public boolean isEmpty() { 64 return n == 0; 65 } 66 67 /** 68 * Is {@code i} an index on this priority queue? 69 * 70 * @param i an index 71 * @return {@code true} if {@code i} is an index on this priority queue; 72 * {@code false} otherwise 73 * @throws IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= i < maxN} 74 */ 75 public boolean contains(int i) { 76 validateIndex(i); 77 return qp[i] != -1; 78 } 79 80 /** 81 * Returns the number of keys on this priority queue. 82 * 83 * @return the number of keys on this priority queue 84 */ 85 public int size() { 86 return n; 87 } 88 89 /** 90 * Insert an element to associate element key with index i 91 * 92 * @param i an index 93 * @param key the key to associate with index {@code i} 94 * @throws IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= i < maxN} 95 * @throws IllegalArgumentException if there already is an item associated 96 * with index {@code i} 97 */ 98 public void insert(int i, Key key) { 99 validateIndex(i); 100 if (contains(i)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("index is already in the priority queue"); 101 // Number of elements+1 102 n++; 103 // Index is i Binary heap location is n 104 qp[i] = n; 105 // Insert new element at bottom of binary heap, value=i 106 pq[n] = i; 107 // Indexes i Corresponding element assignment 108 keys[i] = key; 109 // Last element floating up in binary heap (small value floating up) 110 swim(n); 111 } 112 113 /** 114 * Returns the index of the smallest element 115 * 116 * @return an index associated with a minimum key 117 * @throws NoSuchElementException if this priority queue is empty 118 */ 119 public int minIndex() { 120 if (n == 0) throw new NoSuchElementException("Priority queue underflow"); 121 return pq[1]; 122 } 123 124 /** 125 * Return the minimum element (key) 126 * 127 * @return a minimum key 128 * @throws NoSuchElementException if this priority queue is empty 129 */ 130 public Key minKey() { 131 if (n == 0) throw new NoSuchElementException("Priority queue underflow"); 132 return keys[pq[1]]; 133 } 134 135 /** 136 * Delete the minimum key and return the minimum value 137 * 138 * @return an index associated with a minimum key 139 * @throws NoSuchElementException if this priority queue is empty 140 */ 141 public int delMin() { 142 if (n == 0) throw new NoSuchElementException("Priority queue underflow"); 143 // pq[1]That is, the minimum value of the index 144 int min = pq[1]; 145 // Swap the first and last elements 146 exch(1, n--); 147 // Drop the first element in exchange 148 sink(1); 149 // After verification sinks, the last element is the minimum value 150 assert min == pq[n+1]; 151 // Restore the initial value,-1 That means the element has been deleted 152 qp[min] = -1; // delete 153 // Convenient garbage collection 154 keys[min] = null; 155 // Last element (index) assignment-1 156 pq[n+1] = -1; // not needed 157 return min; 158 } 159 160 /** 161 * Returns the key associated with index {@code i}. 162 * 163 * @param i the index of the key to return 164 * @return the key associated with index {@code i} 165 * @throws IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= i < maxN} 166 * @throws NoSuchElementException no key is associated with index {@code i} 167 */ 168 public Key keyOf(int i) { 169 validateIndex(i); 170 if (!contains(i)) throw new NoSuchElementException("index is not in the priority queue"); 171 else return keys[i]; 172 } 173 174 /** 175 * Change the key associated with index {@code i} to the specified value. 176 * 177 * @param i the index of the key to change 178 * @param key change the key associated with index {@code i} to this key 179 * @throws IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= i < maxN} 180 * @throws NoSuchElementException no key is associated with index {@code i} 181 */ 182 public void changeKey(int i, Key key) { 183 validateIndex(i); 184 if (!contains(i)) throw new NoSuchElementException("index is not in the priority queue"); 185 keys[i] = key; 186 swim(qp[i]); 187 sink(qp[i]); 188 } 189 190 /** 191 * Change the key associated with index {@code i} to the specified value. 192 * 193 * @param i the index of the key to change 194 * @param key change the key associated with index {@code i} to this key 195 * @throws IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= i < maxN} 196 * @deprecated Replaced by {@code changeKey(int, Key)}. 197 */ 198 @Deprecated 199 public void change(int i, Key key) { 200 changeKey(i, key); 201 } 202 203 /** 204 * Decrease the value of index i to key 205 * To update: 206 * 1.Element array keys[] 207 * 2.Small Top Binary Heap pq[] 208 * 209 * @param i the index of the key to decrease 210 * @param key decrease the key associated with index {@code i} to this key 211 * @throws IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= i < maxN} 212 * @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code key >= keyOf(i)} 213 * @throws NoSuchElementException no key is associated with index {@code i} 214 */ 215 public void decreaseKey(int i, Key key) { 216 validateIndex(i); 217 if (!contains(i)) throw new NoSuchElementException("index is not in the priority queue"); 218 // key Same value, error 219 if (keys[i].compareTo(key) == 0) 220 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Calling decreaseKey() with a key equal to the key in the priority queue"); 221 // key Greater than current value, error 222 if (keys[i].compareTo(key) < 0) 223 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Calling decreaseKey() with a key strictly greater than the key in the priority queue"); 224 // key Smaller than the current value, key Assignment in 225 keys[i] = key; 226 // Small values float up ( qp[i]=Indexes i In Binary Heap pq[]Position in) 227 swim(qp[i]); 228 } 229 230 /** 231 * Increase the key associated with index {@code i} to the specified value. 232 * 233 * @param i the index of the key to increase 234 * @param key increase the key associated with index {@code i} to this key 235 * @throws IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= i < maxN} 236 * @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code key <= keyOf(i)} 237 * @throws NoSuchElementException no key is associated with index {@code i} 238 */ 239 public void increaseKey(int i, Key key) { 240 validateIndex(i); 241 if (!contains(i)) throw new NoSuchElementException("index is not in the priority queue"); 242 if (keys[i].compareTo(key) == 0) 243 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Calling increaseKey() with a key equal to the key in the priority queue"); 244 if (keys[i].compareTo(key) > 0) 245 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Calling increaseKey() with a key strictly less than the key in the priority queue"); 246 keys[i] = key; 247 sink(qp[i]); 248 } 249 250 /** 251 * Remove the key associated with index {@code i}. 252 * 253 * @param i the index of the key to remove 254 * @throws IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= i < maxN} 255 * @throws NoSuchElementException no key is associated with index {@code i} 256 */ 257 public void delete(int i) { 258 validateIndex(i); 259 if (!contains(i)) throw new NoSuchElementException("index is not in the priority queue"); 260 int index = qp[i]; 261 exch(index, n--); 262 swim(index); 263 sink(index); 264 keys[i] = null; 265 qp[i] = -1; 266 } 267 268 // throw an IllegalArgumentException if i is an invalid index 269 private void validateIndex(int i) { 270 if (i < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("index is negative: " + i); 271 if (i >= maxN) throw new IllegalArgumentException("index >= capacity: " + i); 272 } 273 274 /*************************************************************************** 275 * General helper functions. 276 ***************************************************************************/ 277 private boolean greater(int i, int j) { 278 return keys[pq[i]].compareTo(keys[pq[j]]) > 0; 279 } 280 281 private void exch(int i, int j) { 282 int swap = pq[i]; 283 pq[i] = pq[j]; 284 pq[j] = swap; 285 qp[pq[i]] = i; 286 qp[pq[j]] = j; 287 } 288 289 290 /*************************************************************************** 291 * Heap helper functions. 292 ***************************************************************************/ 293 private void swim(int k) { 294 // If the parent node value is larger than the current node value, swap, and the parent node is the current node, polling.That is, small values float up. 295 while (k > 1 && greater(k/2, k)) { 296 exch(k, k/2); 297 k = k/2; 298 } 299 } 300 301 private void sink(int k) { 302 while (2*k <= n) { 303 int j = 2*k; 304 if (j < n && greater(j, j+1)) j++; 305 if (!greater(k, j)) break; 306 exch(k, j); 307 k = j; 308 } 309 } 310 311 312 /*************************************************************************** 313 * Iterators. 314 ***************************************************************************/ 315 316 /** 317 * Returns an iterator that iterates over the keys on the 318 * priority queue in ascending order. 319 * The iterator doesn't implement {@code remove()} since it's optional. 320 * 321 * @return an iterator that iterates over the keys in ascending order 322 */ 323 @Override 324 public Iterator<Integer> iterator() { return new HeapIterator(); } 325 326 private class HeapIterator implements Iterator<Integer> { 327 // create a new pq 328 private IndexMinPQ<Key> copy; 329 330 // add all elements to copy of heap 331 // takes linear time since already in heap order so no keys move 332 public HeapIterator() { 333 copy = new IndexMinPQ<Key>(pq.length - 1); 334 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) 335 copy.insert(pq[i], keys[pq[i]]); 336 } 337 338 @Override 339 public boolean hasNext() { return !copy.isEmpty(); } 340 @Override 341 public void remove() { throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); } 342 343 @Override 344 public Integer next() { 345 if (!hasNext()) throw new NoSuchElementException(); 346 return copy.delMin(); 347 } 348 } 349 350 351 /** 352 * Unit tests the {@code IndexMinPQ} data type. 353 * 354 * @param args the command-line arguments 355 */ 356 public static void main(String[] args) { 357 // insert a bunch of strings 358 String[] strings = { "it", "was", "the", "best", "of", "times", "it", "was", "the", "worst" }; 359 360 IndexMinPQ<String> pq = new IndexMinPQ<String>(strings.length); 361 for (int i = 0; i < strings.length; i++) { 362 pq.insert(i, strings[i]); 363 } 364 365 // delete and print each key 366 while (!pq.isEmpty()) { 367 int i = pq.delMin(); 368 StdOut.println(i + " " + strings[i]); 369 } 370 StdOut.println(); 371 372 // reinsert the same strings 373 for (int i = 0; i < strings.length; i++) { 374 pq.insert(i, strings[i]); 375 } 376 377 // print each key using the iterator 378 for (int i : pq) { 379 StdOut.println(i + " " + strings[i]); 380 } 381 while (!pq.isEmpty()) { 382 pq.delMin(); 383 } 384 385 } 386 }
3.2.2 Shortest Path
1 package study.algorithm.graph; 2 3 import study.algorithm.base.In; 4 import study.algorithm.base.IndexMinPQ; 5 import study.algorithm.base.Stack; 6 import study.algorithm.base.StdOut; 7 8 /*** 9 * @Description Single Start Shortest Path Tree for Weighted Directed Graph with Nonnegative Edge Weights 10 * @author denny.zhang 11 * @date 2020/4/23 11:29 morning 12 */ 13 public class DijkstraSP { 14 15 /** 16 * Shortest path array, element: shortest path to all vertices 17 */ 18 private double[] distTo; 19 20 /** 21 * Directed edge array: the last edge array of the shortest path 22 */ 23 private DirectedEdge[] edgeTo; 24 25 /** 26 * Vertex as subscript, index minimum priority queue 27 */ 28 private IndexMinPQ<Double> pq; 29 30 /** 31 * Compute the Shortest Path Edge Weight Graph from Origin S to all other vertices 32 * 33 * @param G the edge-weighted digraph Edge Weight Graph 34 * @param s the source vertex origin 35 * @throws IllegalArgumentException if an edge weight is negative 36 * @throws IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= s < V} 37 */ 38 public DijkstraSP(EdgeWeightedDigraph G, int s) { 39 // Negative Weight Check 40 for (DirectedEdge e : G.edges()) { 41 if (e.weight() < 0) { 42 throw new IllegalArgumentException("edge " + e + " has negative weight"); 43 } 44 } 45 // Shortest path array length=Number of vertices 46 distTo = new double[G.V()]; 47 // Construct an array of shortest path edges whose length is the total number of vertices 48 edgeTo = new DirectedEdge[G.V()]; 49 // Check Origin Value 50 validateVertex(s); 51 // Initialize all vertices to infinity 52 for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) { 53 distTo[v] = Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY; 54 } 55 // Minimum path initialized to origin is 0 56 distTo[s] = 0.0; 57 58 // Construct an index minimum priority queue with a length of total vertices 59 pq = new IndexMinPQ<Double>(G.V()); 60 // Insert the origin, path 0 61 pq.insert(s, distTo[s]); 62 // As long as the queue is not empty(From top to bottom, iterate through in sequence pq[]), 63 while (!pq.isEmpty()) { 64 // Remove Minimum key(That is pq[1]),And returns the minimum value (vertex) 65 int v = pq.delMin(); 66 // Traversal vertices v Contiguity table for each edge 67 for (DirectedEdge e : G.adj(v)) { 68 // Relax the edges 69 relax(e); 70 } 71 } 72 73 // check 74 assert check(G, s); 75 } 76 77 /** 78 * Relax and update pq 79 * @param e 80 */ 81 private void relax(DirectedEdge e) { 82 // Start point, end point 83 int v = e.from(), w = e.to(); 84 // If Origin to End w Distance of > Origin to Start v Distance of+Edge weights indicate origin to w Relaxed 85 if (distTo[w] > distTo[v] + e.weight()) { 86 // Latest Distance 87 distTo[w] = distTo[v] + e.weight(); 88 // To End w Edge assignment to new edge 89 edgeTo[w] = e; 90 // If the priority queue already contains an end point w 91 if (pq.contains(w)) { 92 // The comparison subscript is w Of key If>Current path (that is, the current value is smaller than the median value of the queue), reordering 93 pq.decreaseKey(w, distTo[w]); 94 } else { 95 // Do not include, insert, and sort 96 pq.insert(w, distTo[w]); 97 } 98 } 99 } 100 101 /** 102 * s->v Shortest path 103 * @param v the destination vertex 104 * @return the length of a shortest path from the source vertex {@code s} to vertex {@code v}; 105 * {@code Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY} if no such path 106 * @throws IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= v < V} 107 */ 108 public double distTo(int v) { 109 validateVertex(v); 110 return distTo[v]; 111 } 112 113 /** 114 * s->v Is it reachable 115 * 116 * @param v the destination vertex 117 * @return {@code true} if there is a path from the source vertex 118 * {@code s} to vertex {@code v}; {@code false} otherwise 119 * @throws IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= v < V} 120 */ 121 public boolean hasPathTo(int v) { 122 validateVertex(v); 123 return distTo[v] < Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY; 124 } 125 126 /** 127 * s->v Minimum Iterable Edge (1->2->3) 128 * 129 * @param v the destination vertex 130 * @return a shortest path from the source vertex {@code s} to vertex {@code v} 131 * as an iterable of edges, and {@code null} if no such path 132 * @throws IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= v < V} 133 */ 134 public Iterable<DirectedEdge> pathTo(int v) { 135 validateVertex(v); 136 if (!hasPathTo(v)) { 137 return null; 138 } 139 // Iterable Directed Edge Stack 140 Stack<DirectedEdge> path = new Stack<DirectedEdge>(); 141 // e Is Vertex v The last edge of the shortest path tree, tracing back to the last vertex 3 along the edge->2->1 142 for (DirectedEdge e = edgeTo[v]; e != null; e = edgeTo[e.from()]) { 143 // Stack 144 path.push(e); 145 } 146 return path; 147 } 148 149 150 // check optimality conditions: 151 // (i) for all edges e: distTo[e.to()] <= distTo[e.from()] + e.weight() 152 // (ii) for all edge e on the SPT: distTo[e.to()] == distTo[e.from()] + e.weight() 153 private boolean check(EdgeWeightedDigraph G, int s) { 154 155 // Check edge weight is not negative 156 for (DirectedEdge e : G.edges()) { 157 if (e.weight() < 0) { 158 System.err.println("negative edge weight detected"); 159 return false; 160 } 161 } 162 163 // Vertex-to-vertex path is 0 and vertex-to-vertex edge is empty 164 if (distTo[s] != 0.0 || edgeTo[s] != null) { 165 System.err.println("distTo[s] and edgeTo[s] inconsistent"); 166 return false; 167 } 168 // Traversal vertices 169 for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) { 170 // Start Skip 171 if (v == s) { 172 continue; 173 } 174 // To vertex v The last edge is empty (unreachable) and reaches the vertex v The shortest path does not conflict with infinity (that is, it has value) 175 if (edgeTo[v] == null && distTo[v] != Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY) { 176 System.err.println("distTo[] and edgeTo[] inconsistent"); 177 return false; 178 } 179 } 180 181 // Verify all edges are not relaxed 182 for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) { 183 // Traversal vertices v Adjacent edges of 184 for (DirectedEdge e : G.adj(v)) { 185 int w = e.to(); 186 // Check Relaxation 187 if (distTo[v] + e.weight() < distTo[w]) { 188 System.err.println("edge " + e + " not relaxed"); 189 return false; 190 } 191 } 192 } 193 194 // Check Shortest Path Tree: Satisfy distTo[w] == distTo[v] + e.weight() 195 for (int w = 0; w < G.V(); w++) { 196 // Skip unreachable vertices 197 if (edgeTo[w] == null) { 198 continue; 199 } 200 // Last Edge 201 DirectedEdge e = edgeTo[w]; 202 // Starting point 203 int v = e.from(); 204 //End 205 if (w != e.to()) { 206 return false; 207 } 208 // Check: Shortest-path Tree, Start-point Path+weight=End Path 209 if (distTo[v] + e.weight() != distTo[w]) { 210 System.err.println("edge " + e + " on shortest path not tight"); 211 return false; 212 } 213 } 214 return true; 215 } 216 217 // throw an IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= v < V} 218 private void validateVertex(int v) { 219 int V = distTo.length; 220 if (v < 0 || v >= V) { 221 throw new IllegalArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (V-1)); 222 } 223 } 224 225 /** 226 * Unit tests the {@code DijkstraSP} data type. 227 * 228 * @param args the command-line arguments 229 */ 230 public static void main(String[] args) { 231 // Diagram file name 232 In in = new In(args[0]); 233 // Constructing Edge Weighted Directed Graph 234 EdgeWeightedDigraph G = new EdgeWeightedDigraph(in); 235 // vertex 236 int s = Integer.parseInt(args[1]); 237 238 // Calculate Shortest Path 239 DijkstraSP sp = new DijkstraSP(G, s); 240 241 // Traverse all vertices 242 for (int t = 0; t < G.V(); t++) { 243 // accessible 244 if (sp.hasPathTo(t)) { 245 // Origin to t Path Length 246 StdOut.printf("%d to %d (%.2f) ", s, t, sp.distTo(t)); 247 // Origin to t Path Map 248 for (DirectedEdge e : sp.pathTo(t)) { 249 StdOut.print(e + " "); 250 } 251 // Line Break 252 StdOut.println(); 253 } 254 // Unreachable 255 else { 256 StdOut.printf("%d to %d no path\n", s, t); 257 } 258 } 259 } 260 261 }
4. Test results
4.1 Test Preparation
A file, tinyEWD.txt, exists locally as follows:
8 15 4 5 0.35 5 4 0.35 4 7 0.37 5 7 0.28 7 5 0.28 5 1 0.32 0 4 0.38 0 2 0.26 7 3 0.39 1 3 0.29 2 7 0.34 6 2 0.40 3 6 0.52 6 0 0.58 6 4 0.93
4.2 Test
Run DijkstraSP locally and configure the running parameters. Take idea for example: the first parameter is the file address, the second parameter represents the origin 0, calculates the "shortest path" edge weight graph from the origin (vertex 0) to all other vertices:
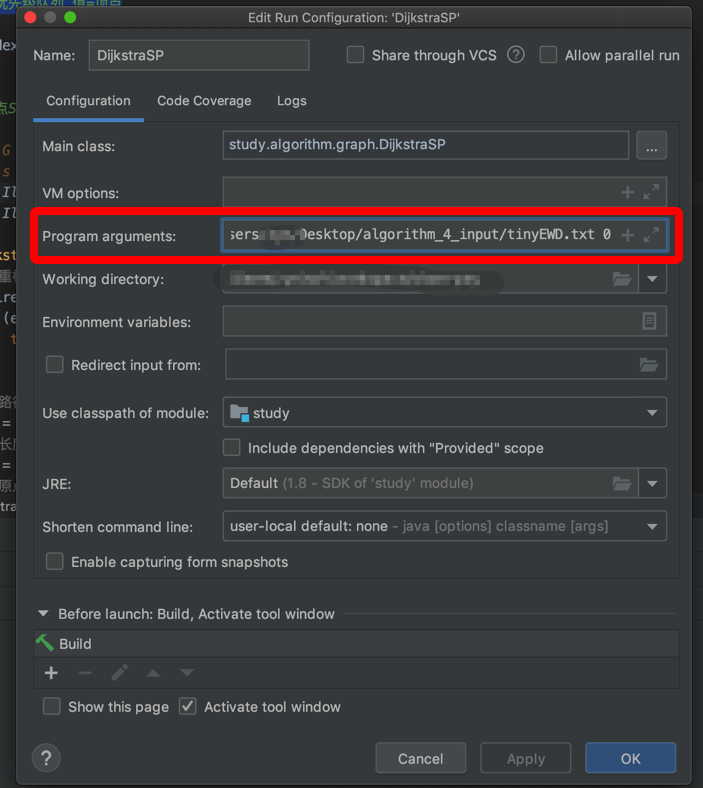
The shortest path to run is as follows:
