Shiro
1. Introduction
- Apache Shiro is a Java security (permissions) framework.
- Shiro can easily develop applications that are good enough not only for JavaSE environments, but also for JavaEE environments.
- Shiro can complete authentication, authorization, encryption, session management, Web integration, caching, and more.
- Download address: https://shiro.apache.org/
2. Operating principle
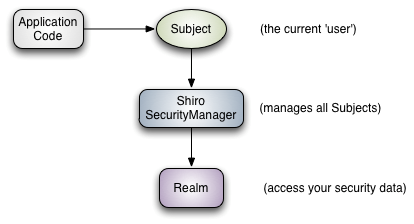
Subject: Subject actually represents the user currently performing the operation, just because "User" generally refers to a person, but a "Subject" can be a person, or any third-party system, service account, and any other third-party software system that is interacting with the current system.
SecurityManager: Security Manager.That is, all security-related operations interact with SecurityManager, and it manages all subject s.
Realm: There can be one or more Realms that can be thought of as security entity data sources, which are used to obtain security entities.
3. Shiro filter
Shiro has built-in filters to implement privilege-related interceptors.
| Common filters | Explain |
|---|---|
| anon | Access without authentication (login) |
| authc | Authentication is required to access |
| user | Direct access if using rememberMe functionality |
| perms | Have access to a resource |
| roles | Have a role to access |
4. Springboot Integration Shiro
4.1, Add Dependency
<!--mysql rely on--> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <version>5.1.40</version> </dependency> <!--spring-jdbc rely on--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId> <version>4.3.7.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <!--thymeleaf--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId> </dependency> <!--springweb--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <!--shiro--> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId> <artifactId>shiro-spring</artifactId> <version>1.4.0</version> </dependency> <!--lombok--> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> <version>1.18.12</version> </dependency> <!--druid--> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId> <artifactId>druid</artifactId> <version>1.1.4</version> </dependency> <!--mybatis-spring-boot-starter --> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>2.1.1</version> </dependency>
4.2, Shiro Configuration Class
@Configuration public class ShiroConfig { /** * Create ShiroFilterFactoryBean */ @Bean public ShiroFilterFactoryBean getShiroFilterFactoryBean(@Qualifier("securityManager") DefaultWebSecurityManager securityManager) { ShiroFilterFactoryBean shiroFilterFactoryBean = new ShiroFilterFactoryBean(); //Set up a security manager shiroFilterFactoryBean.setSecurityManager(securityManager); //Add Shiro built-in filter /** * Shiro Built-in filter for privilege-related interceptors * Common filters: * anon: Access without authentication (login) * authc: Authentication is required to access * user: Direct access if using rememberMe functionality * perms: Have access to a resource * role: Have a role to access */ Map<String, String> filterMap = new LinkedHashMap<String, String>(); // filterMap.put("/add", "authc"); //filterMap.put("/update", "authc"); //filterMap.put("/testThymeleaf", "anon"); //Release the login.html page filterMap.put("/login", "anon"); //Authorization Filter //Note: Shi shiro will automatically jump to an unauthorized page after the current authorization intercept //Content in perms brackets is the value of permission //To grant authorization filterMap.put("/user/add", "perms[user:add]"); //filterMap.put("/update", "perms[user:update]"); //Modify the adjusted login page shiroFilterFactoryBean.setLoginUrl("/toLogin"); //Set up unauthorized prompt page shiroFilterFactoryBean.setUnauthorizedUrl("/noAuth"); shiroFilterFactoryBean.setFilterChainDefinitionMap(filterMap); return shiroFilterFactoryBean; } /** * Create DefaultWebSecurityManager * It mainly defines login, create subject, log out and so on. */ @Bean(name = "securityManager") public DefaultWebSecurityManager getDefaultWebSecurityManager(@Qualifier("userRealm") UserRealm userRealm) { DefaultWebSecurityManager securityManager = new DefaultWebSecurityManager(); //Associated realm securityManager.setRealm(userRealm); return securityManager; } /** * Create Realm */ @Bean(name = "userRealm") public UserRealm getRealm() { return new UserRealm(); } }
4.3, Custom Realm
(1) Authenticating Realm:shiro for authentication, which implements the doGetAuthentcationInfo method for user login authentication logic; (2) AuthorizingRealm: shiro for authorization, doGetAuthrozitionInfo method for user authorization logic, AuthorizingRealm inherits AuthenticatingRealm, so the main use in practice is this AuthenticatingRealm class; (3) Both AuthenticatingRealm and AuthorizingRealm classes are realm interfaces that provide some threads in shiro (4) In a project integrated with spring, shiro's SecurityManager automatically invokes these two methods for authentication and authorization, which can be combined with shiro's CacheManager to save authentication and authorization information in the cache.
public class UserRealm extends AuthorizingRealm { @Autowired private UserService userService; /** * To grant authorization * @param principalCollection * @return */ @Override protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principalCollection) { SimpleAuthorizationInfo info = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo(); info.addStringPermission("user:add"); return null; } /** * Authenticate whenever user information is required * @param authenticationToken * @return * @throws AuthenticationException */ @Override protected SimpleAuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) throws AuthenticationException { //Get User Name UsernamePasswordToken token = (UsernamePasswordToken) authenticationToken; String username = token.getUsername(); //Validate database User user = userService.findByName(username); if(user == null){ return null; } return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo("",user.getPassword(),""); } }