1, shiro internal structure
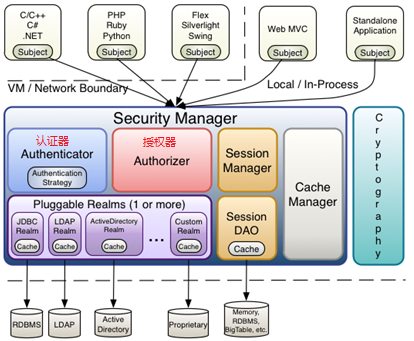
1. Components contained in shiro
shiro mainly includes Authenticator, authorizer, session manager, encryption, remember me and cache manager
2. Introduction to components of shiro
Subject: the subject, which can be understood as the user interacting with the application, contains all the information of the user, such as user information, user role, user authority, whether to log in, etc;
Security Manager: Security Manager shiro manages all modules of shiro through security manager.
Authenticator: authenticator, which is responsible for authenticating whether the user is a legal user. The specific authentication process of authenticator is to process whether the user is a legal user through realm;
Authorizer: authorizer, which is responsible for authorizing users. The specific authorization of authorizer is to obtain the permissions of users through realm;
Realm: you can have one or more realms, or you can customize the realm. In the shiro framework, the realm is very important to handle the user's authentication information and authorization information;
Session manager: responsible for session management;
SessionDAO: curd operation on session;
CacheManager: can cache user permission information to provide performance;
Cryptography: cryptographic module, which encrypts and saltes the password;
shiro manages the authenticator, authorizer, session manager, cache, sessionDao, realm through the securityManager authentication manager. The application side (app) interacts with the securityManager authentication manager through the subject. The authentication manager is responsible for proxy to the authenticator or authorizer. The authenticator authorizer finally obtains the user's authentication information or authorization information through the realm
2, pom files on which shiro depends
<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId> <artifactId>shiro-core</artifactId> <version>1.3.2</version> </dependency>
3, Using shiro as ini file
1. User authentication Demo
The content of shiro1.ini file is as follows
#Users impersonate real users [users] # Format user name = password xiaoming=123 xiaohong=123456
@Test public void testAuthenticate(){ //1. Load ini file create IniSecurityManagerFactory from ini file IniSecurityManagerFactory managerFactory = new IniSecurityManagerFactory("classpath:shiro1.ini"); //2. Get security manager SecurityManager instance = managerFactory.getInstance(); //3. Bind the current SecurityManager to the current environment SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(instance); //4. Get subject subject object Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject(); //5. Set user name and password UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("xiaoming","123"); //6. Log in subject.login(token); //7. Check whether the user logs in successfully true success false failure System.out.println(subject.isAuthenticated()); }
2. User authorization Demo
The content of shiro2.ini file is as follows
#Users impersonate real users [users] # Format user name = password. For example, if the password of xiaoming is 123 and the role of admin corresponds to the role of user:save,user:delete,user:update,user:find xiaoming=123,admin xiaohong=123456,manager #roles simulation role information [roles] #Format role name = the corresponding permissions of the role, such as admin role with user:save,user:delete,user:update,user:find permission manager role with user:find permission admin=user:save,user:delete,user:update,user:find manager=user:find
@Test public void testAuthrizer(){ //1. Load ini file create IniSecurityManagerFactory from ini file IniSecurityManagerFactory managerFactory = new IniSecurityManagerFactory("classpath:shiro2.ini"); //2. Get security manager SecurityManager instance = managerFactory.getInstance(); //3. Bind the current SecurityManager to the current environment SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(instance); //4. Get subject subject object Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject(); //5. Set user name and password UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("xiaohong","123456"); //6. Log in subject.login(token); //7. View roles and permissions owned by users System.out.println(subject.hasRole("manager")); System.out.println(subject.isPermitted("user:update")); }
3. Custom realm Demo
The content of shiro3.ini file is as follows
[main] #Declare custom realm name = custom realm class fully qualified name customerRealm=com.xiao.shiro.CustomerRealm #Register realm to Security Manager securityManager.realms=$customerRealm
Custom realm
public class CustomerRealm extends AuthorizingRealm { //Customize the name of the realm because there may be more than one realm in the shiro framework. According to the name of the realm, decide which realm to use for processing @Override public void setName(String name) { super.setName("CustomerRealm"); } //Authorization when the subject calls to get the user role, the method doGetAuthorizationInfo will be called @Override protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principalCollection) { System.out.println("Authorization start"); //User information can be obtained from principalCollection String primaryPrincipal = (String) principalCollection.getPrimaryPrincipal(); SimpleAuthorizationInfo info = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo(); info.addRoles(Arrays.asList("manager","admin")); info.addStringPermission("user:update"); return info; } //Authentication the method doGetAuthenticationInfo is called when the subject calls the user to log in @Override protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) throws AuthenticationException { System.out.println("Start of certification"); //When the user logs in, subject.login(token); the token type passed in is UsernamePasswordToken //So you can force the authenticationToken to UsernamePasswordToken UsernamePasswordToken token = (UsernamePasswordToken) authenticationToken; String username = token.getUsername(); String pwd = new String (token.getPassword()); //The user name and password found from the database are xiaoming 123 if ("xiaoming".equals(username) && "123".equals(pwd)) { //Authentication is achieved by storing the user information in the AuthenticationInfo object //The three parameters of SimpleAuthenticationInfo are as follows //1. Object principal user information can be any type of object //2. Object credentials password //3. String realmName the name of the current realm AuthenticationInfo authenticationInfo = new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(username,pwd,getName()); return authenticationInfo; } //Exception thrown if authentication fails throw new RuntimeException("Login failed"); } }
@Test public void testCustomerRealm(){ //1. Load ini file create IniSecurityManagerFactory from ini file IniSecurityManagerFactory managerFactory = new IniSecurityManagerFactory("classpath:shiro3.ini"); //2. Get security manager SecurityManager instance = managerFactory.getInstance(); //3. Bind the current SecurityManager to the current environment SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(instance); //4. Get subject subject object Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject(); //5. Set user name and password UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("xiaoming","123"); //6. When logging in the subject, the doGetAuthenticationInfo method in the realm will be called subject.login(token); //7. View the roles and permissions owned by the user. When the subject obtains the roles or permissions, it will call the doGetAuthorizationInfo method in the realm System.out.println(subject.hasRole("manager")); System.out.println(subject.isPermitted("user:find")); }
4. Use cache to save user role information and permission information Demo
Use ehcache as cache
shiro-ehcache.xml configuration information
<ehcache xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="../config/ehcache.xsd"> <defaultCache maxElementsInMemory="1000" maxElementsOnDisk="10000000" eternal="false" overflowToDisk="false" diskPersistent="false" timeToIdleSeconds="120" timeToLiveSeconds="120" diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds="120" memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU"> </defaultCache> </ehcache>
@Test public void testCacheManager(){ //1. Load ini file create IniSecurityManagerFactory from ini file IniSecurityManagerFactory managerFactory = new IniSecurityManagerFactory("classpath:shiro3.ini"); //2. Get security manager if CacheManager is enabled, cachesecuritymanager object is required CachingSecurityManager instance = (CachingSecurityManager) managerFactory.getInstance(); //3. Create cache management objects (ehcache is used for cache, so EhCacheManager is used) other cache objects can be used EhCacheManager ehCacheManager = new EhCacheManager(); //4. Read ehcache configuration file ehCacheManager.setCacheManagerConfigFile("classpath:shiro-ehcache.xml"); //5. Set the EhCacheManager object to the cacheingsecuritymanager Security Manager instance.setCacheManager(ehCacheManager); //6. Bind the current SecurityManager to the current environment SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(instance); //7. Get subject subject object Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject(); //8. Set user name and password UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("xiaoming","123"); //9. Log in subject.login(token); //10. When viewing the roles and permissions owned by users, the first time they get permission information, they will call the doGetAuthorizationInfo method in the realm, and the second time they directly get from the cache, they will not walk away from the realm System.out.println(subject.hasRole("manager")); System.out.println(subject.isPermitted("user:find")); }
5. Clear cached user information
@Test public void testCacheManager(){ //1. Load ini file create IniSecurityManagerFactory from ini file IniSecurityManagerFactory managerFactory = new IniSecurityManagerFactory("classpath:shiro3.ini"); //2. Get security manager if CacheManager is enabled, cachesecuritymanager object is required CachingSecurityManager instance = (CachingSecurityManager) managerFactory.getInstance(); //3. Create cache management objects (ehcache is used for cache, so EhCacheManager is used) other cache objects can be used EhCacheManager ehCacheManager = new EhCacheManager(); //4. Read ehcache configuration file ehCacheManager.setCacheManagerConfigFile("classpath:shiro-ehcache.xml"); //5. Set the EhCacheManager object to the cacheingsecuritymanager Security Manager instance.setCacheManager(ehCacheManager); //6. Bind the current SecurityManager to the current environment SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(instance); //7. Get subject subject object Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject(); //8. Set user name and password UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("xiaoming","123"); //9. Log in subject.login(token); //10. When viewing the roles and permissions owned by users, the first time they get permission information, they will call the doGetAuthorizationInfo method in the realm, and the second time they directly get from the cache, they will not walk away from the realm System.out.println(subject.hasRole("manager")); System.out.println(subject.isPermitted("user:find")); //Get ehcache user cache information Cache<Object, Object> cache = ehCacheManager.getCache("CustomerRealm.authorizationCache"); //Clear the corresponding cache information of xiaoming user cache.remove(new SimplePrincipalCollection("xiaoming", "CustomerRealm")); //Get user role and permission information from the realm after clearing the cache System.out.println(subject.hasRole("manager")); System.out.println(subject.isPermitted("user:find")); }
3, Integrating shiro with springboot
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.xiao.shiro</groupId> <artifactId>shirodemo</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.2.1.RELEASE</version> </parent> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>1.3.1</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <version>8.0.13</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>tk.mybatis</groupId> <artifactId>mapper-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>2.0.2</version> </dependency> <!--shiro core--> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId> <artifactId>shiro-core</artifactId> <version>1.3.2</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.12</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>commons-logging</groupId> <artifactId>commons-logging</artifactId> <version>1.1.3</version> </dependency> <!-- ehcache --> <dependency> <groupId>net.sf.ehcache</groupId> <artifactId>ehcache-core</artifactId> <version>2.6.11</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId> <artifactId>shiro-all</artifactId> <version>1.3.2</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId> <artifactId>fastjson</artifactId> <version>1.2.44</version> </dependency> <!--spring and shiro integration --> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId> <artifactId>shiro-spring</artifactId> <version>1.3.2</version> </dependency> <!--shiro And redis integration--> <dependency> <groupId>org.crazycake</groupId> <artifactId>shiro-redis</artifactId> <version>3.0.0</version> </dependency> <!--thymeleaf --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId> </dependency> </dependencies> </project>
2. Custom realm
public class CustomerRealm extends AuthorizingRealm { @Autowired private UserInfoService userInfoService; //Customize the name of the realm because there may be more than one realm in the shiro framework. According to the name of the realm, decide which realm to use for processing @Override public void setName(String name) { super.setName("CustomerRealm"); } //Authorization when the subject calls to get the user role, the method doGetAuthorizationInfo will be called @Override protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principalCollection) { System.out.println("Authorization start"); //User information can be obtained from principalCollection UserInfo userInfo = (UserInfo) principalCollection.getPrimaryPrincipal(); SimpleAuthorizationInfo info = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo(); UserDto userExtInfo = userInfoService.findUserExtInfo(userInfo.getId()); info.addRoles(userExtInfo.getRoles()); info.addStringPermissions(userExtInfo.getPermissions()); return info; } //Authentication the method doGetAuthenticationInfo is called when the subject calls the user to log in @Override protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) throws AuthenticationException { System.out.println("Start of certification"); //When the user logs in, subject.login(token); the token type passed in is UsernamePasswordToken //So you can force the authenticationToken to UsernamePasswordToken UsernamePasswordToken token = (UsernamePasswordToken) authenticationToken; String username = token.getUsername(); String pwd = new String (token.getPassword()); UserInfo user = userInfoService.findUserByUserNameAndPwd(username, pwd); //The user name and password found from the database are xiaoming 123 if (user != null) { //Authentication is achieved by storing the user information in the AuthenticationInfo object //The three parameters of SimpleAuthenticationInfo are as follows //1. Object principal user information can be any type of object //2. Object credentials password //3. String realmName the name of the current realm AuthenticationInfo authenticationInfo = new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(user, pwd, getName()); return authenticationInfo; } //Exception thrown if authentication fails throw new RuntimeException("Login failed"); } }
3. shiro configuration class
@Configuration public class ShiroConfig { //Give the custom realm to the spring container for management @Bean public CustomerRealm getCustomerRealm(){ return new CustomerRealm(); } @Bean public SecurityManager getSecurityManager(CustomerRealm realm){ //Create a security manager and give the realm to the manager for management DefaultWebSecurityManager securityManager = new DefaultWebSecurityManager(realm); return securityManager; } //Configure shiro filter conditions and jump page @Bean public ShiroFilterFactoryBean shiroFilterFactoryBean(SecurityManager securityManager){ ShiroFilterFactoryBean bean = new ShiroFilterFactoryBean(); //Set up security manager bean.setSecurityManager(securityManager); //Login page bean.setLoginUrl("/tologin"); //Authorization failure jump page bean.setUnauthorizedUrl("/toUnauthorized"); //LinkedHashMap must be used to ensure the order of filtering Map<String, String> map = new LinkedHashMap<>(); //anon anonymous access means access without login and authorization //authc requires authentication login to access //Logout logout logout logout to jump to the page set by bean.setLoginUrl() method //perms[xx] has xx permission to access //roles[xx] can only be accessed by roles of xx map.put("/user/index", "anon"); //Indicates that you have select user permission to access map.put("/user/select", "perms[select-user]"); //Represents the role of system administrator to access map.put("/user/delete", "roles[system administrator]"); //Only authentication login can access map.put("/user/**", "authc"); //Set the filter chain of the request. The filter chain needs to be authenticated in order. It is usually placed after anonymous access bean.setFilterChainDefinitionMap(map); return bean; } }
4. Test controller
@Controller public class TestController { @RequestMapping("/login") public String login(UserInfo userInfo) { try { UsernamePasswordToken upt = new UsernamePasswordToken(userInfo.getUsername(), userInfo.getPassword()); SecurityUtils.getSubject().login(upt); return "Login successful"; } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); return "Login failed"; } } @RequestMapping("/user/index") @ResponseBody public String index(){ return "visit index success"; } @RequestMapping("/user/select") @ResponseBody public String select(){ return "visit select success"; } @RequestMapping("/user/delete") @ResponseBody public String delete(){ return "visit delete success"; } @RequestMapping("/user/login") @ResponseBody public String login(){ return "visit login success"; } //Skip landing page @RequestMapping("/tologin") public String tologin(){ return "login"; } //Skip unauthorized page @RequestMapping("/toUnauthorized") public String toUnauthorized(){ return "unauthorized"; } }
5. Permission control by shiro annotation
(1) . add a dependency to the pom file by referring to the above dependency
(2) The shiro configuration class adds the configuration of the two objects DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator and AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor
@Configuration public class ShiroConfig { //To enable shiro annotation, you need to configure two objects: DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator and AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor @Bean public DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator getDefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator() { DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator autoProxyCreator = new DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator(); //Turn on proxy for spring AOP autoProxyCreator.setProxyTargetClass(true); return autoProxyCreator; } @Bean public CustomerRealm getCustomerRealm(){ return new CustomerRealm(); } @Bean public SecurityManager getSecurityManager(CustomerRealm realm){ //Create a security manager and give the realm to the manager for management DefaultWebSecurityManager securityManager = new DefaultWebSecurityManager(realm); return securityManager; } //Configure launch shiro annotation @Bean public AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor getAuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor(SecurityManager securityManager) { AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor advisor = new AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor(); advisor.setSecurityManager(securityManager); return advisor; } //Configure shiro filter conditions and jump page @Bean public ShiroFilterFactoryBean shiroFilterFactoryBean(SecurityManager securityManager){ ShiroFilterFactoryBean bean = new ShiroFilterFactoryBean(); //Set up security manager bean.setSecurityManager(securityManager); //Login page bean.setLoginUrl("/tologin"); //Authorization failure jump page bean.setUnauthorizedUrl("/toUnauthorized"); //LinkedHashMap must be used to ensure the order of filtering Map<String, String> map = new LinkedHashMap<>(); //anon anonymous access means access without login and authorization //authc requires authentication login to access //Logout logout logout logout to jump to the page set by bean.setLoginUrl() method //perms[xx] has xx permission to access //roles[xx] can only be accessed by roles of xx map.put("/user/index", "anon"); map.put("/login", "anon"); //Indicates that you have select user permission to access map.put("/user/select", "perms[select-user]"); //Represents the role of system administrator to access map.put("/user/delete", "roles[system administrator]"); //Only authentication login can access map.put("/**", "authc"); //Set the filter chain of the request. The filter chain needs to be authenticated in order. It is usually placed after anonymous access bean.setFilterChainDefinitionMap(map); return bean; }
(3) , test controller
@Controller public class TestController { //Skip landing page @RequestMapping("/tologin") public String tologin(){ return "login"; } //Skip unauthorized page @RequestMapping("/toUnauthorized") public String toUnauthorized(){ return "unauthorized"; } //User add and user delete permission are available to access @RequiresPermissions(value = {"user-add","user-delete"}) @RequestMapping("/testPermission") @ResponseBody public String testPermission(){ return "test Permission success"; } //Only administrator role can access @RequiresRoles(value = "administrators") @RequestMapping("/testRoles") @ResponseBody public String tesRoles(){ return "test role success"; } }
shiro's method based on filter chain (such as map.put("/**", "authc")) is different from that based on annotation (such as @ RequiresRoles) when they no longer have access
If you do not have permission, you will jump to the address set by setunauthorized URL ("/ tounauthorized")
If you do not have permission to annotate, you will throw an AuthorizationException exception. You can customize a global exception to handle annotation. The code is as follows
@ControllerAdvice public class CustomerExceptionHandler { //Catch an exception of type AuthorizationException @ExceptionHandler(value = AuthorizationException.class) @ResponseBody public String error(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,AuthorizationException e) { return "Unauthorized"; } }
4, shiro password encryption
public static void main(String[] args) { //The three parameters are as follows //1. Object source original password //2. Object salt value //3. int hashIterations salt several times Md5Hash pwd = new Md5Hash("12345", "salt", 2); System.out.println(pwd.toString()); }
5, Spring boot integrates session management of shiro to store sessions in redis
shiro provides three default implementations of session manager by default
(1) . DefaultSessionManager: for Java se environment
(2) . ServletContainerSessionManager: used in the web environment. By default, the web environment uses this implementation class session information in the httpSession
(3) . DefaultWebSessionManager: used in the web environment. The session information can be stored in the specified place, such as mysql and redis
1. Introducing Shiro redis dependency
<dependency> <groupId>org.crazycake</groupId> <artifactId>shiro-redis</artifactId> <version>3.0.0</version> </dependency>
2. Introduce redis configuration into application.yml
spring: redis: host: 127.0.0.1 port: 6379
3. Customize shiro session manager
public class CustomerSessionManager extends DefaultWebSessionManager { /** * sessionid in header information * Request header: Authorization: sessionid * * Specify how to get sessionId */ @Override protected Serializable getSessionId(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response) { //Get data in request header Authorization String id = WebUtils.toHttp(request).getHeader("Authorization"); if(StringUtils.isEmpty(id)) { //If it is not carried, a new sessionId will be generated return super.getSessionId(request,response); }else{ //Specify the source of sessionId specify to get sessionId from the request header do not specify to get sessionId from the cookie by default request.setAttribute(ShiroHttpServletRequest.REFERENCED_SESSION_ID_SOURCE, "header"); //sessionId request.setAttribute(ShiroHttpServletRequest.REFERENCED_SESSION_ID, id); request.setAttribute(ShiroHttpServletRequest.REFERENCED_SESSION_ID_IS_VALID, Boolean.TRUE); return id; } } }
4. Configure shiro session management to store in redis
package com.xiao.shiro.config; import com.xiao.shiro.realm.CustomerRealm; import com.xiao.shiro.session.CustomerSessionManager; import org.apache.shiro.mgt.SecurityManager; import org.apache.shiro.spring.LifecycleBeanPostProcessor; import org.apache.shiro.spring.security.interceptor.AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor; import org.apache.shiro.spring.web.ShiroFilterFactoryBean; import org.apache.shiro.web.mgt.DefaultWebSecurityManager; import org.apache.shiro.web.session.mgt.DefaultWebSessionManager; import org.crazycake.shiro.RedisCacheManager; import org.crazycake.shiro.RedisManager; import org.crazycake.shiro.RedisSessionDAO; import org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.LinkedHashMap; import java.util.Map; @Configuration public class ShiroConfig { @Bean public CustomerRealm getCustomerRealm(){ return new CustomerRealm(); } @Bean public SecurityManager getSecurityManager(CustomerRealm realm){ //Create a security manager and give the realm to the manager for management DefaultWebSecurityManager securityManager = new DefaultWebSecurityManager(realm); //Register a custom session manager with the Security Manager securityManager.setSessionManager(sessionManager()); //Register the customized redis cache manager to the Security Manager securityManager.setCacheManager(cacheManager()); return securityManager; } //Configure launch shiro annotation @Bean public AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor getAuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor(SecurityManager securityManager) { AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor advisor = new AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor(); advisor.setSecurityManager(securityManager); return advisor; } //Configure shiro filter conditions and jump page @Bean public ShiroFilterFactoryBean shiroFilterFactoryBean(SecurityManager securityManager){ ShiroFilterFactoryBean bean = new ShiroFilterFactoryBean(); //Set up security manager bean.setSecurityManager(securityManager); //Login page bean.setLoginUrl("/tologin"); //Authorization failure jump page bean.setUnauthorizedUrl("/toUnauthorized"); //LinkedHashMap must be used to ensure the order of filtering Map<String, String> map = new LinkedHashMap<>(); //anon anonymous access means access without login and authorization //authc requires authentication login to access //Logout logout logout logout to jump to the page set by bean.setLoginUrl() method //perms[xx] has xx permission to access //roles[xx] can only be accessed by roles of xx map.put("/user/index", "anon"); map.put("/login", "anon"); //Indicates that you have select user permission to access map.put("/user/select", "perms[select-user]"); //Represents the role of system administrator to access map.put("/user/delete", "roles[system administrator]"); //Only authentication login can access map.put("/**", "authc"); //Set the filter chain of the request. The filter chain needs to be authenticated in order. It is usually placed after anonymous access bean.setFilterChainDefinitionMap(map); return bean; } //To enable shiro annotation, you need to configure two objects: DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator and AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor @Bean public DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator getDefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator() { DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator autoProxyCreator = new DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator(); //Turn on proxy for spring AOP autoProxyCreator.setProxyTargetClass(true); return autoProxyCreator; } @Value("${spring.redis.host}") private String host; @Value("${spring.redis.port}") private int port; /** * 1.redis Operating redis */ public RedisManager redisManager() { RedisManager redisManager = new RedisManager(); redisManager.setHost(host); redisManager.setPort(port); return redisManager; } /** * 2.sessionDao */ public RedisSessionDAO redisSessionDAO() { RedisSessionDAO sessionDAO = new RedisSessionDAO(); sessionDAO.setRedisManager(redisManager()); return sessionDAO; } /** * 3.Session manager */ public DefaultWebSessionManager sessionManager() { CustomerSessionManager sessionManager = new CustomerSessionManager(); sessionManager.setSessionDAO(redisSessionDAO()); return sessionManager; } /** * 4.Cache manager */ public RedisCacheManager cacheManager() { RedisCacheManager redisCacheManager = new RedisCacheManager(); redisCacheManager.setRedisManager(redisManager()); return redisCacheManager; } }
5,AuthenticationInfo authenticationInfo = new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(user, pwd, getName());
The user object here implements two interfaces: serializable and authcacheprincipal
public class UserInfo implements Serializable,AuthCachePrincipal { private Long id; private String username; private String password; public Long getId() { return id; } public void setId(Long id) { this.id = id; } public String getUsername() { return username; } public void setUsername(String username) { this.username = username; } public String getPassword() { return password; } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } //Just write getAuthCacheKey method @Override public String getAuthCacheKey() { return null; }