According to the previous understanding, this time privilege-based authorization is implemented by initializing authorization from the database.
1. Analyse Shiro filter chain
<! - Some interception rules for shiro configuration must have the same id as the shiro interceptor name in web.xml - >
<bean id="shiroFilter" class="org.apache.shiro.spring.web.ShiroFilterFactoryBean">
<! - Shiro's core security interface, this property is necessary - > Shiro's core security interface.
<property name="securityManager" ref="securityManager" />
<! - If the authentication fails, jump to the configuration of the login page - >
<property name="loginUrl" value="/login" />
<! - After successful login page - >
<property name="successUrl" value="/admin/index" />
<! - If the authentication fails, jump to the specified page - >.
<property name="unauthorized Url" value="/unauthorized"/> <!--page jumped after accessing unauthorized pages after login - >"
<! -- Shiro Connection Constraint Configuration, the Definition of Filter Chain - >
<property name="filterChainDefinitions">
<value>
<! - Note: The rules are orderly. From top to bottom, the interception range must be small to large.
url = interception rule (anon is anonymous, authc is to be logged in before access, logout logout filtering) --> ____________
/login = anon
/logout = logout
/admin/userlist = perms[userlist]
/admin/addUser = perms[addUser]
/admin/** = authc
/**= anon
</value>
</property>
</bean>Click on the filter Chain Definitions property to see the source code
1) You can see that it is an attribute of ShiroFilterFactoryBean:
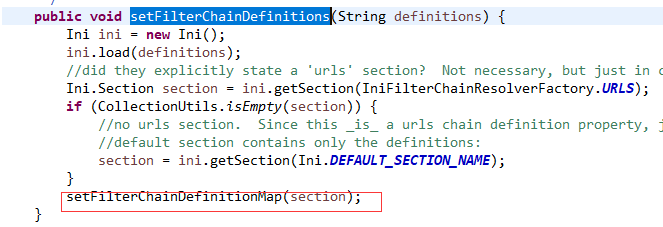
2) After a series of initialization, it calls the setFilterChain DefinitionMap method and opens the method:

3) Through debug, you can see that filter Chain Definition Map is a LinkedHashMap when initializing, and its content is what we configure in the configuration file.
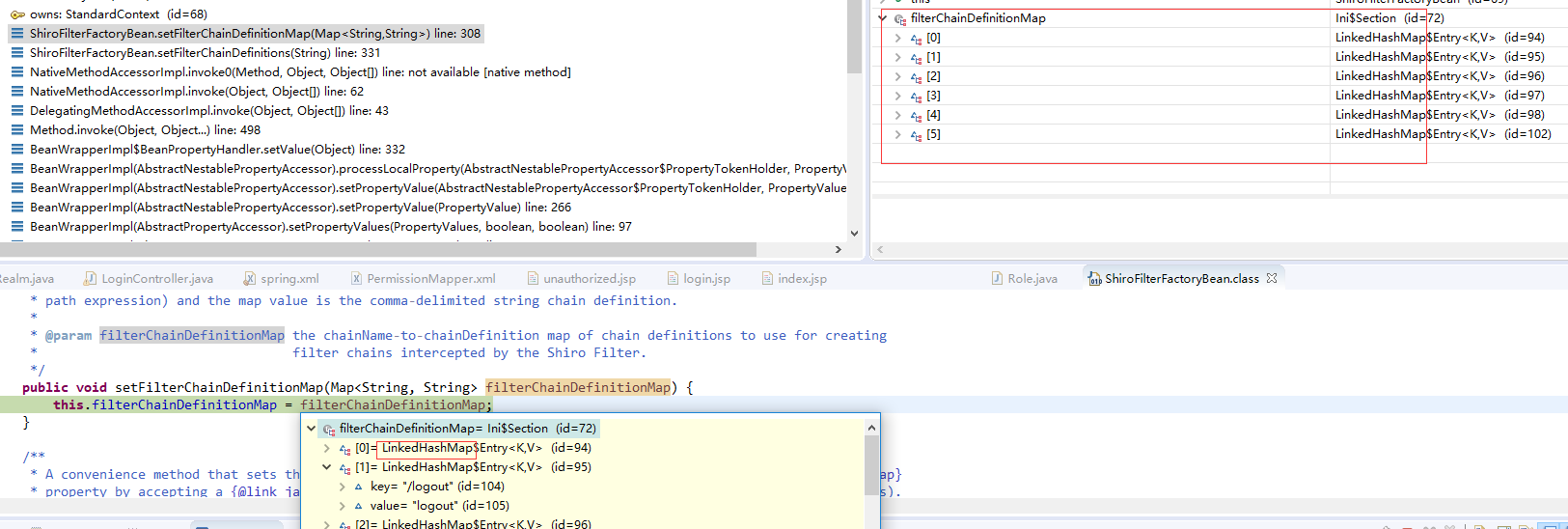
So we can configure a separate bean filter Chain Definition Map as an attribute of ShiroFilterFactoryBean.
Then we generate Map instances registered by instance factories, and then we need to build and configure a new Bean.
2. After analysis, modify spring.xml
Database:
Put authorization information in the database (pre-constraint, perms use p: roles use r:)
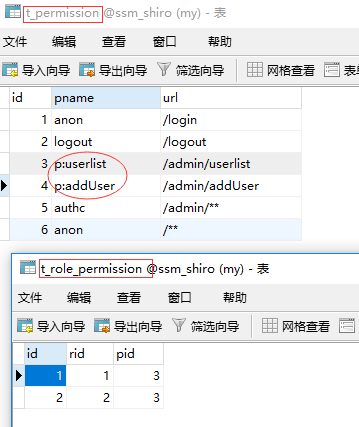
The other tables remain the same as before.
User admin, which only has roles admin and user and permission resources to access / admin/userlist, is accessible if pid is 3 and 4.
Note: The data order of t_permission: From top to bottom, the interception range must be small to large.
1) Configuring bean s
<! - Some interception rules for shiro configuration must have the same id as the shiro interceptor name in web.xml - >
<bean id="shiroFilter" class="org.apache.shiro.spring.web.ShiroFilterFactoryBean">
<! - Shiro's core security interface, this property is necessary - > Shiro's core security interface.
<property name="securityManager" ref="securityManager" />
<! - If the authentication fails, jump to the configuration of the login page - >
<property name="loginUrl" value="/login" />
<! - After successful login page - >
<property name="successUrl" value="/admin/index" />
<! - If the authentication fails, jump to the specified page - >.
<property name="unauthorized Url" value="/unauthorized"/> <!--page jumped after accessing unauthorized pages after login - >"
<property name="filterChainDefinitionMap" ref="filterChainDefinitionMap"></property>
<! -- Shiro Connection Constraint Configuration, the Definition of Filter Chain - >
<!-- <property name="filterChainDefinitions">
<value>
Note: The rules are orderly. From top to bottom, the interception range must be small to large.
url = interception rule (anon is anonymous, authc is accessible only after logout is filtered)
/login = anon
/logout = logout
/admin/userlist = perms[userlist]
/admin/addUser = perms[addUser]
/admin/** = authc
/**= anon
</value>
</property> -->
</bean>
<! - Configuration of beans through instance factory pattern: Configuring a bean injection is a Map instance - >
<bean id="filterChainDefinitionMap" factory-bean="filterChainDefinitionMapFactory" factory-method="getFilterChainDefinitionMap"></bean>
<bean id="filterChainDefinitionMapFactory" class="cn.jq.ssm.service.shiro.FilterChainDefinitionMapFactory"></bean>2) Create this bean
import cn.jq.ssm.dao.PermissionMapper;
import cn.jq.ssm.model.Permission;
public class FilterChainDefinitionMapFactory {
@Autowired
private PermissionMapper permissionMapper;
public Map<String, String> getFilterChainDefinitionMap(){
//Getting data from a database
List<Permission> permissions = permissionMapper.getAllPermissions();
LinkedHashMap<String, String> permsMap = new LinkedHashMap<>();
for (Permission permission : permissions) {
if(permission.getPname().contains("p:")) {
//Construct perms[userlist]
String perms = permission.getPname().replace("p:", ""); //Delete prefix
permsMap.put(permission.getUrl(), "perms["+ perms +"]");
}else {
permsMap.put(permission.getUrl(), permission.getPname());
}
}
return permsMap;
}
}PermissionMapper method:
<select id="getAllPermissions" resultType="cn.jq.ssm.model.Permission"> select p.id,p.pname,p.url from t_permission p </select>
3) Customize ShiroRealm class and handle constraints p:
public class ShiroRealm extends AuthorizingRealm{
/*
* public class ShiroRealm extends AuthenticatingRealm{
*/
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Autowired
private RoleMapper RoleMapper;
@Autowired
private PermissionMapper permissionMapper;
/**
* The method of login authentication in shiro
* @param token
* @return
* @throws AuthenticationException
*/
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
UsernamePasswordToken token2 = (UsernamePasswordToken) token;
String username = token2.getUsername();
User user = userMapper.getUserByUsername(username);
if(user == null) {
throw new UnknownAccountException("Error in username or password!");
}
if(user.getStatus() == 0) {
throw new UnknownAccountException("User name has been disabled, please contact the system administrator!");
}
/**
* principals: User name, or d, can be used to log in to the user's object
* hashedCredentials: Passwords retrieved from the database
* credentialsSalt: Salt Value of Cryptographic Encryption
* RealmName: Class name (Shiro Realm)
*/
ByteSource credentialsSalt = ByteSource.Util.bytes("JQSalt");
AuthenticationInfo info = new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(user, user.getPazzword(), credentialsSalt, getName());
return info;
}
/**
* Approaches to Authorization in shiro
*/
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principals) {
//1 Get the user information after the current successful login from the parameter principals
User user = principals.oneByType(User.class);
//2. Obtain the role information according to the user information in the first step (if the user information contains the role/authority information, take it out directly, if not, get it from the database)
Set<String> roles = RoleMapper.getRolesByUserid(user.getId());
// Obtain role-related permisssion information through user-related role information
Set<String> permissions = permissionMapper.getPermissionsByUserid(user.getId());
Set<String> newPermissions = new HashSet<>();
for (String permission : permissions) {
if(permission.contains("p:")) {
//Delete the Convention prefix
newPermissions.add(permission.replaceAll("p:", ""));
}else {
newPermissions.add(permission);
}
}
//3 Inject the acquired role and privilege resource information associated with the logged-in user into the returned SimpleAuthorizationInfo object
SimpleAuthorizationInfo info = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo();
info.addRoles(roles);
info.addStringPermissions(newPermissions);
return info;
}
}3. Login access project:
The results are consistent with the analysis.
end ~