1, ServletContext class
(1) , what is a ServletConfig object
- ServletContext is an interface
- ServletContext is a domain object
- For a web project, Tomcat will only create a ServletContext object.
(2) , what is a domain object
**Domain object is an object that can be stored like a Map collection (domain refers to the scope of scope). * the domain in the domain object here refers to the effective operation range of data stored in the object. The effective operation range of ServletContext and object is the entire Web project.
| function | Map set | Domain object |
|---|---|---|
| Save data | put() | setAttribute() |
| get data | get() | getAttribute() |
(3) , ServletContext class
- Get the context parameters configured in web.xml
- Get the project path of the current project
- Gets the sentence pair path of the resource or directory on the server disk after the project is published to the server.
- Data can be stored like a map.
(4) , example demonstration
1. Get ServletContext class object
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { // Get ServletContext object // Method 1 ServletConfig config = getServletConfig(); ServletContext context = config.getServletContext(); // Method 2 usually uses this ServletContext context1 = getServletContext(); }
2. Specific function realization
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { // Create a ServletContext object ServletContext context = getServletContext(); // Get the configuration parameters in web.xml < context param > System.out.println("Context parameters url Value:"+context.getInitParameter("url")); // Get the project path of the current project System.out.println("Project path:"+context.getContextPath()); /* * Gets the sentence pair path of the resource or directory on the server disk after the project is published to the server. * The parameter '/' in getRealPath() is to map the path to the WebContent folder of the project * */ System.out.println("Absolute path on server disk:"+context.getRealPath("/")); // Get pictures in img System.out.println("Obtain img Picture path in:"+context.getRealPath("/img/servlet.PNG")); }
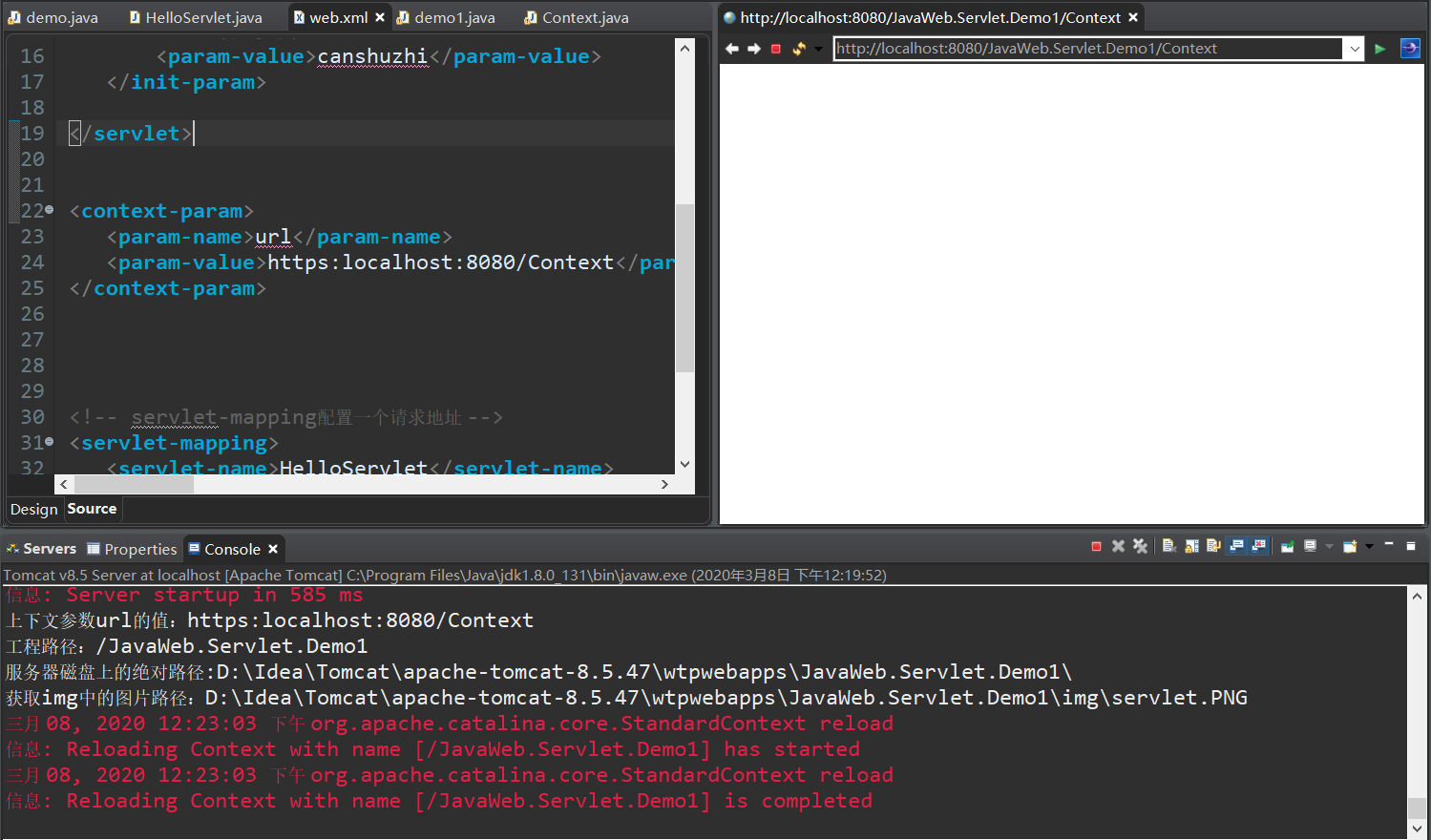
4. ServletContext object stores data
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { ServletContext context = getServletContext(); // Storing data with setAttribute() context.setAttribute("abc","abcValue"); // Get data with getAttribute() System.out.println("from ServletContext Get data in domain object abc Value:"+context.getAttribute("abc")); }
2, HTTP protocol related content
(1) GET request protocol
1. Request line information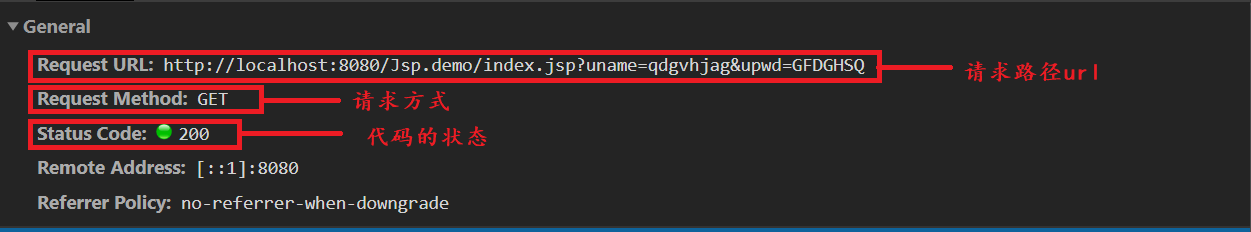
2. Requestor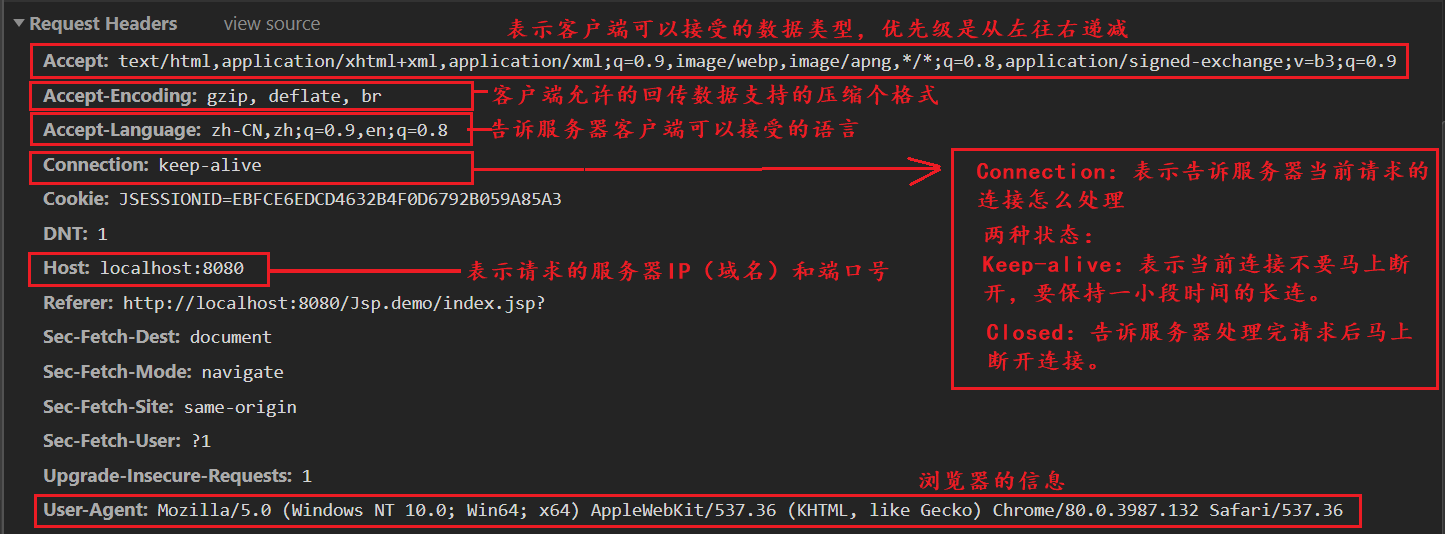
(2) Request protocol for POST
1. Request line information: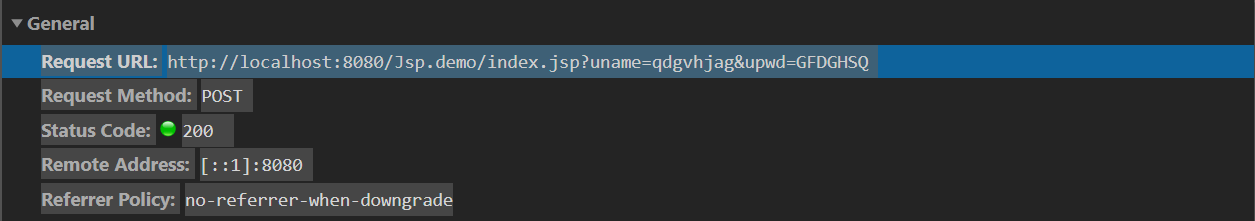
2. Request header information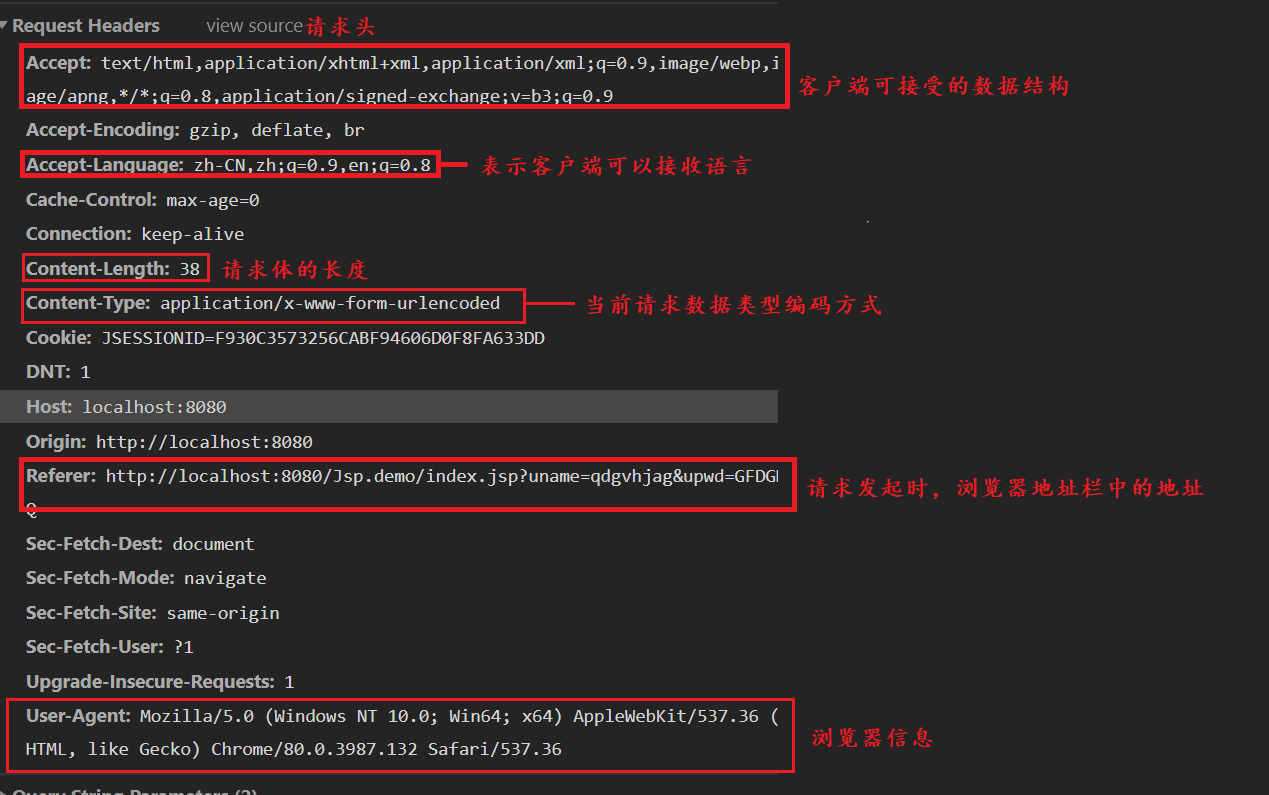
3. Request body information
(2) , the HTTP protocol format of the response

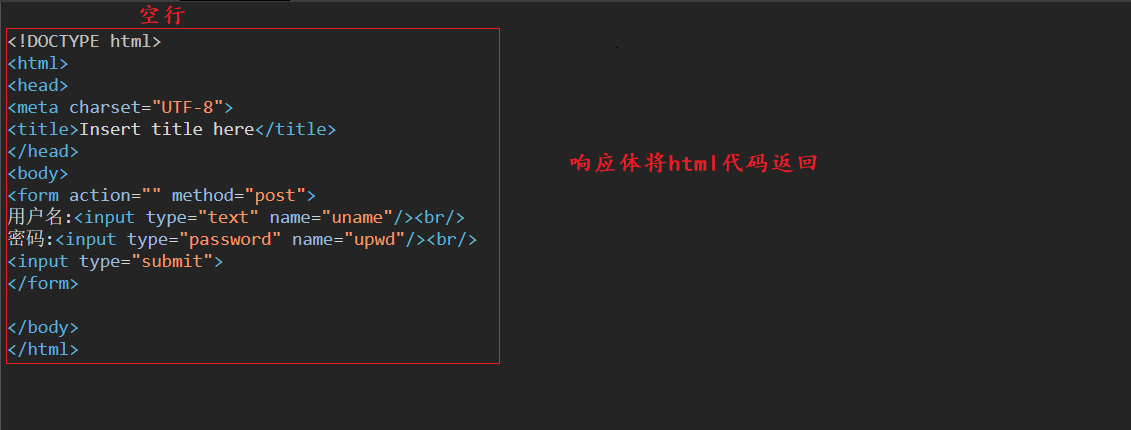
(3) Those in the page are GET requests and those are POST requests (3)
1. GET request
- Enter the request address in the browser address bar, and then click enter
- a tag Script, link, img, iframe introduce form tag method=GET
2. Only method="post" under the form tag is available for POST requests
(4) . common response code
| Response code | Meaning |
|---|---|
| 200 | Indicates that the server successfully processed the client request |
| 302 | Indicates request request jump |
| 304 | Indicates that the client cache version is up to date |
| 404 | Indicates that the server has received the request, but your request is low on resources |
| 500 | Indicates that the server has received the request, but the server has an internal error (code) |

