1. Introduction to ServletContext
- When the web container starts, it creates a ServletContext object for each web application, which represents the current web application.
- Multiple Servlets Share Data through ServletContext Objects
- Getting Initialization Parameters of web Applications
- Implementation of Request Forwarding with ServletContext
- Reading resource files using ServletContext objects
2. Implementing data sharing through servletContext object
1. Get ServletContext through this to share data
//Store data
response.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
ServletContext context = this.getServletContext();
String username="learn java The lightning man";
context.setAttribute("name",username);
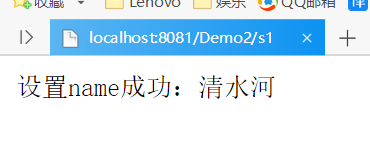
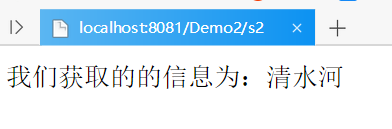
response.getWriter().print("Set up name Success:"+username);//Read data
response.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
ServletContext context = this.getServletContext();
String name = (String) context.getAttribute("name");
response.getWriter().print("The information we get is:"+name);2. Operation results
3. Read the Web Site Configuration File through the servletContext Object
1. Create a new properties file
driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver username=root password=123456 url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/smbms
2. Write servlet classes
//Get the path to the configuration file
String realPath = this.getServletContext().getRealPath(
"WEB-INF/classes/resources/database.properties");
System.out.println("Access path:"+realPath);
Properties properties = new Properties();
FileInputStream is = new FileInputStream(realPath);
//Loading file streams into configuration file objects
properties.load(is);
String driver = properties.getProperty("driver");
String username = properties.getProperty("username");
String password = properties.getProperty("password");
String url = properties.getProperty("url");
//Response to Web pages
response.getWriter().print(driver);
response.getWriter().print(username);
response.getWriter().print(password);
response.getWriter().print(url);3. Configure web.xml
<servlet>
<servlet-name>ServletTest03</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.kuang.servlet.ServletTest03</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>ServletTest03</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/s3</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>4. Visit View
localhost: 8080/demo02/s3

4. Simple Verification Code
//Automatically refresh web pages
response.setHeader("refresh","2");
//Verification code is a picture. We need to make a picture.
BufferedImage image = new BufferedImage(100,30,BufferedImage.TYPE_3BYTE_BGR);
//Write something in the picture
Graphics2D graphics = image.createGraphics();
graphics.setColor(Color.red);
String num = String.valueOf(newRandom());
graphics.drawString(num,10,10);
//Find ways to let browsers know that we're giving a picture
response.setContentType("image/jpg");
//Let the website open the picture
ImageIO.write(image,"jpg",response.getOutputStream());
}
//Generating Random Numbers
public int newRandom(){
int num = (int)(Math.random()*9+1)*100000;
return num;
}