Engineering Overview
All means aimed at improving efficiency, reducing cost and quality assurance belong to engineering
Create project
- Create project structure with scaffolding tools
code
- formatting code
- Compile, build, package
Preview / test
- Web Server/Mock
- HMR
- Source Map
Submit
- Git Hooks
- Continuous integration
deploy
- CI/CD
- Auto publish
Scaffolding tools
Essence: create project infrastructure and provide project specifications and conventions
Yeoman (Universal scaffold tool)
Basic use
Install yeoman
npm install -g yo
Then install the required Generators, which are npm packages called generator XYZ. Install node generator here
npm install -g generator-node
Implement new scaffolding projects
yo node
Sub Generator
You need to determine whether there is a Sub Generator according to the corresponding Generator document
Install the corresponding sub Generator
yo node:cli
Link current module to global
npm link
Execute view results
my-module --help
// output
testing
Usage
$ my-module [input]
Options
--foo Lorem ipsum. [Default: false]
Examples
$ my-module
unicorns
$ my-module rainbows
unicorns & rainbowsSummary of use steps
- Identify requirements and find the right Generator
- Global installation of generators found
- Run the corresponding Generator through yo
- Fill in options interactively through the command line
- Generate the required project structure
Custom Generator
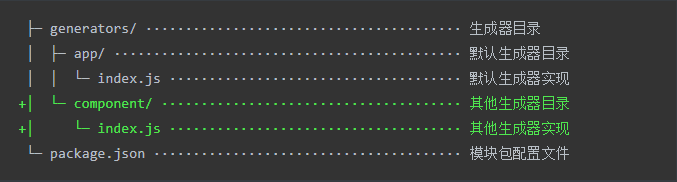
Installing the generator base class
yarn add yeoman-generator
Create generators/app/index.js as the core entry of the Generator
// This file serves as the core entry for the Generator
// You need to export a type that inherits from Yeoman Generator
// Yeoman Generator will automatically call some life cycle methods defined in this type when working
// In these methods, we can call some tools and methods provided by the parent class to realize some functions, such as file writing
const Generator = require("yeoman-generator");
module.exports = class extends Generator {
writing() {
// Yeoman automatically calls this method during the file generation phase
this.fs.write(this.destinationPath("temp.txt"), Math.random().toString());
}
};After npm link is executed, a new module is created and executed
yo sample
Create files from templates
// Template
module.exports = class extends Generator {
writing() {
// Template file path
const tmpl = this.templatePath("foo.txt");
// Output file path
const output = this.destinationPath("foo.txt");
// Template data context
const context = { title: "hello", success: true };
this.fs.copyTpl(tmpl, output, context);
}
};Receive user input
module.exports = class extends Generator {
prompting() {
// Yeoman will automatically call this method when asking the user
// In this method, you can call the prompt() method of the parent class to issue a command-line query to the user
return this.prompt([
{
type: "input", // User input class
name: "title", // Key to receive parameters
message: "message title", // Tips
default: "hello", // Default value
},
{
type: "input", // User input class
name: "success", // Key to receive parameters
message: "message status", // Tips
default: false, // Default value
},
]).then((answer) => {
this.answer = answer;
});
}
writing() {
// Template file path
const tmpl = this.templatePath("foo.txt");
// Output file path
const output = this.destinationPath("input.txt");
// //Template data context
// const context = { title: "hello", success: true };
this.fs.copyTpl(tmpl, output, this.answer);
}
};Drop (create a specific type of file)
Basic use
- Install the plop module as a project development dependency
- Create a plopfile.js file in the root directory of the project
- Define scaffolding tasks in the plopfile.js file
- Write templates for generating specific types of files
- Run scaffolding tasks through cli provided by plop
Installing the plop extension module
yarn add plop --dev
Create the plopfile.js entry file in the project root directory
// The plop entry file needs to export a function
// This function receives a plop object and the user creates a generator task
module.exports = (plop) => {
plop.setGenerator("component", {
description: "create component",
prompts: [
{
type: "input",
name: "name",
message: "component name",
default: "myComponent",
},
],
actions: [
{
type: "add",
path: "src/components/{{name}}/index.js",
templateFile: "templates/component.js.hbs",
},
{
type: "add",
path: "src/components/{{name}}/index.css",
templateFile: "templates/component.css.hbs",
},
{
type: "add",
path: "src/components/{{name}}/index.html",
templateFile: "templates/component.html.hbs",
},
],
});
};Write a template component.html.hbs for generating a specific type of file
console.log("{{name}}")function
yarn plop component
Principle of scaffold tools
- Ask user questions through command line interaction
- Generate files according to the results of user answers
The entry configuration of Node CLI is bin in package.json file. The application entry file must have such a file header. In case of Linux or macOS system, the read-write permission of this file needs to be modified to 755
#!/usr/bin/env node
File configuration
#!/usr/bin/env node
console.log("start......");
const inquirer = require("inquirer");
const fs = require("fs");
const path = require("path");
const ejs = require("ejs");
inquirer
.prompt([
{
type: "input",
name: "name",
message: "project name",
},
])
.then((answer) => {
console.log(answer);
// templates directory
const tmplDir = path.join(__dirname, "templates");
// Target directory
const destDir = process.cwd();
// Convert all files under the template to the target directory
fs.readdir(tmplDir, (err, files) => {
if (err) throw err;
files.forEach((file) => {
// Render files through the template engine
ejs.renderFile(path.join(tmplDir, file), answer, (err, result) => {
if (err) throw err;
// Write results to destination file path
fs.writeFileSync(path.join(destDir, file), result);
});
});
});
});