1. Basic overview
1. What is rpm?
The full name of RPM is the abbreviation of RedHat Package Manager, which is developed by red hat for software package installation, upgrade, uninstall and query
2.rpm package name component?
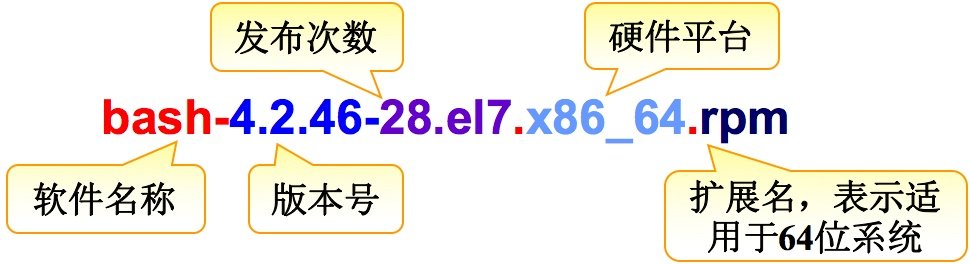
The RPM package is named after - dividing the software into parts bash-4.2.46-28.el7.x86_64.rpm
bash:Software name 4.2.46-28.el7: 4 Is the large version, 2 is the small version, 46 is the number of revisions, 28 is the number of releases, el7 Yes: enterprise linux 7,use linux7 system x86_64: 64 Bit architecture
3. How to obtain rpm package
When we first started to learn about rpm packages, we suggested using the local CentOS7 image, but in the actual production environment, the rpm packages are obtained through networking( Learn first, you know?)
We first load the image through the virtual machine, and then execute mount /dev/cdrom /mnt in linux. At this time, you will see many rpm package files in the / mnt/Packages directory. Then you can start the journey of rpm package management.
4. Expansion: in addition to rpm installation software in Linux, is there another way to install software?
| classification | install | edition |
|---|---|---|
| rpm package | Pre compiled and packaged, easy installation | Low software version |
| Source package | Manual compilation and packaging, cumbersome installation | The software version is optional |
| Binary package (green package) | Decompression can be used, easy to install | The source code cannot be modified |
2.RPM usage example
1. How to install RPM package
The following lists the common parameters for installing software with the rpm command
| option | describe |
|---|---|
| -i | Install rpm |
| -v | Display installation details |
| -h | Display installation progress |
| –force | Force reinstallation |
| –nodeps | Ignore dependencies |
#To install the software package, you need to specify the absolute path of the software package # mount /dev/cdrom /mnt [root@lqz ~]# rpm -ivh /mnt/Packages/tree-1.6.0-10.el7.x86_64.rpm [root@lqz ~]# rpm -ivh /mnt/Packages/vsftpd-3.0.2-22.el7.x86_64.rpm #The absolute path can not be specified in the directory where the software package is located [root@lqz ~]# cd /mnt/Packages/ [root@lqz Packages]# rpm -ivh zsh-5.0.2-28.el7.x86_64.rpm #If the package exists, force it to be installed again [root@lqz ~]# rpm -ivh --force /mnt/Packages/tree-1.5.3-3.el6.x86_64.rpm #Installing samba service depends on other components. Use -- nodeps to force the installation again [root@lqz ~]# rpm -ivh --nodeps /mnt/Packages/tree-1.6.0-10.el7.x86_64.rpm # yum setup automatically handles dependencies # For other uses, use the connection address directly # https://developer.aliyun.com/mirror/ # https://developer.aliyun.com/mirror/zabbix?spm=a2c6h.13651102.0.0.3e221b113DCKcf # https://mirrors.aliyun.com/zabbix/zabbix/ # Install 3 first and then 4 to test and upgrade # zabbix-agent-3.0.9-1.el7.x86_64.rpm [root@lqz ~]# rpm -ivh https://mirrors.aliyun.com/zabbix/zabbix/3.0/rhel/7/x86_64/zabbix-agent-3.0.9-1.el7.x86_64.rpm # Upgrade with U [root@lqz ~]# rpm -Uvh https://mirrors.aliyun.com/zabbix/zabbix/4.2/rhel/7/x86_64/zabbix-agent-4.2.8-1.el7.x86_64.rpm # Unload (cannot unload with dependency) rpm -e zabbix-agent rpm -q zabbix-agent yum remove samba
2. How to query the installed rpm package
| option | describe |
|---|---|
| rpm -q | Check whether the specified software package is installed (key) |
| rpm -qa | View a list of all RPM packages installed in the system |
| rpm -qi | View details of the specified software |
| rpm -ql | Query the directory and file list of the specified software package (key) |
| rpm -qc | Query the configuration file of the specified software package (only the configuration file, etc) |
| rpm -qf | Query which RPM software the file or directory belongs to |
| rpm -qip | Query the details of uninstalled rpm packages |
| rpm -qlp | Query which files will be generated by uninstalled packages |
#Query vsftpd whether the rpm package is installed [root@lqz ~]# rpm -q vsftpd #Fuzzy Lookup system installed rpm package [root@lqz ~]# rpm -qa |grep ftp #Query vsftpd package related information [root@lqz ~]# rpm -qi vsftpd #Query the files installed by the rpm package [root@lqz ~]# rpm -ql vsftpd #Query the configuration files related to the rpm package [root@lqz ~]# rpm -qc vsftpd #Query which rpm package the configuration file or command comes from (only those installed) [root@lqz ~]# rpm -qf /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf # View this configuration file is [root@lqz ~]# rpm -qf /usr/sbin/vsftpd [root@lqz ~]# rpm -qf /usr/sbin/ifconfig # Want to see what's not installed yum provides vim #Query which files will be generated by uninstalled packages [root@lqz ~]# rpm -qlp /mnt/Packages/samba-3.6.23-41.el6.x86_64.rpm #Query which files will be generated by uninstalled packages [root@lqz ~]# rpm -qip /mnt/Packages/samba-3.6.23-41.el6.x86_64.rpm
3.RPM package upgrade
| option | describe |
|---|---|
| rpm -U | If the old version does not exist, install it completely. If there is a new version, upgrade it |
# wget https://mirrors.aliyun.com/zabbix/zabbix/3.0/rhel/7/x86_64/zabbix-agent-3.0.9-1.el7.x86_64.rpm
# wget https://mirrors.aliyun.com/zabbix/zabbix/4.2/rhel/7/x86_64/zabbix-agent-4.2.0-1.el7.x86_64.rpm
#1. Install the lower version first
[root@www.lqz.com ~]# rpm -ivh zabbix-agent-3.0.9-1.el7.x86_64.rpm
#2. Try to install a higher version (an error will occur)
[root@www.lqz.com ~]# rpm -ivh zabbix-agent-4.2.0-1.el7.x86_64.rpm
#3. Use the upgrade method to perfectly solve the replacement problem
[root@www.lqz.com ~]# rpm -Uvh zabbix-agent-4.2.0-1.el7.x86_64.rpm
4.RPM package unloading
When uninstalling a package, you need to uninstall the dependent package first. If the dependent package is necessary for the system, you cannot uninstall the package, otherwise the system will crash.
#Query first and then uninstall [root@www.lqz.com ~]# rpm -qa |grep sh [root@www.lqz.com ~]# rpm -e zsh
5.RPM package verification (extended understanding)
The software related databases are stored in the / var/lib/rpm directory
| parameter | describe |
|---|---|
| S | Is the file size changed |
| M | Whether the file type or file attribute has been modified |
| 5 | The content of MD5 fingerprint encryption is different |
| L | The path has been changed |
| U | The owner of the file has been modified |
| G | The group to which the file belongs has been modified |
| T | The creation time of the file has been changed |
[root@www.lqz.com ~]# rpm -V vsftpd S.5....T. c /etc/pam.d/vsftpd .......T. c /etc/vsftpd/ftpusers S.5....T. c /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf .M....... /var/ftp/pub
6.RPM package summary
How to query which files are installed in util Linux package?
How to query which RPM package installed the mkdir command?
What is the difference between the - i, - U, and options when installing the. rpm package?
3. Basic introduction to yum
1. What is YUM
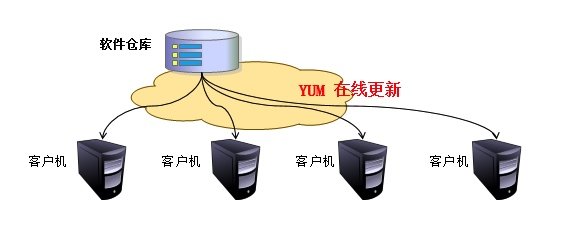
Yum is the package manager in RedHat and CentOS. The. rpm package can be downloaded and installed through the Internet, and the dependency relationship can be handled automatically without cumbersome downloading and installation again and again( PS: YUM is a production best practice)
2. What is the yum source
1 to successfully use Yum tool to install update software or system, we need a repository (software warehouse) containing various rpm software packages. This software warehouse is commonly called Yum source( Can be local source, network source)
3.YUM source configuration example
1. Alibaba yum source
# yum repolist # Check how many sources there are now. Nginx does not exist. You can configure the nginx warehouse # Extended epel source: [root@www.lqz.com ~]# wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/epel-7.repo #The default system is a foreign source and needs to be replaced with a domestic source [root@www.lqz.com ~]# wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/Centos-7.repo #Extended source, there are many software not available in the basic source [root@www.lqz.com ~]# wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/epel-7.repo
2.Nginx official source. For example, when learning nginx, you need to use the official yum source to install it
[root@www.lqz.com ~]# vim /etc/yum.repos.d/nginx.repo [nginx] name=nginx repo baseurl=http://nginx.org/packages/centos/7/$basearch/ gpgcheck=0 enabled=1
PS: the source search methods are basically the same, zabbix, Docker, Nginx, saltstack and openstack
4.YUM practice case
1. Query the package using yum
[root@www.lqz.com ~]# yum list [root@www.lqz.com ~]# yum list|grep ftp [root@www.lqz.com ~]# yum info ftp
2. Install the package using yum
[root@www.lqz.com ~]# yum install tree [root@www.lqz.com ~]# yum install tree -y #Non interactive #Install the local rpm package. If there are dependencies, the required dependencies will be automatically downloaded from the software warehouse [root@www.lqz.com ~]# yum localinstall /mnt/Packages/bind-9.9.4-50.el7.x86_64.rpm #Directly install the rpm package on the network [root@www.lqz.com ~]# yum install http://repo.zabbix.com/zabbix/3.4/rhel/7/x86_64/zabbix-release-3.4-2.el7.noarch.rpm
3. Reinstall the package using yum or up2date
#1. If you accidentally delete the vsftpd configuration file [root@www.lqz.com ~]# rm -f /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf #2. The software can be reinstalled [root@www.lqz.com ~]# yum reinstall vsftpd #3. Check the configuration file of the software [root@www.lqz.com ~]# rpm -qc vsftpd /etc/logrotate.d/vsftpd /etc/pam.d/vsftpd /etc/vsftpd/ftpusers /etc/vsftpd/user_list /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf
4 update the package using yum or up2date
#Compare the installed Linux software with the software in the yum warehouse. What needs to be upgraded [root@www.lqz.com ~]# yum check-update #Update acl software [root@www.lqz.com ~]# yum update acl -y #The following execution is dangerous, which means updating all the software of the whole system, including the kernel [root@www.lqz.com ~]# yum update -y
5. Delete the package using yum or up2date
[root@www.lqz.com ~]# yum install samba -y [root@www.lqz.com ~]# yum erase samba -y [root@www.lqz.com ~]# yum remove samba -y
6. Instructions related to yum warehouse (extended understanding)
#Lists the software warehouses available from yum source [root@www.lqz.com ~]# yum repolist #Lists the available and disabled warehouses for all yum sources [root@www.lqz.com ~]# yum repolist all #Find which package a command or file belongs to (commonly used in production) [root@www.lqz.com ~]# yum provides /etc/my.cnf [root@www.lqz.com ~]# yum provides cd
7. Instructions related to yum cache (extended understanding)
#1. Cache rpm package mode 1. Modify yum global configuration file [root@www.lqz.com ~]# vim /etc/yum.conf [main] cachedir=/var/cache/yum/$basearch/$releasever keepcache=1 #Start cache #2. Cache rpm package mode 2, only download but not install [root@www.lqz.com ~]# yum install -y yum-plugin-downloadonly #plug-in unit [root@www.lqz.com ~]# yum install httpd -y --downloadonly --downloaddir=/tmp #3. Clear all yum cached packages and metadata [root@www.lqz.com ~]# yum clean all #4. Clear only cached packages [root@www.lqz.com ~]# yum clean packages
8. Package related instructions, (extended understanding)
[root@www.lqz.com ~]# yum groups list #Install an entire set of software [root@lqz ~]# yum groups install Development tools Compatibility libraries Base Debugging Tools #Delete package group using yum or up2date [root@www.lqz.com ~]# yum groups remove -y Base
9. History command, (extended understanding)
#1. View the history and execute the yum command [root@www.lqz.com ~]# yum history #2. Query historical execution yum command ID details [root@www.lqz.com ~]# yum history info N #3. Undo historically executed yum commands [root@www.lqz.com ~]# yum history undo N
PS: YUM also has configuration files and signature verification that we need to extend to understand Please click the portal
5. Build local warehouse
1. Sometimes your linux system can't be connected to the Internet. Of course, you can't easily use the connected yum source. At this time, you need to make a yum source by using the linux system CD. The specific steps are as follows:
#1. Mount the image [root@lqz ~]# mount /dev/cdrom /mnt #2. Back up the original warehouse [root@lqz ~]# gzip /etc/yum.repos.d/ #3. Add the local warehouse using the yum config manager command [root@lqz ~]# yum-config-manager --add-repo="file:///mnt" #4. Or add the repo file manually [root@lqz ~]# vim /etc/yum.repos.d/cdrom.repo [cdrom] name=This is local cdrom baseurl=file:///mnt enabled=1 gpgcheck=0 [] #Warehouse name name 3 Warehouse description information baseurl #YUM source url address, which can be file:// ftp:// http:// enabled #Whether to use this YUM source (0 = disabled, 1 = active) gpgcheck #Verify software signature (0 = disabled, 1 = active) #5. Generate cache [root@lqz ~]# yum makecache
2. Many times, not only one machine can't access the Internet, but many machines can't access the Internet, but there is a need to download software online. At this time, is every machine hung on the CD? Sure, but what if the software is updated?
Basic software package provided on local CD: Base
yum cache provides common software packages: nginx, zabbix, docker
1. Environmental preparation
| system | IP | role |
|---|---|---|
| centos7 | 10.0.0.99 | yum warehouse server |
| centos7 | 10.0.0.98 | yum warehouse client |
2. The server prepares to build the yum warehouse
#1. Close the firewall and selinux
[root@yum_server ~]# systemctl stop firewalld
[root@yum_server ~]# setenforce 0
#2. Install ftp service, start and join startup
[root@yum_server ~]# yum -y install vsftpd
[root@yum_server ~]# systemctl start vsftpd
[root@yum_server ~]# systemctl enable vsftpd
#3. Enable the yum cache function
[root@yum_server ~]# vim /etc/yum.conf
[main] cachedir=/var/cache/yum/$basearch/$releasever
keepcache=1
[root@yum_server ~]# yum clean all
#4. Provide basic base software package
[root@yum_server ~]# mkdir /var/ftp/centos7
[root@yum_server ~]# mount /dev/cdrom /mnt
[root@yum_server ~]# cp -rp /mnt/Packages/.rpm /var/ftp/centos7/
#5. Provide third-party sources
[root@yum_server ~]# mkdir /var/ftp/ops
[root@yum_server ~]# yum -y install nginx docker
#6. Copy the cached Nginx docker and dependent packages to the custom YUM warehouse directory
[root@yum_server_69_112 ~]# find /var/cache/yum/x86_64/7/
-iname ".rpm" -exec cp -rf {} /var/ftp/ops ;
#7. Install createrepo and create reopdata repository
[root@yum_server_ ~]# yum -y install createrepo
[root@yum_server_ ~]# createrepo /var/ftp/ops
#PS: if the warehouse adds software every time, it needs to be regenerated
3. Configure the yum source on the client to point to the server
#1. The client configures and uses the base basic source [root@yum_client ~]# gzip /etc/yum.repos.d/ [root@yum_client ~]# vim /etc/yum.repos.d/centos7.repo [centos7] name=centos7_base baseurl=ftp://10.0.0.99/centos7 gpgcheck=0 #2. The client configures and uses the ops source [root@yum_client ~]# vim /etc/yum.repos.d/ops.repo [ops] name=local ftpserver baseurl=ftp://10.0.0.99/ops gpgcheck=0
6. Source package management practice
1. What is the source package
Source code package refers to the development of written program source code, but it is not compiled into a normal tool.
2. Why learn the source code package
1. Some software official websites only provide source packages, which need to be compiled and installed by themselves.
2. When some software has some features in the new version and has not been made into rpm package in time, you can compile the software by yourself to use its new features.
3. Advantages and disadvantages of source package
1. You can modify the source code yourself
2. Relevant functions required can be customized
3. The source code of the new version of software shall be updated first
4. The disadvantages are: 1) it is much more complicated to install software than yum. 2) If it is difficult to implement standardization, automation cannot be implemented.
4. How to obtain the source code package
Common software packages can be obtained from the official website, such as apache, nginx, mysql and so on
5 the steps to compile the source package into binary executable files are as follows, which is referred to as the installation three-step program for short

PS: this method is not 100% common for all source packages. It is recommended to unzip the source package and go to the directory to find the relevant README help documents
6. Source code compilation example
Let's learn more about the compilation process of the source package by compiling Nginx.
#1. Basic environmental preparation [root@node1 ~]# yum install -y gcc make wget #2. Download the source package [root@node1 ~]# wget http://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.15.12.tar.gz #3. Unzip the source package and enter the corresponding directory [root@node1 ~]# tar xf nginx-1.15.12.tar.gz [root@node1 ~]# cd nginx-1.15.12 #4. Configure relevant options and generate Makefile [root@node1 nginx-1.15.12]# ./configure --help [root@node1 nginx-1.15.12]# ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx [root@node1 nginx-1.15.12]# echo $? # Check whether the previous command was executed successfully #5. Compile the Makefile file into the executable binary program. At this time, the / usr/local/nginx executable file is not available. You need to execute make install to copy it [root@node1 nginx-1.15.12]# make #6. Copy the binary file to the corresponding directory [root@node1 nginx-1.15.12]# make install #7. Establish soft connection (easy to upgrade in the future) [root@node1 nginx-1.15.12]# ln -s nginx-1.18.0 nginx #8 catalog introduction conf:configuration file html: Website file storage logs: journal sbin:Executable file # 9 command nginx # start-up nginx -s reload # Reload nginx -s stop # restart nginx -s stop # stop it
Source code compilation error information processing
checking for C compiler ... not found ./configure: error: C compiler cc is not found # yum -y install gcc gcc-c++ make ./configure: error: the HTTP rewrite module requires the PCRE library. You can either disable the module by using --without-http_rewrite_module option, or install the PCRE library into the system, or build the PCRE library statically from the source with nginx by using --with-pcre=<path> option. # yum install -y pcre-devel ./configure: error: the HTTP gzip module requires the zlib library. You can either disable the module by using --without- http_gzip_module option, or install the zlib library into the system, or build the zlib library statically from the source with nginx by using --with-zlib=<path> option. # yum -y install zlib-devel ./configure: error: SSL modules require the OpenSSL library. You can either do not enable the modules, or install the OpenSSL library into the system, or build the OpenSSL library statically from the source with nginx by using --with-openssl=<path> option. # yum -y install openssl-devel tall the zlib library into the system, or build the zlib library statically from the source with nginx by using --with-zlib=<path> option. # yum -y install zlib-devel ./configure: error: SSL modules require the OpenSSL library. You can either do not enable the modules, or install the OpenSSL library into the system, or build the OpenSSL library statically from the source with nginx by using --with-openssl=<path> option. # yum -y install openssl-devel