Definition and characteristics of pattern
Definition of Chain of Responsibility mode: in order to avoid coupling the request sender with multiple request handlers, all request handlers are connected into a chain by remembering the reference of the next object through the previous object; When a request occurs, it can be passed along the chain until an object processes it.
In the responsibility chain mode, the customer only needs to send the request to the responsibility chain, and does not need to care about the processing details of the request and the transmission process of the request. The request will be transmitted automatically. Therefore, the responsibility chain decouples the sender of the request from the handler of the request.
- 1. * * reduces the coupling between objects** This mode makes an object do not need to know which object handles its request and the structure of the chain, and the sender and receiver do not need to have each other's clear information.
- 2. * * the scalability of the system is enhanced** New request processing classes can be added as needed to meet the opening and closing principle.
- 3. Enhance the flexibility of assigning responsibilities to objects. When the workflow changes, you can dynamically change the members in the chain or transfer their order, or dynamically add or delete responsibilities.
- 4. * * responsibility chain simplifies the connection between objects** Each object only needs to maintain a reference to its successor without maintaining the references of all other processors, which avoids the use of many if or if ·· else statements.
- 5. Responsibility sharing. Each class only needs to deal with its own work that should be handled, and the work that should not be handled should be transferred to the next object for completion. The scope of responsibility of each class should be defined and in line with the principle of single responsibility of the class.
Its main disadvantages are as follows:
- There is no guarantee that every request will be processed. Since a request has no specific receiver, it cannot be guaranteed that it will be processed. The request may not be processed until it reaches the end of the chain.
- For a long responsibility chain, the processing of requests may involve multiple processing objects, and the system performance will be affected to some extent.
- The rationality of the establishment of responsibility chain depends on the client, which increases the complexity of the client, and may lead to system errors due to the wrong setting of responsibility chain, such as circular call.
Structure and implementation of pattern
Usually, the data structure of responsibility chain mode can be realized through data link list
1. Structure of the model
The responsibility chain model mainly includes the following roles.
- Abstract Handler role: define an interface for processing requests, including abstract processing methods and a subsequent connection.
- Concrete Handler role: implement the processing method of the abstract handler to judge whether the request can be processed. If the request can be processed, process it. Otherwise, transfer the request to its successor.
- Client role: create a processing chain and submit a request to the specific handler object of the chain head. It does not care about the processing details and the transmission process of the request.
The essence of responsibility chain mode is to decouple request and processing, so that requests can be transmitted and processed in the processing chain; Understanding the responsibility chain model should understand its model, not its specific implementation. The unique feature of the responsibility chain model is that it combines its node processors into a chain structure, and allows the node to decide whether to process or forward the request, which is equivalent to making the request flow.
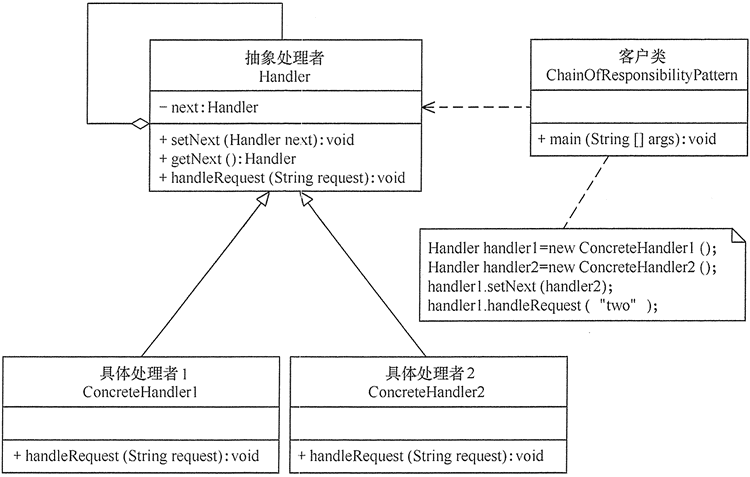
2. Implementation of mode
The implementation code of responsibility chain mode is as follows:
public class ChainOfResponsibilityPattern {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Assembly responsibility chain
Handler handler1 = new ConcreteHandler1();
Handler handler2 = new ConcreteHandler2();
handler1.setNext(handler2);
//Submit request
handler1.handleRequest("two");
}
}
//Abstract handler role
abstract class Handler {
private Handler next;
public void setNext(Handler next) {
this.next = next;
}
public Handler getNext() {
return next;
}
//Method of processing request
public abstract void handleRequest(String request);
}
//Specific processor role 1
class ConcreteHandler1 extends Handler {
public void handleRequest(String request) {
if (request.equals("one")) {
System.out.println("Specific handler 1 is responsible for processing the request!");
} else {
if (getNext() != null) {
getNext().handleRequest(request);
} else {
System.out.println("No one is processing the request!");
}
}
}
}
//Specific processor role 2
class ConcreteHandler2 extends Handler {
public void handleRequest(String request) {
if (request.equals("two")) {
System.out.println("Specific handler 2 is responsible for processing the request!");
} else {
if (getNext() != null) {
getNext().handleRequest(request);
} else {
System.out.println("No one is processing the request!");
}
}
}
}
/*
The running results of the program are as follows:
Specific handler 2 is responsible for processing the request!
*/
/*
In the above code, we hard code the message as String type, but in real business, the message is diverse, which can be int, String or user-defined type. Therefore, based on the above code, the message type can be abstracted Request, which enhances the compatibility of messages.*/
Precautions and details of responsibility chain model
- 1) The request and processing are separated to realize decoupling and improve the flexibility of the system.
- 2) The object is simplified so that the object does not need to know the structure of the chain.
- 3) The performance will be affected, especially when the chain is relatively long. Therefore, it is necessary to control the maximum number of nodes in the chain. Generally, set a maximum number of nodes in the Handler and judge whether the threshold has been exceeded in the setNext() method. If the threshold is exceeded, the chain is not allowed to be established to avoid the unintentional damage to the system performance caused by the super long chain.
- 4) Inconvenient debugging. Similar to recursion, the logic may be complex during debugging
- 5) Best application scenario: when there are multiple objects that can process the same request, such as multi-level request, leave / salary increase approval process, Tomcat Encoding processing in Java Web, interceptor