preface
The previous article introduced the basic knowledge of chaos, including three classical chaotic maps and Hodgkin Huxley model. This paper will introduce text encryption based on chaotic mapping.
This chapter first introduces the cryptosystem based on the traditional DES algorithm and the typical text cryptosystem based on chaotic mapping, uses the classical chaotic mapping and Hodgkin Huxley model to encrypt the text, and compares and analyzes the security of different algorithms based on the performance analysis index of cryptosystem proposed in Chapter 2. Aiming at the defect that the typical text chaotic encryption algorithm does not have ciphertext sensitivity, an improved text chaotic encryption algorithm is designed. Taking Hodgkin Huxley model as an example, the typical text chaotic encryption algorithm and the improved text chaotic encryption algorithm are compared and analyzed.
1, Traditional DES cryptographic algorithm
DES algorithm is the most classic representative of symmetric block cipher, and it is also the text encryption standard algorithm recommended by NIST. The encryption and decryption process of DES algorithm is shown in Figure 5-1.
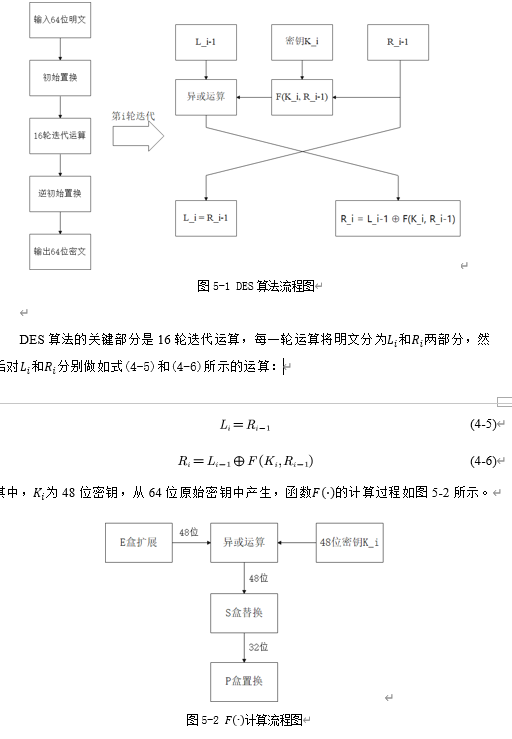
There are many articles about DES algorithm on the network, which will not be introduced here.
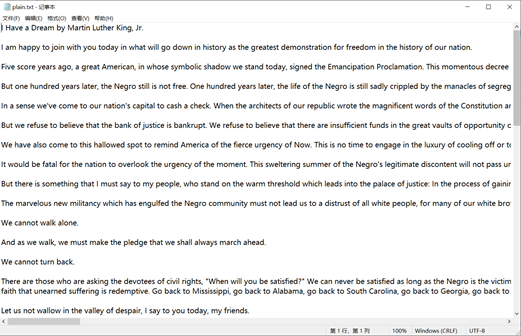
This paper encrypts and decrypts the text file of Txt. The plaintext used is the famous speech I Have a Dream delivered by Martin Luther King in 1963. The text is shown in Figure 5-3. Expand the ASCII code of plaintext from left to right and from top to bottom into a one-dimensional column vector with the size of 8866 * 1. The histogram of ASCII code is shown in the figure:
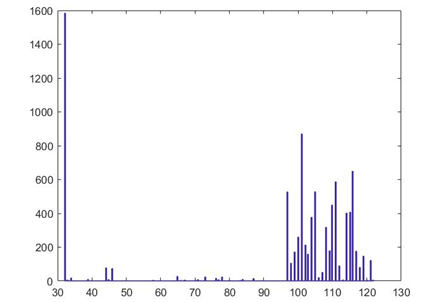
It can be seen from figure 5-4 that the ASCII code distribution of plaintext text is mainly concentrated between 32 (space) and 97122 (lowercase letter az), with obvious non-uniform distribution characteristics.
Let the initial key of DES algorithm be K=133457799BBCDFF1 (hexadecimal). The DES algorithm shown in Fig. 5-1 is used for experiments in Matlab. The experimental results are shown in Fig. 5-5 and Fig. 5-6:

As can be seen from Fig. 5-5 and Fig. 5-6, the traditional DES algorithm can achieve the purpose of hiding the original information through encryption and correctly recovering the original information through decryption.
2, Typical text chaotic encryption algorithm
The typical chaotic text cipher system based on chaotic sequence cipher is shown in Figure 5-7:
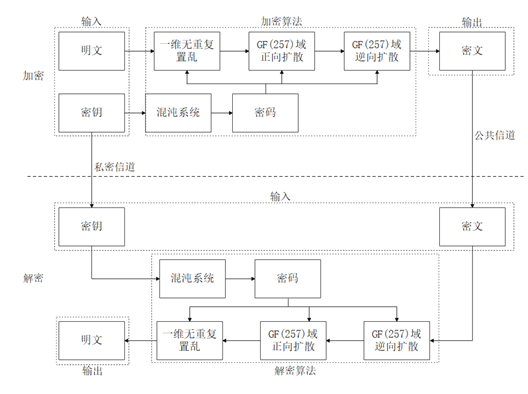
In Figure 5-7, the scrambling algorithm adopts one-dimensional non re scrambling algorithm, and the diffusion algorithm adopts the diffusion algorithm based on the multiplication of finite field GF\left(257\right).
Next, text chaotic encryption based on different chaotic maps is analyzed. Firstly, the classical chaotic map introduced in Chapter 3 is used to encrypt the text, and then the Hodgkin Huxley model introduced in Chapter 4 is used to encrypt the text.
1. Logistic mapping
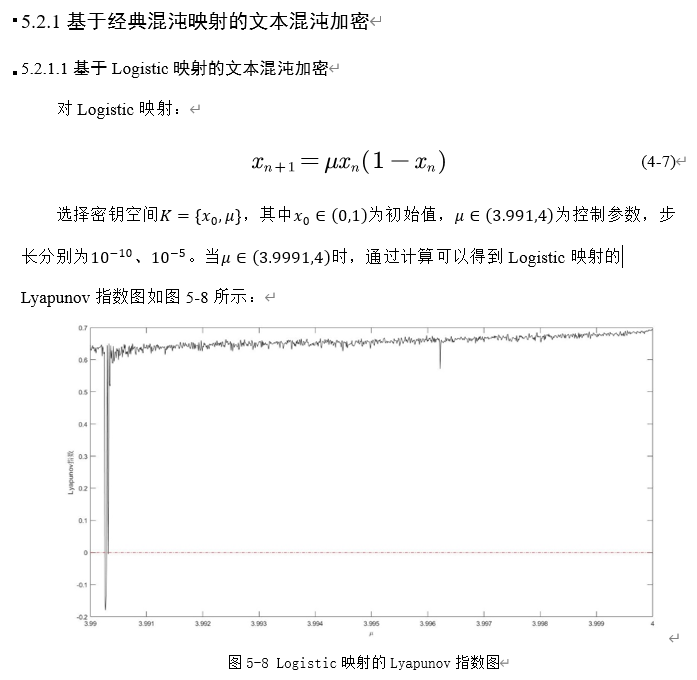
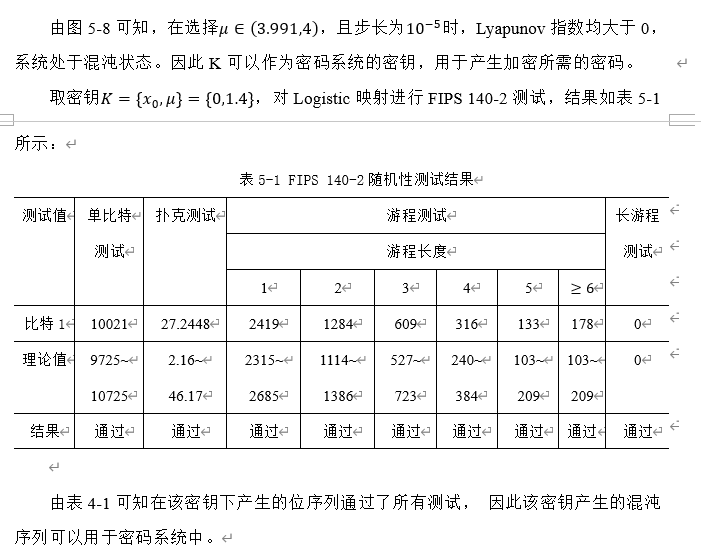


2. Henon mapping
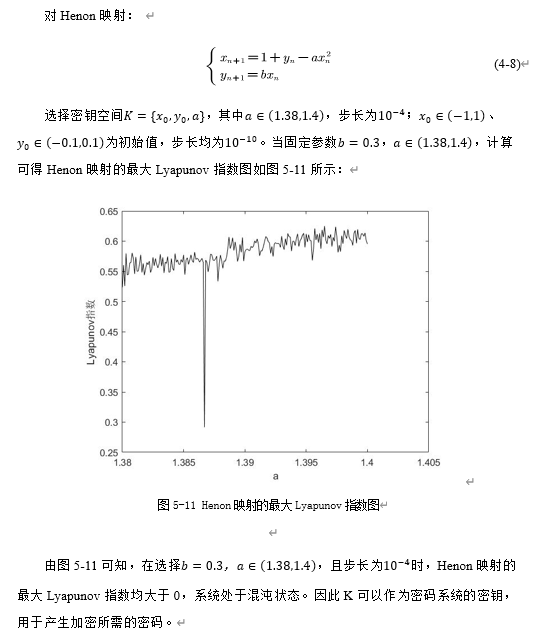
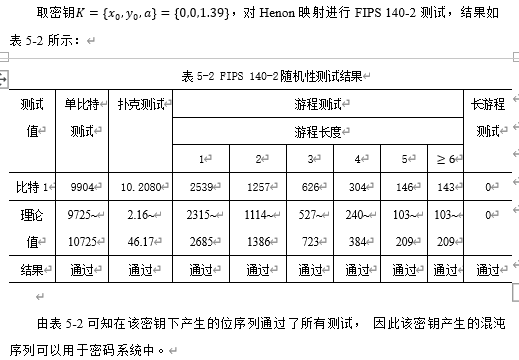

3. Lorenz mapping
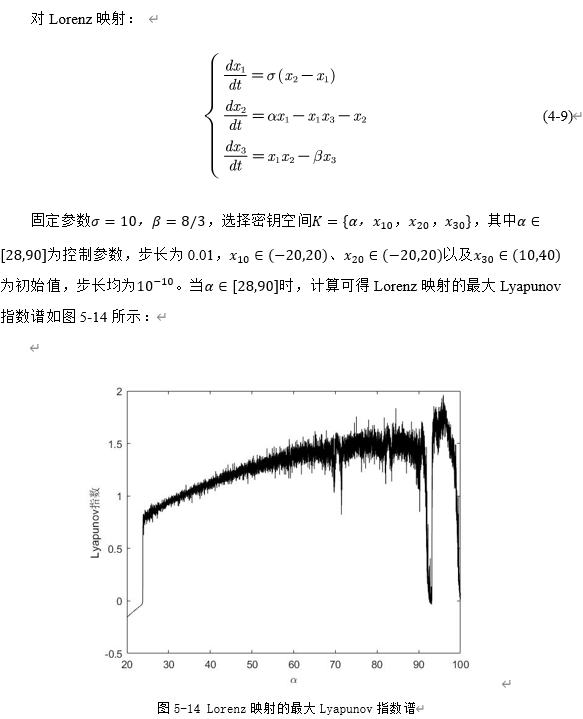

4. Hodgkin Huxley model

code
Due to space reasons, only HH model is given as an example.
% FIPS 140-1 Random characteristic test
clear
clc
sigma = 10; alpha = 28; beta= 8/3;
K0 = [0.00002, 0.05293, 0.31768, 0.59612, 1, 1, 1];
[T1,Y1] = ode45(@(t,x)HHfun(t,x,sigma,alpha,beta),[0,5000],K0);
s = Y1(end-20000+1:end,1);
s = mod(floor((s+1000)*pow2(16)),2);
test = zeros(1,4);
% Single bit test
k1 = sum(s); k0 = length(s) - k1;
if (9725 <= k1) && (k1 <= 10725) && (9725 <= k0) && (k0 <= 10725)
test(1) = 1;
end
% Poker test
f0 = zeros(1,16);
for i = 1:5000
v = s(4*i-3)*8 + s(4*i-2)*4 + s(4*i-1)*2 + s(4*i);
f0(v+1) = f0(v+1) + 1;
end
p = sum(f0.^2)*16/5000 - 5000;
if (p >= 2.16) && (p <= 46.17)
test(2) = 1;
end
% poker test
run0 = zeros(1,100);
run1 = zeros(1,100);
t0 = 0; t1 = 0;
for i = 1:20000
if i == 1
if s(i) == 1
t1 = 1;
else
t0 = 1;
end
elseif i == 20000
if s(i) == 1 && t1 > 0
t1 = t1 + 1;
run1(t1) = run1(t1) + 1;
end
if s(i) == 0 && t0 > 0
t0 = t0 + 1;
run0(t0) = run0(t0) + 1;
end
if s(i) == 1 && t1 == 0
run1(1) = run1(1) + 1;
run0(t0) = run0(t0) + 1;
end
if s(i) == 0 && t0 == 0
run0(1) = run0(1) + 1;
run1(t1) = run1(t1) + 1;
end
else
if s(i) == 1 && t1 > 0
t1 = t1 + 1;
end
if s(i) == 0 && t0 > 0
t0 = t0 + 1;
end
if s(i) == 1 && t1 == 0
t1 = 1;
run0(t0) = run0(t0) + 1;
t0 = 0;
end
if s(i) == 0 && t0 == 0
t0 = 1;
run1(t1) = run1(t1) + 1;
t1 = 0;
end
end
end
run0_1 = run0(1); run0_2 = run0(2); run0_3 = run0(3); run0_4 = run0(4);
run0_5 = run0(5); run0_6 = sum(run0(6:100)); run0_26 = sum(run0(26:100));
run1_1 = run1(1); run1_2 = run1(2); run1_3 = run1(3); run1_4 = run1(4);
run1_5 = run1(5); run1_6 = sum(run1(6:100)); run1_26 = sum(run1(26:100));
if (run0_1 >= 2315) && (run0_1 <= 2685) && (run1_1 >= 2315) && (run1_1 <= 2685)
if (run0_2 >= 1114) && (run0_2 <= 1386) && (run1_2 >= 1114) && (run1_2 <= 1386)
if (run0_3 >= 527) && (run0_3 <= 723) && (run1_3 >= 527) && (run1_3 <= 723)
if (run0_4 >= 240) && (run0_4 <= 384) && (run1_4 >= 240) && (run1_4 <= 384)
if (run0_5 >= 103) && (run0_5 <= 209) && (run1_5 >= 103) && (run1_5 <= 209)
if (run0_6 >= 103) && (run0_6 <= 207) && (run1_6 >= 103) && (run1_6 <= 207)
test(3) = 1;
end
end
end
end
end
end
if (run0_26 == 0) && (run1_26 == 0)
test(4) = 1;
end
clearvars -except k1 p run0_* run1_* test
%%
function df = HHfun(t,x,sigma,alpha,beta)
df = zeros(7,1);
df(1) = x(5) - (120*x(2)^3*x(4)*(x(1) - 115) + 36*x(3)^4*(x(1) + 12) + 0.3*(x(1) - 10.599));
df(2) = alpham(x(1))*(1-x(2)) - betam(x(1))*x(2);
df(3) = alphan(x(1))*(1-x(3)) - betan(x(1))*x(3);
df(4) = alphah(x(1))*(1-x(4)) - betah(x(1))*x(4);
df(5) = sigma*(x(6) - x(5));
df(6) = alpha*x(5) - x(5)*x(7) - x(6);
df(7) = x(5)*x(6) - beta*x(7);
end
function am = alpham(V)
am = 0.1*(V - 25)/(1 - exp((25 - V)/10));
end
function bm = betam(V)
bm = 4*exp(-V/18);
end
function an = alphan(V)
an = 0.01*(V - 10)/(1 - exp((10 - V)/10));
end
function bn = betan(V)
bn = 0.125*exp(-V/80);
end
function ah = alphah(V)
ah = 0.07*exp(-V/20);
end
function bh = betah(V)
bh = 1/(1 + exp((30 - V)/10));
end
%% HH_Lorenz Performance analysis of chaotic encryption system
clear
clc
% Read plaintext
plaintext = importdata('D:\Learning materials\Undergraduate graduation thesis\code\encryption\plain.txt');
[m,~] = size(plaintext);
ascsize = zeros(m,1);
plaintext_asc = [];
for i = 1:m
text = char(plaintext(i));
asc = abs(text);
ascsize(i) = length(asc);
if i > 1
ascsize(i) = ascsize(i) + ascsize(i-1);
end
plaintext_asc = [plaintext_asc asc];
end
plaintext_asc = plaintext_asc';
clearvars -except plaintext* ascsize m
%%
% secret key K=[alpha,V0,m0,n0,h0]
K = [28, 0.00002, 0.05293, 0.31768, 0.59612];
% encryption
tic
ciphetext_asc = Encrypt(plaintext_asc,K);
toc
ciphetext = cell(m,1);
for i = 1:m
if i == 1
asc = ciphetext_asc(1:ascsize(1))';
else
asc = ciphetext_asc(ascsize(i-1)+1:ascsize(i))';
end
text = char(asc);
ciphetext(i) = cellstr(text);
end
ciphetext = char(ciphetext);
% decrypt
tic
plaintext2_asc = Decrypt(ciphetext_asc,K);
toc
plaintext2 = cell(m,1);
for i = 1:m
if i == 1
asc = plaintext2_asc(1:ascsize(1))';
else
asc = plaintext2_asc(ascsize(i-1)+1:ascsize(i))';
end
text = char(asc);
plaintext2(i) = cellstr(text);
end
plaintext2 = char(plaintext2);
clearvars -except K plaintext* ciphetext* ascsize m
%% encryption/Decryption speed
K = [28, 0.00002, 0.05293, 0.31768, 0.59612];
N = 100;
time1 = zeros(N,1); time2 = zeros(N,1);
for j = 1:N
time1(j) = cputime;
ciphe = Encrypt(plaintext_asc,K);
time1(j) = cputime - time1(j);
time2(j) = cputime;
Decrypt(ciphe,K);
time2(j) = cputime - time2(j);
end
En_time = sum(time1)/N;
De_time = sum(time2)/N;
clearvars j N time*
%% Histogram chi square test
figure
hist(plaintext_asc,256);
figure
hist(ciphetext_asc,256);
figure
hist(plaintext2_asc,256);
fp = hist(plaintext_asc,256);
fc = hist(ciphetext_asc,256);
g = ascsize(end)/256;
% Value of chi square statistics
chai1 = sum((fp-g).^2)/g;
chai2 = sum((fc-g).^2)/g;
clearvars M N fp fc g
%% NPCR and UACI value
NU = NPCRUACI(plaintext_asc, ciphetext_asc);
%%
% Expected value of given text and random text
NUExpect = NPCRUACIExpect(plaintext_asc);
% Theoretical values of two random texts
NUTheory = NPCRUACITheory();
%% Key sensitivity of encryption system
N = 100;
alpha = roundn(rand(1,N)*24, -2) + 66;
V0 = roundn(rand(1,N)*10, -10);
m0 = roundn(rand(1,N)*0.1, -10);
n0 = roundn(rand(1,N)*0.1, -10) + 0.3;
h0 = roundn(rand(1,N)*0.2, -10) + 0.4;
NU_alpha = zeros(1,2);
NU_V0 = zeros(1,2);
NU_m0 = zeros(1,2);
NU_n0 = zeros(1,2);
NU_h0 = zeros(1,2);
for i = 1:N
K1 = [alpha(i), V0(i), m0(i), n0(i), h0(i)];
ciphe_asc1 = Encrypt(plaintext_asc, K1);
K2 = [alpha(i)+10^(-10), V0(i), m0(i), n0(i), h0(i)];
if K2(1) >= 90
K2(1) = alpha(i) - 10^(-10);
end
ciphe_asc2 = Encrypt(plaintext_asc, K2);
K3 = [alpha(i), V0(i)+10^(-10), m0(i), n0(i), h0(i)];
if K3(2) >= 10
K3(2) = V0(i) - 10^(-10);
end
ciphe_asc3 = Encrypt(plaintext_asc, K3);
K4 = [alpha(i), V0(i), m0(i)+10^(-10), n0(i), h0(i)];
if K4(3) >= 0.1
K4(3) = m0(i) - 10^(-10);
end
ciphe_asc4 = Encrypt(plaintext_asc, K4);
K5 = [alpha(i), V0(i), m0(i), n0(i)+10^(-10), h0(i)];
if K5(4) >= 0.4
K5(4) = n0(i) - 10^(-10);
end
ciphe_asc5 = Encrypt(plaintext_asc, K5);
K6 = [alpha(i), V0(i), m0(i), n0(i), h0(i)+10^(-10)];
if K6(5) >= 0.6
K6(5) = h0(i) - 10^(-10);
end
ciphe_asc6 = Encrypt(plaintext_asc, K6);
NU_alpha = NU_alpha + NPCRUACI(ciphe_asc1, ciphe_asc2);
NU_V0 = NU_V0 + NPCRUACI(ciphe_asc1, ciphe_asc3);
NU_m0 = NU_m0 + NPCRUACI(ciphe_asc1, ciphe_asc4);
NU_n0 = NU_n0 + NPCRUACI(ciphe_asc1, ciphe_asc5);
NU_h0 = NU_h0 + NPCRUACI(ciphe_asc1, ciphe_asc6);
end
NU_alpha = NU_alpha/N;
NU_V0 = NU_V0/N;
NU_m0 = NU_m0/N;
NU_n0 = NU_n0/N;
NU_h0 = NU_h0/N;
%% Sensitivity analysis of plaintext
N = 50;
alpha = roundn(rand(1,N)*24, -2) + 66;
V0 = roundn(rand(1,N)*10, -10);
m0 = roundn(rand(1,N)*0.1, -10);
n0 = roundn(rand(1,N)*0.1, -10) + 0.3;
h0 = roundn(rand(1,N)*0.2, -10) + 0.4;
NU = zeros(N,2);
NU_plain = zeros(1,2);
for i = 1:N
K1 = [alpha(i), V0(i), m0(i), n0(i), h0(i)];
ciphe_asc1 = Encrypt(plaintext_asc, K1);
ixy = mod(floor(rand*10^10), ascsize(end))+1;
plain_asc = plaintext_asc;
plain_asc(ixy) = mod(plain_asc(ixy)+1,256);
ciphe_asc2 = Encrypt(plain_asc, K1);
NU(i,:) = NPCRUACI(ciphe_asc1,ciphe_asc2);
NU_plain = NU_plain + NPCRUACI(ciphe_asc1, ciphe_asc2);
end
NU_plain = NU_plain/N;
clearvars i* K* ciphe_asc* plain_asc N
%% Sensitivity analysis of ciphertext
N = 100;
alpha = roundn(rand(1,N)*24, -2) + 66;
V0 = roundn(rand(1,N)*10, -10);
m0 = roundn(rand(1,N)*0.1, -10);
n0 = roundn(rand(1,N)*0.1, -10) + 0.3;
h0 = roundn(rand(1,N)*0.2, -10) + 0.4;
NU = zeros(N,2);
NU_ciphe = zeros(1,2);
for i = 1:N
K1 = [alpha(i), V0(i), m0(i), n0(i), h0(i)];
ciphe_asc = Encrypt(plaintext_asc, K1);
ixy = mod(floor(rand*10^10), ascsize(end))+1;
ciphe_asc(ixy) = mod(ciphe_asc(ixy)+1,256);
plain_asc = Decrypt(ciphe_asc, K1);
NU(i,:) = NPCRUACI(plaintext_asc,plain_asc);
NU_ciphe = NU_ciphe + NPCRUACI(plaintext_asc, plain_asc);
end
NU_ciphe = NU_ciphe/N;
clearvars i* ciphe_asc plain_asc K1 N
%% Information entropy
alpha = roundn(rand*24, -2) + 66;
V0 = roundn(rand*10, -10);
m0 = roundn(rand*0.1, -10);
n0 = roundn(rand*0.1, -10) + 0.3;
h0 = roundn(rand*0.2, -10) + 0.4;
ciphe_asc = Encrypt(plaintext_asc, [alpha, V0, m0, n0, h0]);
Hplain = Entropy(plaintext_asc);
Hciphe = Entropy(ciphe_asc);
clearvars ciphe_asc
% HH Encryption function of chaotic encryption system Encrypt
function ciphetext_asc = Encrypt(P,K)
% P In clear text, K For key
num1 = length(P);
num2 = 3*num1;
s = zeros(1,num2);
% Generating chaotic sequence
sigma = 10; alpha = K(1); beta= 8/3;
K0 = [K(2), K(3), K(4), K(5), 1, 1, 1];
[T,Y] = ode45(@(t,x)HHfun(t,x,sigma,alpha,beta),[0,5000],K0);
s = Y(end-num2+1:end,1);
% Scrambling algorithm cipher stream
X = mod(floor(s(1:num1)*10^10),num1)+1;
[~,idx] = unique(X);
X1 = zeros(1,num1);
X1(1:length(idx)) = X(sort(idx));
X1(length(idx)+1:num1) = setdiff(1:num1,X1);
X = X1;
% Diffusion algorithm cipher stream
S = mod(floor(s(num1+1:3*num1)*pow2(16)),256);
S1 = S(1:num1); S2 = S(num1+1:2*num1);
% Generate multiplication table
TBL = GF257Table();
% Scrambling algorithm
A = P;
for i = 1:floor(num1/2)
t = A(X(i));
A(X(i)) = A(X(num1-i+1));
A(X(num1-i+1)) = t;
end
% Diffusion algorithm
B = zeros(num1,1); C = zeros(num1,1);
B0 = 0;
B(1) = LookUpGF257(B0,S1(1),A(1),TBL);
for i = 2:num1
B(i) = LookUpGF257(B(i-1),S1(i),A(i),TBL);
end
C0 = 0;
C(num1) = LookUpGF257(C0,S2(num1),B(num1),TBL);
for i = num1-1:-1:1
C(i) = LookUpGF257(C(i+1),S2(i),B(i),TBL);
end
ciphetext_asc = C;
end
% Logistic Decryption function of chaotic encryption system Decrypt
function plaintext2_asc = Decrypt(C,K)
% C As ciphertext, K For key
num1 = length(C);
num2 = 3*num1;
s = zeros(1,num2);
% Generating chaotic sequence
sigma = 10; alpha = K(1); beta= 8/3;
K0 = [K(2), K(3), K(4), K(5), 1, 1, 1];
[T,Y] = ode45(@(t,x)HHfun(t,x,sigma,alpha,beta),[0,5000],K0);
s = Y(end-num2+1:end,1);
% Scrambling algorithm cipher stream
X = mod(floor(s(1:num1)*10^10),num1)+1;
[~,idx] = unique(X);
X1 = zeros(1,num1);
X1(1:length(idx)) = X(sort(idx));
X1(length(idx)+1:num1) = setdiff(1:num1,X1);
X = X1;
% Diffusion algorithm cipher stream
S = mod(floor(s(num1+1:3*num1)*pow2(16)),256);
S1 = S(1:num1); S2 = S(num1+1:2*num1);
% Generate division table
[TBL1,TBL2] = GF257TableEx();
% Inverse algorithm of diffusion algorithm
A = C;
D = zeros(num1,1); E = zeros(num1,1);
A0 = 0;
D(num1) = LookUpGF257Ex2(A(num1),A0,S2(num1),TBL1,TBL2);
for i = num1-1:-1:1
D(i) = LookUpGF257Ex2(A(i),A(i+1),S2(i),TBL1,TBL2);
end
E0 = 0; E(1) = LookUpGF257Ex2(D(1),E0,S1(1),TBL1,TBL2);
for i = 2:num1
E(i) = LookUpGF257Ex2(D(i),D(i-1),S1(i),TBL1,TBL2);
end
% Inverse algorithm of scrambling algorithm
for i = 1:floor(num1/2)
t = E(X(i));
E(X(i)) = E(X(num1-i+1));
E(X(num1-i+1)) = t;
end
plaintext2_asc = E;
end
function ah = alphah(V) ah = 0.07*exp(-V/20); end
function am = alpham(V) am = 0.1*(V - 25)/(1 - exp((25 - V)/10)); end
function an = alphan(V) an = 0.01*(V - 10)/(1 - exp((10 - V)/10)); end
function bh = betah(V) bh = 1/(1 + exp((30 - V)/10)); end
function bm = betam(V) bm = 4*exp(-V/18); end
function bn = betan(V) bn = 0.125*exp(-V/80); end
function fvalue = f(x1,x2,sigma) fvalue = sigma*(x2 - x1); end
function fvalue = f1(m,n,h,V,x) fvalue = x - (120*m^3*h*(V-115) + 36*n^4*(V+12) + 0.3*(V-10.599)); end
function gvalue = g(x1,x2,x3,alpha) gvalue = alpha*x1 - x1*x3 - x2; end
function gvalue = g1(m,V) gvalue = alpham(V)*(1-m) - betam(V)*m; end
function gvalue = g2(n,V) gvalue = alphan(V)*(1-n) - betan(V)*n; end
function gvalue = g3(h,V) gvalue = alphah(V)*(1-h) - betah(V)*h; end
% be based on GF(257)Field multiplication table function T = GF257Table() T = mod(transpose(0:256).*(0:256),257); end
% be based on GF(257)Field multiplication and division table
function [T1,T2] = GF257TableEx()
T1 = mod(transpose(0:256).*(0:256),257);
T2 = zeros(257,257);
T2(:,1) = transpose(0:256);
for j = 1:256
for k = 1:256
T2(mod(j*k,257)+1,j+1) = k;
end
end
end
function df = HHfun(t,x,sigma,alpha,beta) df = zeros(7,1); df(1) = x(5) - (120*x(2)^3*x(4)*(x(1) - 115) + 36*x(3)^4*(x(1) + 12) + 0.3*(x(1) - 10.599)); df(2) = alpham(x(1))*(1-x(2)) - betam(x(1))*x(2); df(3) = alphan(x(1))*(1-x(3)) - betan(x(1))*x(3); df(4) = alphah(x(1))*(1-x(4)) - betah(x(1))*x(4); df(5) = sigma*(x(6) - x(5)); df(6) = alpha*x(5) - x(5)*x(7) - x(6); df(7) = x(5)*x(6) - beta*x(7); end
function lvalue = l(x1,x2,x3,beta) lvalue = x1*x2 - beta*x3; end
% be based on GF(257)Multiplication function of field function y = LookUpGF257(x0,x1,x2,TBL) y = TBL(TBL(x0+2,x1+2)+1,x2+2)-1; end
% be based on GF(257)Division function of field function y = LookUpGF257Ex2(x0,x1,x2,TBL1,TBL2) t = TBL1(x1+2,x2+2)+1; y = TBL2(x0+2,t)-1; end
% calculation NPCR,UACI and BACI value function u = NPCRUACI(A,B) m = length(A); u = zeros(1,2); u(1) = sum(sum(A ~= B))/m*100; u(2) = sum(sum(abs(A - B)))/(255*m)*100; end
% Calculate the between a given text and random text NPCR Expectations and UACI expected value
function u = NPCRUACIExpect(A)
m = length(A);
u = zeros(1,2);
u(1) = 255/256*100;
tot_n = zeros(1,256);
tot_s = 0:255;
for i = 1:m
for k = 0:255
if k <= A(i)
tot_n(k+1) = tot_n(k+1)+1;
end
if k <= 255 - A(i)
tot_n(k+1) = tot_n(k+1)+1;
end
end
end
tot_n(1) = tot_n(1)/2;
u(2) = sum(tot_s.*tot_n)/sum(tot_n)/255*100;
end
% Two random text NPCR and UACI Theoretical value function u = NPCRUACITheory() u = zeros(1,2); u(1) = 255/256*100; a = 255:-1:1; b = 1:255; u(2) = sum(a.*b)*2/(256^2*255)*100; end