String function of C language
C language string function , in C language, char * character array can be used to realize string, and a variety of string operation functions are also defined in C language standard library string.h.
Strings are widely used and need to meet the following requirements:
- Efficient string operations, such as append, copy, compare, and get length
- It can save any binary data, such as pictures
- Save memory as much as possible
Why doesn't Redis directly use C language strings?
- C language char * identifies the end of the string with '\ 0', then the string containing '\ 0' in the middle cannot be correctly represented; Because of this, there is no way to save binary data such as images.
- The time complexity of C language char * to obtain the length of string is O(N); The time complexity of append string is also O(N), and it may not be appended due to insufficient free space.
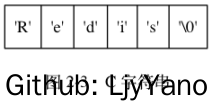
The following code shows the effect of '\ 0' end character on string in C language. The following figure shows a C string with the value "Redis":
#include "stdio.h"
#include "string.h"
int main(void) {
char *a = "red\0is";
char *b = "redis\0";
printf("%lu\n", strlen(a));
printf("%lu\n", strlen(b));
}
The output results are 3 and 5.
SDS definition
SDS (simple dynamic string) is short for simple dynamic string. Redis uses SDS as the data structure of the string. All key underlying layers in redis are implemented by SDS.
For example:
redis> SET msg "hello world" OK
redis> RPUSH fruits "apple" "banana" "cherry" (integer) 3
Redis sds source code is mainly in sds.h and sds.c. Redis aliases char *:
typedef char *sds;
SDS internal structure
There is a metadata flag in the SDS structure, which represents the SDS type (minimum 3 bits). In fact, five types of SDS are designed, namely sdshdr5, sdshdr8, sdshdr16, sdshdr32 and sdshdr64. The main difference between these five types lies in the existing length len of the character array and the allocated space length alloc in their data structure. The data types of these two metadata are different.
/* Note: sdshdr5 is never used, we just access the flags byte directly.
* However is here to document the layout of type 5 SDS strings. */
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr5 {
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, and 5 msb of string length */
char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr8 {
uint8_t len; /* used */
uint8_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr16 {
uint16_t len; /* used */
uint16_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr32 {
uint32_t len; /* used */
uint32_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr64 {
uint64_t len; /* used */
uint64_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
char buf[];
};


static inline size_t sdslen(const sds s) {
unsigned char flags = s[-1];
switch(flags&SDS_TYPE_MASK) {
case SDS_TYPE_5:
return SDS_TYPE_5_LEN(flags);
case SDS_TYPE_8:
return SDS_HDR(8,s)->len;
case SDS_TYPE_16:
return SDS_HDR(16,s)->len;
case SDS_TYPE_32:
return SDS_HDR(32,s)->len;
case SDS_TYPE_64:
return SDS_HDR(64,s)->len;
}
return 0;
}
Get the remaining capacity: sdsavail function, total capacity alloc - used length len, time complexity O(1).
static inline size_t sdsavail(const sds s) {
unsigned char flags = s[-1];
switch(flags&SDS_TYPE_MASK) {
case SDS_TYPE_5: {
return 0;
}
case SDS_TYPE_8: {
SDS_HDR_VAR(8,s);
return sh->alloc - sh->len;
}
case SDS_TYPE_16: {
SDS_HDR_VAR(16,s);
return sh->alloc - sh->len;
}
case SDS_TYPE_32: {
SDS_HDR_VAR(32,s);
return sh->alloc - sh->len;
}
case SDS_TYPE_64: {
SDS_HDR_VAR(64,s);
return sh->alloc - sh->len;
}
}
return 0;
}
Main operation API s of SDS

Basic methods include:
sds sdsnewlen(const void *init, size_t initlen);
sds sdstrynewlen(const void *init, size_t initlen);
sds sdsnew(const char *init);
sds sdsempty(void);
sds sdsdup(const sds s);
void sdsfree(sds s);
sds sdsgrowzero(sds s, size_t len);
sds sdscatlen(sds s, const void *t, size_t len);
sds sdscat(sds s, const char *t);
sds sdscatsds(sds s, const sds t);
sds sdscpylen(sds s, const char *t, size_t len);
sds sdscpy(sds s, const char *t);
sds sdscatvprintf(sds s, const char *fmt, va_list ap);
#ifdef __GNUC__
sds sdscatprintf(sds s, const char *fmt, ...)
__attribute__((format(printf, 2, 3)));
#else
sds sdscatprintf(sds s, const char *fmt, ...);
#endif
sds sdscatfmt(sds s, char const *fmt, ...);
sds sdstrim(sds s, const char *cset);
void sdssubstr(sds s, size_t start, size_t len);
void sdsrange(sds s, ssize_t start, ssize_t end);
void sdsupdatelen(sds s);
void sdsclear(sds s);
int sdscmp(const sds s1, const sds s2);
sds *sdssplitlen(const char *s, ssize_t len, const char *sep, int seplen, int *count);
void sdsfreesplitres(sds *tokens, int count);
void sdstolower(sds s);
void sdstoupper(sds s);
sds sdsfromlonglong(long long value);
sds sdscatrepr(sds s, const char *p, size_t len);
sds *sdssplitargs(const char *line, int *argc);
sds sdsmapchars(sds s, const char *from, const char *to, size_t setlen);
sds sdsjoin(char **argv, int argc, char *sep);
sds sdsjoinsds(sds *argv, int argc, const char *sep, size_t seplen);
/* Callback for sdstemplate. The function gets called by sdstemplate
* every time a variable needs to be expanded. The variable name is
* provided as variable, and the callback is expected to return a
* substitution value. Returning a NULL indicates an error.
*/
typedef sds (*sdstemplate_callback_t)(const sds variable, void *arg);
sds sdstemplate(const char *template, sdstemplate_callback_t cb_func, void *cb_arg);
/* Low level functions exposed to the user API */
sds sdsMakeRoomFor(sds s, size_t addlen);
void sdsIncrLen(sds s, ssize_t incr);
sds sdsRemoveFreeSpace(sds s);
size_t sdsAllocSize(sds s);
void *sdsAllocPtr(sds s);
/* Export the allocator used by SDS to the program using SDS.
* Sometimes the program SDS is linked to, may use a different set of
* allocators, but may want to allocate or free things that SDS will
* respectively free or allocate. */
void *sds_malloc(size_t size);
void *sds_realloc(void *ptr, size_t size);
void sds_free(void *ptr);
String initialization
As a whole, it is very similar to Java StringBuilder_ o
/* Create a new sds string starting from a null terminated C string. */
sds sdsnew(const char *init) {
size_t initlen = (init == NULL) ? 0 : strlen(init);
return sdsnewlen(init, initlen);
}
First, judge the length of the input init string, and then call sdsnewlen to allocate memory space and assign a value.
sds sdsnewlen(const void *init, size_t initlen) {
return _sdsnewlen(init, initlen, 0);
}
Core function_ sdsnewlen is as follows: first ensure that the space is sufficient and allocate space, and then call memcpy to copy * init to the corresponding memory space.
/* Create a new sds string with the content specified by the 'init' pointer
* and 'initlen'.
* If NULL is used for 'init' the string is initialized with zero bytes.
* If SDS_NOINIT is used, the buffer is left uninitialized;
*
* The string is always null-termined (all the sds strings are, always) so
* even if you create an sds string with:
*
* mystring = sdsnewlen("abc",3);
*
* You can print the string with printf() as there is an implicit \0 at the
* end of the string. However the string is binary safe and can contain
* \0 characters in the middle, as the length is stored in the sds header. */
sds _sdsnewlen(const void *init, size_t initlen, int trymalloc) {
void *sh;
sds s;
char type = sdsReqType(initlen);
/* Empty strings are usually created in order to append. Use type 8
* since type 5 is not good at this. */
if (type == SDS_TYPE_5 && initlen == 0) type = SDS_TYPE_8;
int hdrlen = sdsHdrSize(type);
unsigned char *fp; /* flags pointer. */
size_t usable;
assert(initlen + hdrlen + 1 > initlen); /* Catch size_t overflow */
sh = trymalloc?
s_trymalloc_usable(hdrlen+initlen+1, &usable) :
s_malloc_usable(hdrlen+initlen+1, &usable);
if (sh == NULL) return NULL;
if (init==SDS_NOINIT)
init = NULL;
else if (!init)
memset(sh, 0, hdrlen+initlen+1);
s = (char*)sh+hdrlen;
fp = ((unsigned char*)s)-1;
usable = usable-hdrlen-1;
if (usable > sdsTypeMaxSize(type))
usable = sdsTypeMaxSize(type);
switch(type) {
case SDS_TYPE_5: {
*fp = type | (initlen << SDS_TYPE_BITS);
break;
}
case SDS_TYPE_8: {
SDS_HDR_VAR(8,s);
sh->len = initlen;
sh->alloc = usable;
*fp = type;
break;
}
case SDS_TYPE_16: {
SDS_HDR_VAR(16,s);
sh->len = initlen;
sh->alloc = usable;
*fp = type;
break;
}
case SDS_TYPE_32: {
SDS_HDR_VAR(32,s);
sh->len = initlen;
sh->alloc = usable;
*fp = type;
break;
}
case SDS_TYPE_64: {
SDS_HDR_VAR(64,s);
sh->len = initlen;
sh->alloc = usable;
*fp = type;
break;
}
}
if (initlen && init)
memcpy(s, init, initlen);
s[initlen] = '\0';
return s;
}
Redis source code concise analysis series
The most concise Redis source code analysis series
Java programming ideas - the most complete mind map - GitHub download link , you can get your own partners if you need them~
It's not easy to be original. I hope you can contact me first and mark the original link.