Construction of Redis master-slave cluster and analysis of master-slave replication principle
preface
In the last article, I analyzed how to build a master-slave cluster and the principle of master-slave replication; This article continues to analyze the continuous sinking of clusters, common runtime detection tools, the principle of sentinel mechanism, and the treatment of common problems
Redis client and monitoring cluster
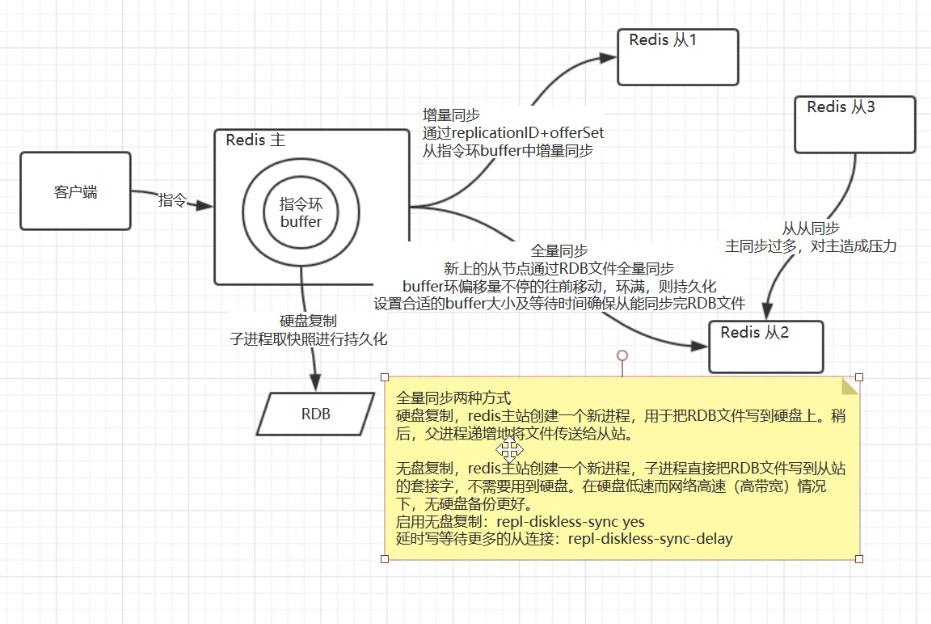
Redis data synchronization process in cluster
Integrated in spring, the implementation is very simple, as long as the master node is connected, and the slave node will be found automatically. And in the setting ReadFrom.SLAVE_PREFERRED Read / write will be selected automatically
@Configuration
@Profile("replication-rw") // Master slave read write separation mode
public class ReplicationRWRedisAppConfig {
@Value("${redis_host}")
private String redisHost;
@Value("${redis_port}")
private int redisPort;
@Bean
public LettuceConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory() {
System.out.println("Use read write split version");
LettuceClientConfiguration clientConfig = LettuceClientConfiguration.builder()
.readFrom(ReadFrom.SLAVE_PREFERRED)
.build();
// master:192.168.1.128 slave:192.168.1.145
// The default slave can only be read, not written
// If your application needs to write data to redis, it is recommended to connect to the master
RedisStandaloneConfiguration serverConfig = new RedisStandaloneConfiguration(redisHost, redisPort);
return new LettuceConnectionFactory(serverConfig, clientConfig);
}
}Monitor command
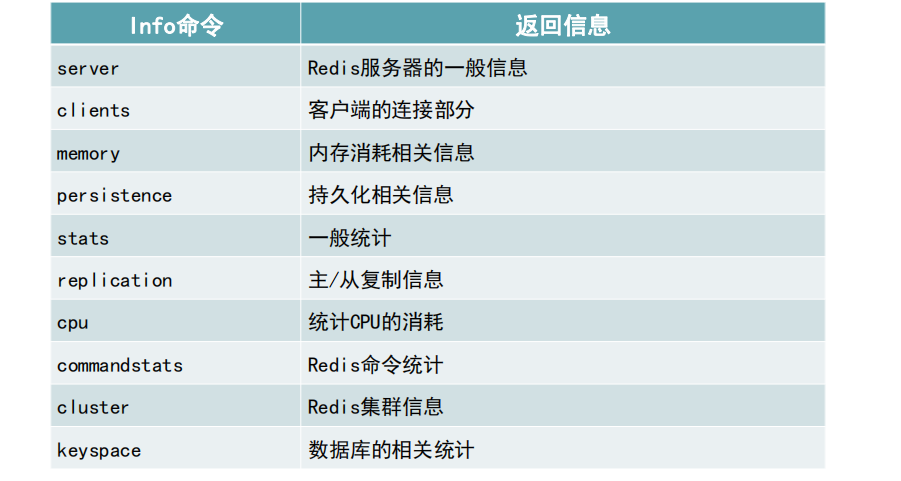
Info command
Graphical monitoring tool - RedisLive
The git address of this tool is: GitHub - nkrod / reuse: visualize your re emerging instances and analyze query patterns and peaks.
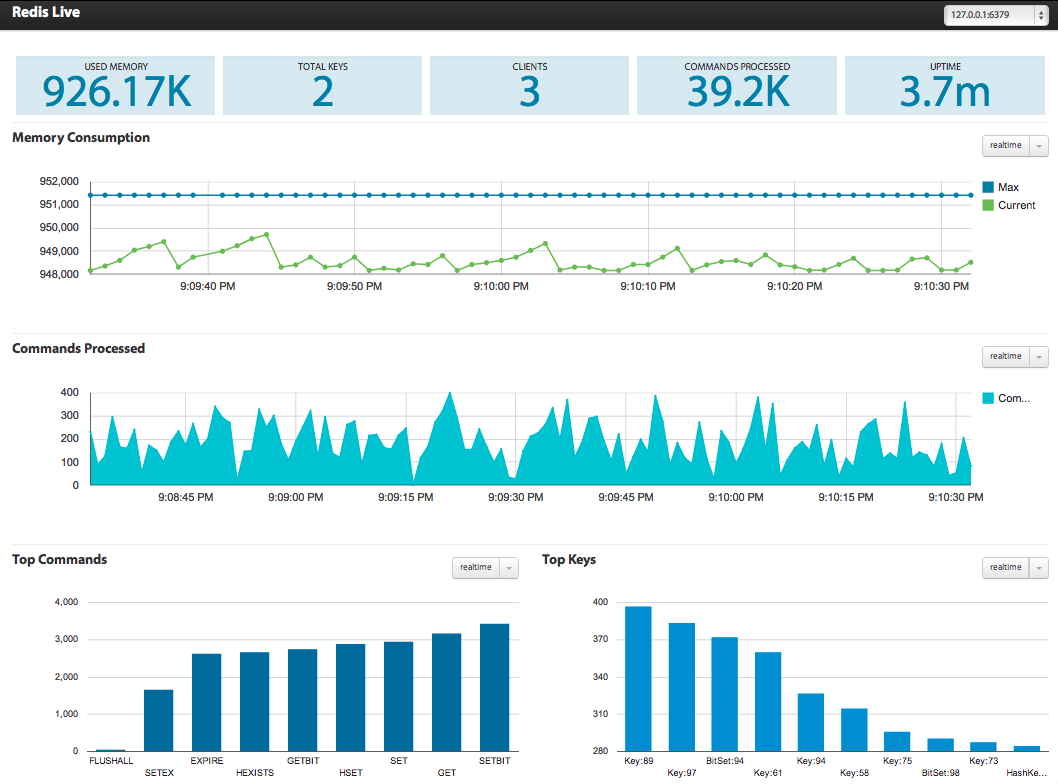
Visualize your recurring instances and analyze query patterns and peaks.
As an open source Redis graphical monitoring tool, RedisLive provides monitoring of the memory usage, client commands received, number of requests received and keys of Redis instances. The working principle of RedisLive is based on the INFO and MONITOR commands of Redis. The current running data of Redis instance is obtained by sending INFO and MONITOR commands to Redis instance.
Install directly using git command
git clone https://github.com/kumarnitin/RedisLive.git
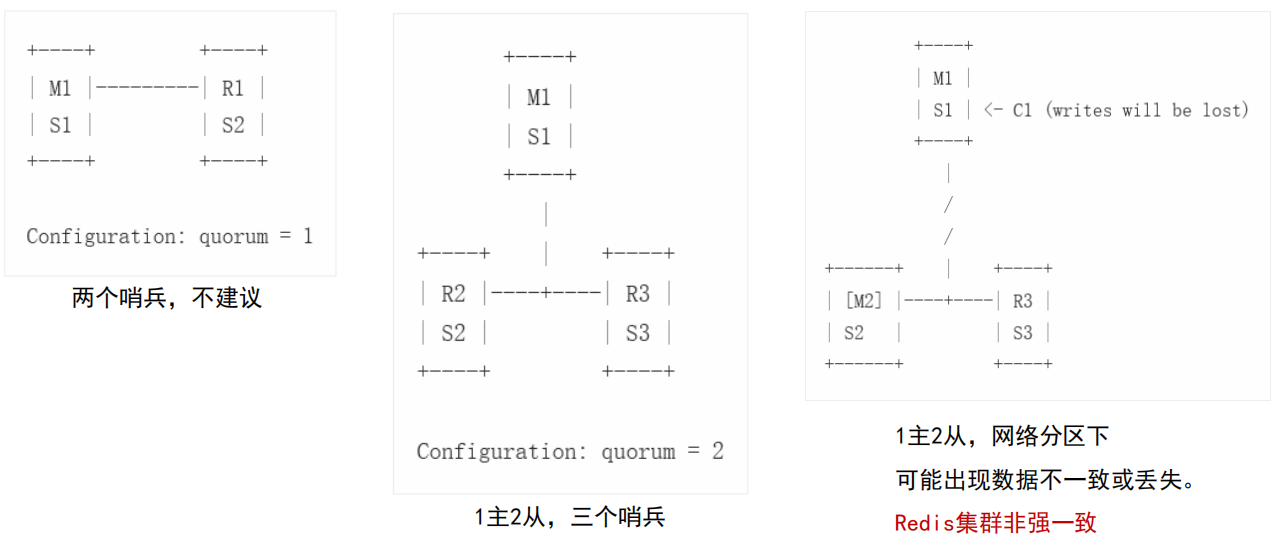
Sentinel mechanism
Redis Sentinel is a distributed system that provides high availability solutions for redis. Multiple Sentinel processes (progress) can be run in one architecture. These processes use gossip protocols to receive information about whether the master server is offline, and use agreement protocols to decide whether to perform automatic failover and which slave server to select as the new master server.
How to configure a sentinel high availability building can be built according to the following documents
redis sentry high availability build extraction code: mth1
# Note that the ip address of ECS should be written correctly and the port should be open # Note that the firewall of the virtual machine should close systemctl stop firewalld.service
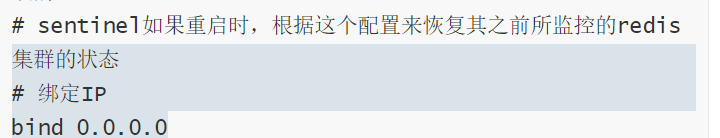
# Configuration file: sentinel.conf, which will be dynamically modified during sentinel operation # If sentinel restarts, it will restore the status of the previously monitored redis cluster according to this configuration # Bind IP bind 0.0.0.0 # Background operation daemonize yes # The default is yes. If no password or IP is specified, the external network cannot be accessed protected-mode no # The sentinel port through which the client can discover redis port 26380 # The Sentinel's own IP, which can be set manually or found automatically, is used to communicate with other sentinels # sentinel announce-ip # Temporary folder dir /tmp # journal logfile "/usr/local/redis/logs/sentinel-26380.log" # The name of the master monitored by sentinel is mymaster, and the initial address is 192.168.100.241 6380,2, which means that two or more sentinels are considered dead sentinel monitor mymaster 192.168.100.241 6380 2 # Send heartbeat PING to confirm whether the master is alive # If the master does not respond to PONG within a "certain time range" or replies to an error message, the sentinel will subjectively (unilaterally) think that the master is no longer available sentinel down-after-milliseconds mymaster 1000 # If the failover operation cannot be completed within this time (ms), the failover is considered to have failed sentinel failover-timeout mymaster 3000 # Specifies the maximum number of secondary Redis instances that can synchronize new primary instances during failover. When there are many secondary Redis instances, the smaller the number, the longer the synchronization time, and the longer the time required to complete failover sentinel parallel-syncs mymaster 1
Start direct use / usr/local/redis/bin/redis-server /usr/local/redis/conf/sentinel-26380.conf --sentinel Start both
Configuring in spring
@Configuration
@Profile("sentinel")
public class SentinelRedisConfig {
@Bean
public LettuceConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory() {
System.out.println("Use sentinel version");
RedisSentinelConfiguration sentinelConfig = new RedisSentinelConfiguration()
.master("mymaster")
// Sentinel address
.sentinel("192.168.100.16", 26379)
.sentinel("192.168.100.8", 26380)
.sentinel("192.168.100.8", 26381);
return new LettuceConnectionFactory(sentinelConfig);
}
}This name corresponds to the name in the configuration file
Sentinel core mechanism
- Simplify the configuration selection of the client. The client can only configure the Sentinel's address without connecting to the master node
-
The sentry mechanism is introduced. The Sentry can sense monitoring, notification, automatic failover and configuration provision through ping.
-
Master node failure , If it is selected, it will go to the new master node, slave of no one Select the new master node and reset the master node of the slave node.
-
Sentinels have subjective offline and objective offline. When a sentinel thinks offline, it is a subjective offline. Only most sentinels think offline is an objective offline. If it is a real offline, you can configure parameters to set it
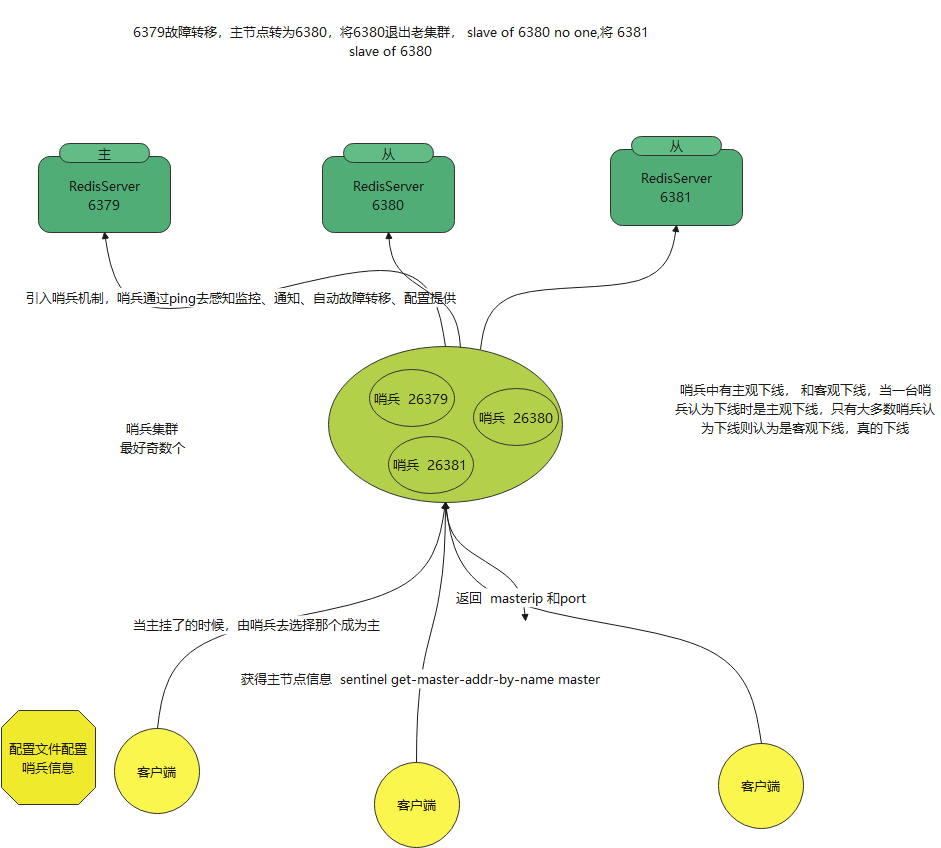
Service discovery and health check process

Failover process

Common orders of Sentinels
Check the Sentinel's port number directly through sentinel sentinels, etc
Use the sentry's orders Use sentinel slave mymaster to view slave node information
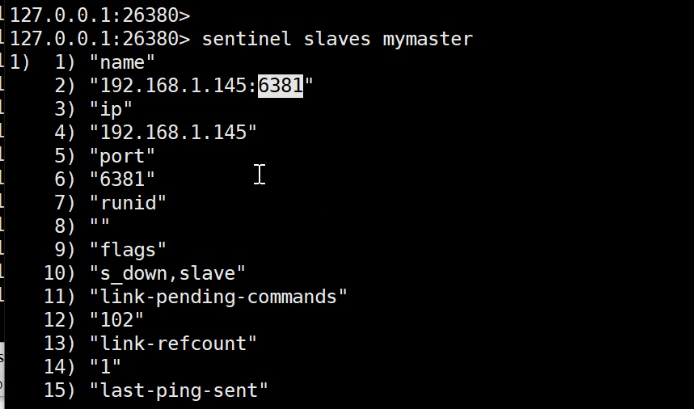
In the sentinel or redis service, the brain crack may occur in the distributed case due to network interruption. Because there are most mechanisms, this problem does not exist. If the network is disconnected and most cases are not reached, it will not be used. When reconnecting, the data will be updated according to the offset
Sentinel 7 core concepts
1. How do sentinels know Redis master-slave information (automatic discovery mechanism)

# The name of the master monitored by sentinel is mymaster, and the initial address is 192.168.100.241 6380,2, which means that two or more sentinels are considered dead sentinel monitor mymaster 192.168.100.241 6380 2
2. What is master offline
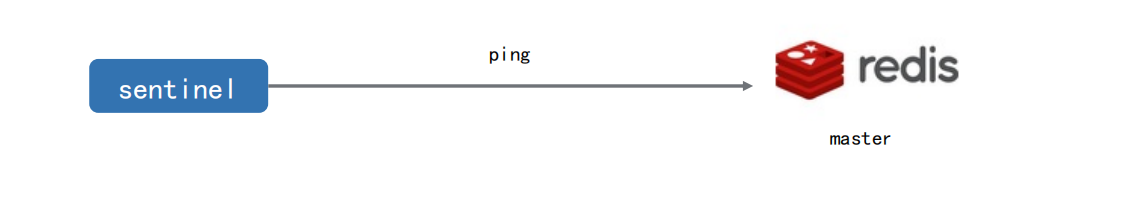
# Send heartbeat PING to confirm whether the master is alive # If the master does not respond to PONG within a "certain time range" or replies to an error message, the sentinel will subjectively (unilaterally) think that the master is no longer available sentinel down-after-milliseconds mymaster 1000
3. What is objective offline
Objective offline: a certain number of sentinel task master s have been offline.
# Send heartbeat PING to confirm whether the master is alive # If the master does not respond to PONG within a "certain time range" or replies to an error message, the sentinel will subjectively (unilaterally) think that the master is no longer available sentinel down-after-milliseconds mymaster 1000
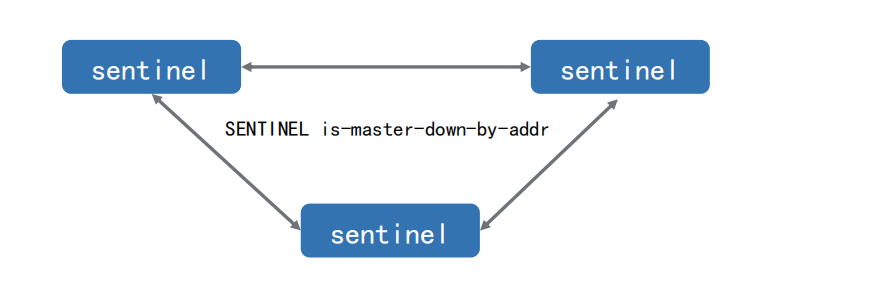
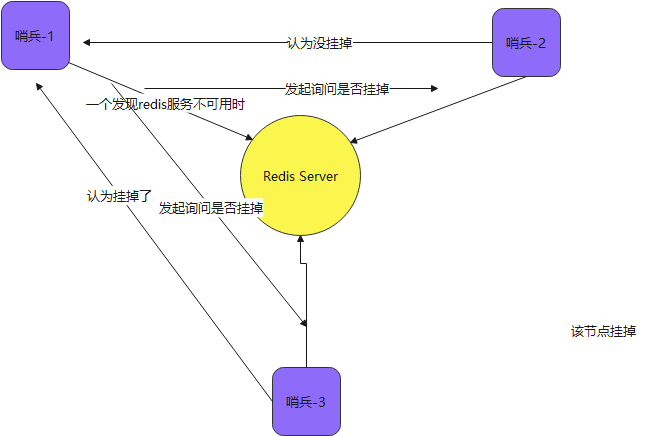
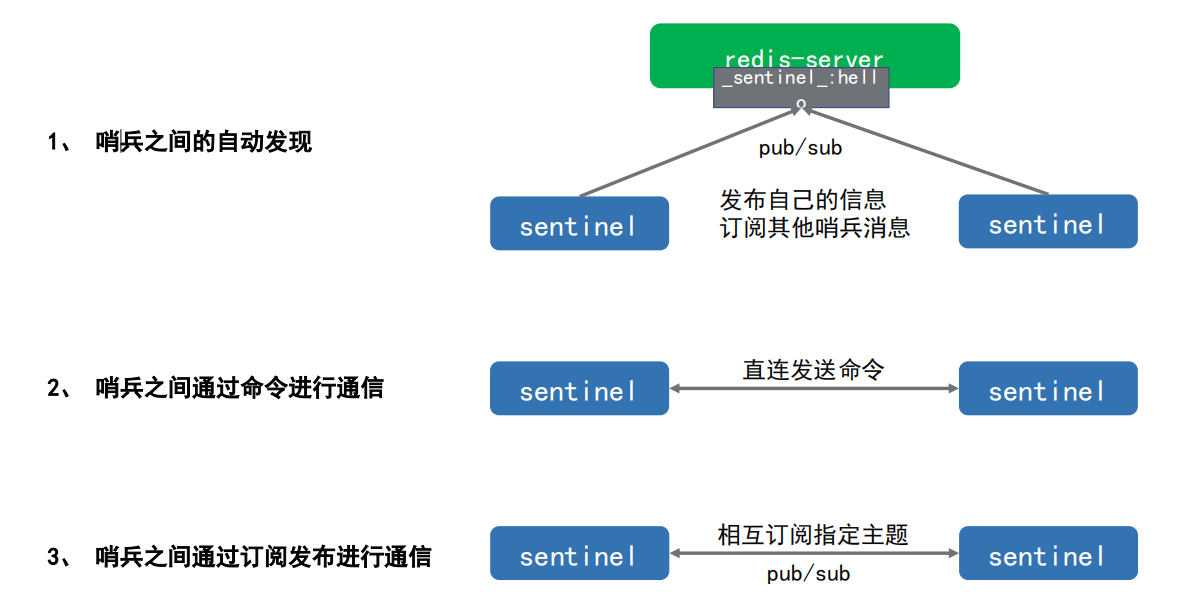
4. How to communicate between sentinels (automatic discovery between sentinels)
In case of multi sentinel mode, sentinel nodes can also perceive each other

The following is the change of sentinel.cnf after three sentinel nodes are enabled successively on the basis of Redis master-slave replication
It can be found that when three sentinel nodes are enabled, the sentinel.cnf configuration file will be rewritten automatically. The main points are as follows:
1. A sentinel myid is added to identify the uniqueness of sentinel nodes
2. Automatically add the information of the sentinel node itself (so that sentinel nodes will automatically discover each other) and the slave information of redis data service
3. Automatically remove the password of the master node
4. The relative path of dir is modified to absolute path
In general, publish and subscribe to pub/sub Channel to monitor Communicate through the offset port of 2000.
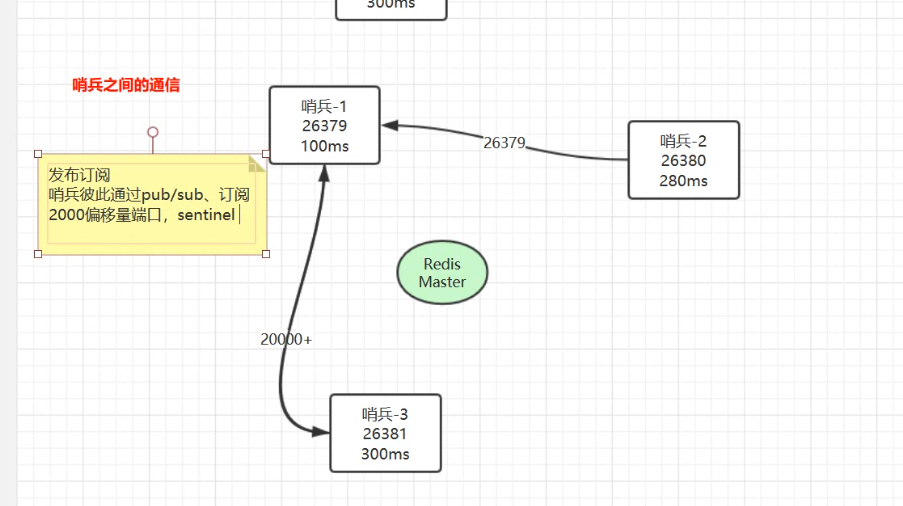
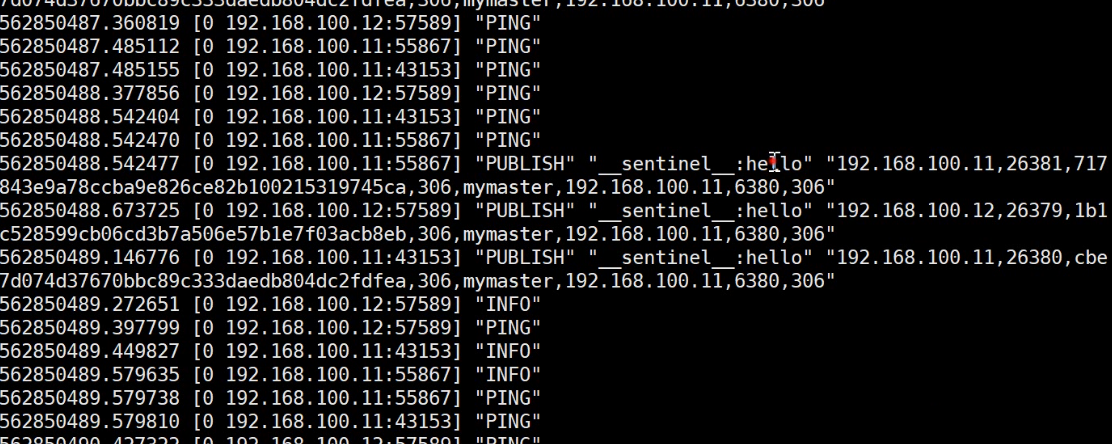

5. Which Sentry is responsible for failover? (sentinel leadership election mechanism)
1. Each online sentinel node can become a leader. When it confirms (for example, sentinel 3) that the master node is offline, it will send the is master down by addr command to other sentinels to ask for judgment and set itself as the leader, and the leader will handle the failover;
2. When other sentinels receive this order, they can agree or refuse it to become a leader;
3. If sentry 3 finds that his number of votes in the election is greater than or equal to the number of sentries / 2 + 1, he will become a leader. If not, continue the election....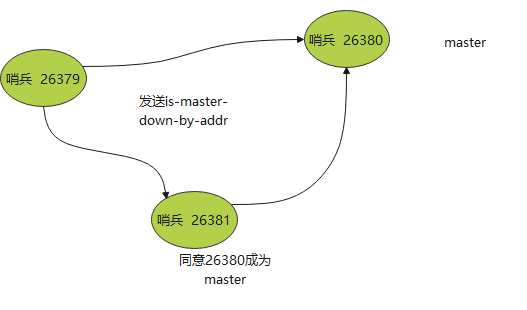
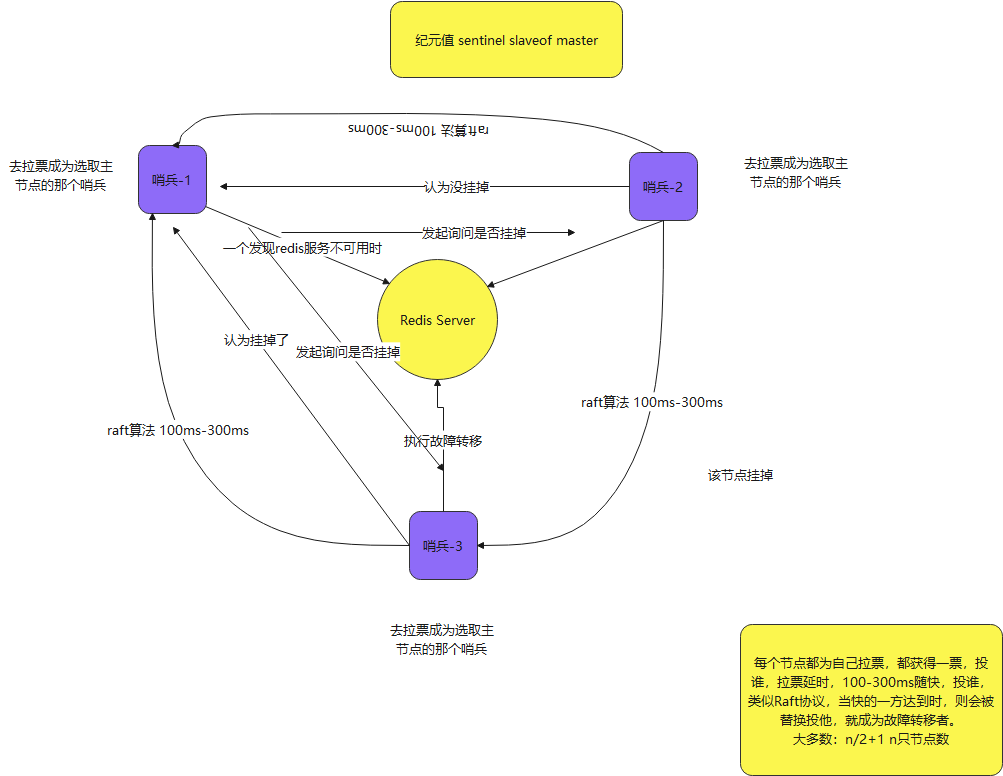
6. slave election mechanism
The slave election mechanism has most mechanisms, including the Sentinel's own choice, and also follows the raft algorithm, which is a little simpler than the paxos algorithm in zookeeper
7. Final master-slave switching process