Definition of recursion: in the process of calling a function, the function itself is called directly or indirectly, which is called the recursion call of the function. This function is called the recursive function. If the p function is called in the p function definition, it is called direct recursion. If the q function is called in the p function definition, and the p function is called in the q function definition, it is called indirect recursion.
Two elements of recursion:
- Recursive expression (recursive equation)
- Recursive end condition (boundary condition)
Problems that can be solved recursively should meet the following three conditions
- The problem to be solved can be transformed into one or more sub problems, and the solution method of these sub problems is exactly the same as the original problem, but different in quantity and scale
- The number of recursive calls must be limited
- There must be a condition to end recursion to terminate recursion
When to use recursion:
- The definition is recursive (factorial, Fibonacci sequence, etc.)
- The data structure is recursive (single linked list, binary tree, etc.)
- The solution method of the problem is recursive (Hanoi Tower, backtracking method, etc.)
Advantages and disadvantages of recursion:
- Advantages: clear structure, strong readability, and it is easy to prove the correctness of the algorithm by mathematical induction. Therefore, it brings great convenience to design the algorithm and debug the program
- Disadvantages: the operation efficiency of recursive algorithm is low, and it consumes more computing time and storage space than non recursive algorithm
- Solution: in some recursive algorithms, recursive calls can be eliminated and transformed into non recursive algorithms
Recursive expression of factorial:
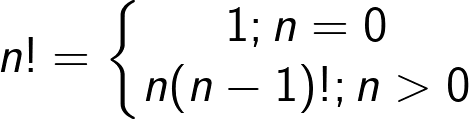
Recursive expression of fiboracci sequence:
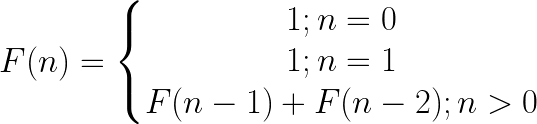
Kimi sequence
Title Description
Kimi recently studied a series: * F(0) = 7 * F(1) = 11 * F(n) = F(n-1) + F(n-2) (n≥2) Kimi calls it the Kimi sequence. Please help confirm whether the nth number in the sequence is a multiple of 3.
input
The input contains multiple sets of data. Each group of data contains an integer n, (0 ≤ n ≤ 30).
output
There is one line of output corresponding to each group of inputs. If F(n) is a multiple of 3, "Yes" is output; Otherwise, output "No".
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Method stub automatically generated by TODO
Scanner num=new Scanner(System.in);
while(num.hasNext()) {
int n=num.nextInt();
if(func(n)%3==0) {
System.out.println("Yes");
}else {
System.out.println("No");
}
}
System.out.println();
}
public static int func(int n) {
if(n==0) {
return 7;
}else if(n==1) {
return 11;
}else {
return func(n-1)+func(n-2);
}
}
}Recursive count
Title Description
Write a recursive program that returns the number of uppercase letters in a string. For example, enter "AbcD" and output 2.
input
Multiple sets of inputs, each containing a string consisting only of uppercase and lowercase letters.
output
The number of uppercase letters in the output string.
sample input
AbcD
sample output
2
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Method stub automatically generated by TODO
int a;
Scanner str=new Scanner(System.in);
while(str.hasNext()) {
String str1=str.nextLine();
char [] c=str1.toCharArray();
a=c.length;
System.out.println(func(c,a-1));
}
}
public static int func(char [] c,int x) {
if(x==-1) {
return 0;
}else {
if(c[x]>='A'&&c[x]<='Z') {
return 1+func(c,x-1);
}else {
return func(c,x-1);
}
}
}
}
Hive problem
Title Description
A trained bee can only climb to the adjacent hive on the right, not in the opposite direction. Please program to calculate the number of possible routes for bees to climb from hive a to hive b.
The structure of the hive is as follows.
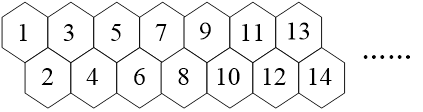
input
Multiple groups of data input, each group of data contains two positive integers a, b, and a < B.
output
The number of possible routes for bees to climb from hive a to hive b.
sample input
1 2 3 4
sample output
1 1
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Method stub automatically generated by TODO
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
while(input.hasNext()){
int a=input.nextInt();
int b=input.nextInt();
System.out.println(func(a,b));
}
}
public static int func(int x,int y){
if(x==(y-1)){
return 1;
}
else if(x==(y-2)){
return 2;
}
else return func(x,y-1)+func(x,y-2);
}
}
Reverse order output
Title Description
Write a program using recursion and output a non negative integer in reverse order. For example, input 1234 and output 4321 (excluding leading 0).
input
Multiple groups of inputs, each group input a non negative integer.
output
Output the results in reverse order, and each result occupies one line.
sample input
12 1230 0
sample output
21 321 0
public class Main {
public static int func(int n){
if(n >= 10){
System.out.print(n%10);
n = n/10;
return func(n);
}else {
return n%10;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
while (input.hasNext()){
int n = input.nextInt();
if(n==0){
System.out.println(n);
continue;
} else if(n > 0){
while(n%10==0){
n = n/10;
}
System.out.println(func(n));
}
}
}
}Dominoes cover
Title Description
Use size 1 × 2's dominoes are covered with a size of 2 × N rectangular grid, write a program, input n and output the total number of placement schemes. For example, enter n=3, that is, the size is 2 × 3 grid, output 3. Three dominoes laying schemes are shown in the figure below:
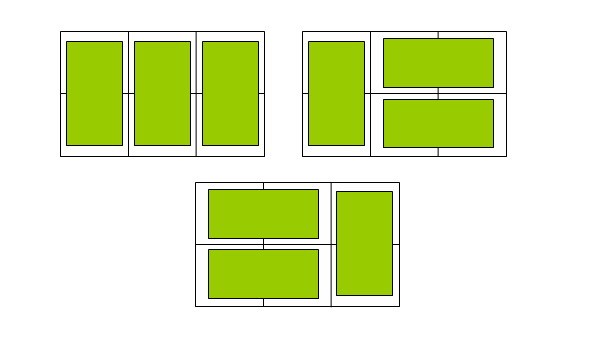
input
Multiple groups of test cases, each group is a positive integer.
output
Each group of output occupies one line.
You only need to output the total number of placement schemes, and you do not need to output specific placement schemes.
sample input
3
sample output
3
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Method stub automatically generated by TODO
Scanner num=new Scanner(System.in);
while(num.hasNext()) {
int n=num.nextInt();
System.out.println(function(n));
}
}
public static int function(int n) {
if(n==1) {
return 1;
}else if(n==2) {
return 2;
}else {
return function(n-1)+function(n-2);
}
}
}