I have to say that binary trees are easy to confuse people. I have been learning to explore binary trees these two days. It seems that the content is quite simple. In fact, it's not so easy to implement, let alone to achieve proficiency. What a long long road! Let's share the implementation first, and continue to study tomorrow.
This part includes: the realization of binary tree, the recursive algorithm of traversing binary tree in pre order, middle order and post order. Later, we will continue to implement the related algorithms about trees.
The implemented binary tree structure is as follows: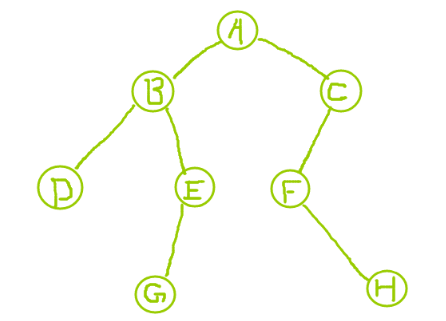
The implementation of binary tree includes three parts of code: node class, binary tree class, creating binary tree and testing.
Node class
package tree;
//Node classes of binary trees
public class BinaryNode {
public Object data;
public BinaryNode left;
public BinaryNode right;
//Construct an empty node
public BinaryNode() {
this(null);
}
//Construct a binary tree with left and right child domains empty
public BinaryNode(Object data){
this(data,null,null);
}
//constructs a branch node with given data,left subtree,right subtree
public BinaryNode(Object data, BinaryNode left, BinaryNode right) {
super();
this.data = data;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
Two fork tree class
package tree;
//Two fork tree class
public class BinaryTree {
private BinaryNode root;//Root node, node structure is a binary list
public BinaryTree() { //Construct an empty tree
this.setRoot(null);
}
public BinaryTree(BinaryNode root) {//Construct a tree
this.setRoot(root);
}
public boolean isEmpty() { //Judge whether the tree is empty
return this.getRoot() == null;
}
/*
* Next, we implement the algorithm of traversing the tree
*/
//Traversing print subtree first
public void printPreorder(BinaryNode root){
if(root!=null){
System.out.print(" "+root.data);
printPreorder(root.left);
printPreorder(root.right);
}
}
//Sequential traversal
public void printMidorder(BinaryNode root){
if(root!=null){
printMidorder(root.left);
System.out.print(" "+root.data);
printMidorder(root.right);
}
}
//Post order traversal
public void printAftorder(BinaryNode root){
if(root!=null){
printAftorder(root.left);
printAftorder(root.right);
System.out.print(" "+root.data);
}
}
public BinaryNode getRoot() {
return root;
}
public void setRoot(BinaryNode root) {
this.root = root;
}
}
Building binary tree and test class
package tree;
public class DebugBTree {
//Building a binary tree
public BinaryTree createBinTree()
{
BinaryNode d = new BinaryNode("D");
BinaryNode g = new BinaryNode("G");
BinaryNode h = new BinaryNode("H");
BinaryNode e = new BinaryNode("E", g, null);
BinaryNode b = new BinaryNode("B", d, e);
BinaryNode f = new BinaryNode("F", null, h);
BinaryNode c = new BinaryNode("C", f, null);
BinaryNode a = new BinaryNode("A", b, c);
return new BinaryTree(a); //Create a binary tree with root node a
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
DebugBTree debug = new DebugBTree();
BinaryTree bt = debug.createBinTree();
BinaryNode root = bt.getRoot(); //Get a binary tree with root node a
bt.printPreorder(root);//Preorder traversal
System.out.println("\n================");
bt.printMidorder(root);//Sequential traversal
System.out.println("\n================");
bt.printAftorder(root);//Post order traversal
}
}
The results of the operation are as follows: