[Objective]
Array implementation of ring queue
[Idea analysis]
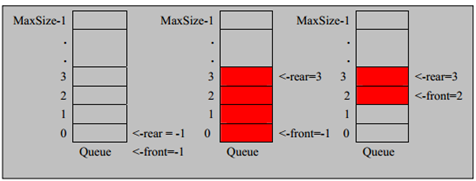
1. The meaning of the front variable is adjusted: front points to the first element of the queue, that is, arr[front] is the first element of the queue.
The initial value of front = 0
2. The meaning of the rear variable is adjusted: rear points to the last position of the last element of the queue, because you want to make a space available as a convention.
The initial value of rear = 0
3. When the queue is full, the condition is (rear + 1)% maxSize = front [full]
4. Queue empty condition, rear = front empty
5. When we do this analysis, the number of valid data in the queue (rear + maxSize - front)% maxSize // rear = 1 front = 0
6. We can modify the original queue to a circular queue.
[Code implementation]
import java.util.Scanner;
public class CircleArrayQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Test a handful
System.out.println("Examples of test arrays simulating ring queues~~~");
// Create a circular queue
CircleArray queue = new CircleArray(4); //Explanation Set 4, the maximum valid data for its queue is 3
char key = ' '; // Receive user input
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);//
boolean loop = true;
// Output a menu
while (loop) {
System.out.println("s(show): Display queue");
System.out.println("e(exit): Exit procedure");
System.out.println("a(add): Add data to queues");
System.out.println("g(get): Extract data from the queue");
System.out.println("h(head): View the data of the queue head");
key = scanner.next().charAt(0);// Receive a character
switch (key) {
case 's':
queue.showQueue();
break;
case 'a':
System.out.println("Output a number");
int value = scanner.nextInt();
queue.addQueue(value);
break;
case 'g': // Remove data
try {
int res = queue.getQueue();
System.out.printf("The data taken out is%d\n", res);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
case 'h': // View the data of the queue head
try {
int res = queue.headQueue();
System.out.printf("The data of the queue head is%d\n", res);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
case 'e': // Sign out
scanner.close();
loop = false;
break;
default:
break;
}
}
System.out.println("Program exit~~");
}
}
class CircleArray {
private int maxSize; // Represents the maximum capacity of an array
//The meaning of the front variable is adjusted: front points to the first element of the queue, that is, arr[front] is the first element of the queue.
//The initial value of front = 0
private int front;
//The meaning of the rear variable is adjusted: rear points to the last position of the last element of the queue, because you want to leave a space as a convention.
//The initial value of rear = 0
private int rear; // Queue tail
private int[] arr; // This data is used to store data and simulate queues.
public CircleArray(int arrMaxSize) {
maxSize = arrMaxSize;
arr = new int[maxSize];
}
// Judging whether the queue is full
public boolean isFull() {
return (rear + 1) % maxSize == front;
}
// Determine whether the queue is empty
public boolean isEmpty() {
return rear == front;
}
// Add data to queues
public void addQueue(int n) {
// Judging whether the queue is full
if (isFull()) {
System.out.println("The queue is full and data cannot be added~");
return;
}
//Add data directly
arr[rear] = n;
//Moving the rear backward, we must consider taking the model here.
rear = (rear + 1) % maxSize;
}
// Get the data of the queue and get out of the queue
public int getQueue() {
// Determine whether the queue is empty
if (isEmpty()) {
// By throwing an exception
throw new RuntimeException("Queue empty, unable to retrieve data");
}
// Here you need to analyze that front is the first element that points to the queue
// 1. Save the value of front to a temporary variable first
// 2. Move the front backward and consider taking the model
// 3. Return temporarily saved variables
int value = arr[front];
front = (front + 1) % maxSize;
return value;
}
// Display all data for the queue
public void showQueue() {
// ergodic
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Queue empty, no data~~");
return;
}
// Thought: How many elements do you traverse from front?
for (int i = front; i < front + size() ; i++) {
System.out.printf("arr[%d]=%d\n", i % maxSize, arr[i % maxSize]);
}
}
// Find out the number of valid data in the current queue
public int size() {
// rear = 2
// front = 1
// maxSize = 3
return (rear + maxSize - front) % maxSize;
}
// Display the header data of the queue, note that it's not fetching the data
public int headQueue() {
// judge
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("Queue empty, no data~~");
}
return arr[front];
}
}[Result Display]

