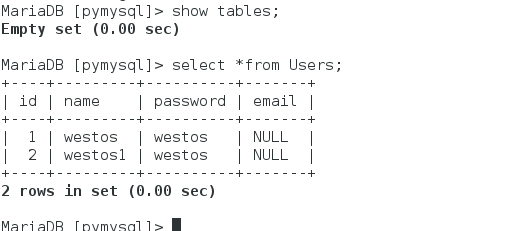
After learning database, we can use database to make a user management system. Realize the functions of registration, login, view, delete users, etc.
Step 1: specifically divided into two parts, the first part is to connect the database, and create a table to encapsulate the table into a class.
The specific implementation is as follows:
from sqlalchemy import create_engine,Column,Integer,SmallInteger,String
from sqlalchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_base
from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker
engine=create_engine("mysql+pymysql://root:westos@192.168.122.191/pymysql",
encoding='utf8',
# echo=True
)
Session =sessionmaker(bind=engine)
session=Session()
Base=declarative_base()
class Users(Base):
__tablename__='Users'
id =Column(Integer,primary_key=True,autoincrement=True)
name=Column(String(20),nullable=False)
password=Column(String(20),nullable=False)
email=Column(String(30),unique=True)
def __repr__(self):
return self.name
if __name__ == '__main__':
Base.metadata.create_all(engine)
After encapsulation, the management system can be written.
The specific implementation is as follows:
import db
cookie={}
class UserManage(object):
def login(self,name,password):
#Get the user name and password from the database. Verify whether it is correct. If it is correct, the login succeeds. Otherwise, it fails.
obj=db.session.query(db.Users).filter_by(name=name).filter_by(password=password).first()
if obj:
print("%s Login successfully"%name)
cookie['name']=name
else:
print("Incorrect user name or password.")
def logout(self):
cookie.pop('name')
print("Logout succeeded.")
def register(self,user,password):
#Get information from the database. If the user already exists, the user will be prompted to exist. Otherwise, the registration is successful.
username = db.session.query(db.Users).filter_by(name=user).first()
if username:
print("The user already exists.")
else:
obj=db.Users(name=user,password=password)
db.session.add(obj)
db.session.commit()
print("%s User registration succeeded."%user)
def deltel(self,user):
#Get object information from the database. If so, delete.
obj=db.session.query(db.Users).filter_by(name=user).first()
if obj:
print(obj)
db.session.delete(obj)
db.session.commit()
print("%s User deleted successfully."%user)
else:
print("The user does not exist.")
def is_exists(self):
obj=db.session.query(db.Users).all()
print(obj)
if __name__ == '__main__':
db.Base.metadata.create_all(db.engine)
user1=UserManage()
# Register with westos,
user1.register('westos','westos')
#Register with westos1
user1.register('westos1','westos')
#Verifying landing
user1.login('westos','westos')
# user1.deltel('westos')
#Query all users.
user1.is_exists()
Below is the result of our program running.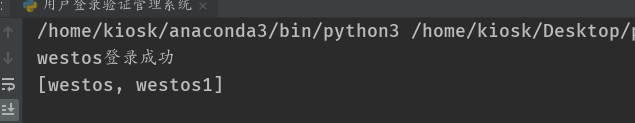
We can see that the content of the database is consistent, which shows that our system is ready.